Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
Le chordoma is a rare bone tumor. It can appear in anyone, at any age. Its diagnosis is often late. It is usually detected when it interferes with the functioning of other organs.
What is a chordoma? What are its causes and symptoms? How to make your diagnosis? How to treat it? What about the prognosis and life expectancy in the case of this bone cancer? The answers in this article.
A few words about chordoma
Le chordoma refers to a malignant bone tumor that develops from residual cells of the notochord. It is one of the sarcomas which include all malignant tumors and soft tissues.
The notochord, also called notochord or dorsal chord, corresponds to a dorsal rigid structure present in the embryo. It has the shape of an elastic cord. The notochord participates in the formation of the spine.
When the fetus reaches about 8 weeks of age, the chord regresses. In some people, these cells do not completely disappear. Some cells persist in some bones of the spine (from the head to the coccyx). They take on the appearance of a gelatinous mass.
The term " chordoma » translates the degeneration of these remaining cells into cancerous cells.
Locations of chordoma
In general, this bone tumor fits in:
- the bones of the base of the skull or the clivus (approximately 30% of cases);
- the bones of the spine mobile : cervical spine, thoracic et lumbar (about 20% of cases);
- the sacrum (about 50% of cases).
In rare cases, it can occur in other places in the spine, or even in more distant bones such as those in the feet, legs or ribs.
Different types of chordoma
According to the appearance under the microscope, 3 types of chordomas can be distinguished.
- Le conventional chordoma ou loan: this is the most common form of this malignant bone tumor. It is characterized by a unique cell type similar to notochordal cells.
- Le poorly differentiated chordoma: it is a recently identified form. Compared to classic chordoma, this one can be faster and more aggressive. It corresponds to a loss of a gene called INI-1. Poorly differentiated chordoma mainly affects young adults and children. It is most common in tumors at the base of the skull.
- Le dedifferentiated chordoma ou undifferentiated: this is the most aggressive and fastest form. It is also the type of chordoma that is most likely to metastasize. In this form, loss of the INI-1 gene may also occur. Undifferentiated chordoma is rare. It affects about 5% of patients, most of whom are pediatric patients.
We can also talk about chondroid chordoma. Previously, this term facilitated the differentiation between conventional chordoma and chondrosarcoma (cartilaginous tumors).
Currently, this distinction is easier, because the involvement of a gene called " Brachyury is visible in almost all conventional chordomas, which is not the case with chondrosarcomas. However, there is no evidence to prove whether the behavior of chordomas with a chondroidal appearance is different from that of classic chordomas whose appearance is not the same.
The causes of chordoma
The exact origin of the degeneration of the residual cells of the notochord remains unknown. Research is continuing on this.
Epidemiology of chordoma
This bone tumor can appear at any age. But according to statistics, it affects more fifties and sixties with twice as many men as women. The prevalence indicates one new case in a million each year.
In France, there are about 80 cases each year. Chordoma accounts for 0,2% of central nervous system tumors as well as 2 to 4% of primary bone tumors in adults.
While chordoma of the base of the skull mainly affects young patients, chordoma of the spine, on the other hand, is a form that occurs late.
Chordoma risk factors
We identified no environmental, lifestyle, or diet-related risk factors for degeneration of chordal remnants. The majority of chordomas appear spontaneously.
As in all tumors, there are some genetic changes in chordoma cells. More than 95% of patients suffering from this bone tumor have an anomaly in the DNA sequence of the Brachyury gene. Although this anomaly increases the risk of developing chordoma, it cannot cause it directly.
Children with complex tuberous sclerosis (genetic disease) also have a higher risk of developing chordoma. This occurs especially when the TSC1 and TSC2 genes are involved.
Symptoms of Chordoma
At the start of the tumor, the chordoma is often asymptomatic. Its evolution is slow and silent.
Over time, symptoms may appear. They may differ from patient to patient depending on the location of the bone tumor.
Signs of a chordoma at the base of the skull
When the chordoma is located at the base of the skull, these neurological signs may appear:
- headaches;
- visual disturbances;
- hearing loss;
- swallowing disorders;
- vertigo ;
- paralysis of cranial nerves...
Signs of a spinal chordoma
When the chordoma is located in the spine, these signs may occur:
- back pain;
- nausea;
- tingling;
- feeling of weakness in a limb;
- very rarely, joint destruction causing instability during movement.
Signs of a Sacral Chordoma
A chordoma located at the level of the sacrum can result in these signs:
- pain ;
- bladder and bowel disorders;
- urinary disorders;
- urinary and fecal incontinence.
The diagnosis of chordoma
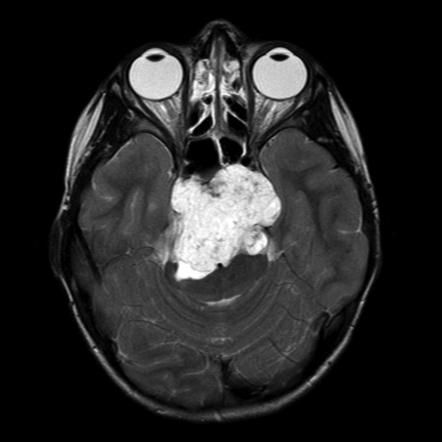
To diagnose a chordoma, doctors usually order a CT scan or MRI. MRI is often more effective in identifying chordomas, due to the unique features of the tumor on an MRI scan.
However, the correct identification of a chordoma on an MRI requires experience and expertise, as these tumors are rare. When a chordoma is suspected, other tests may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and determine the best treatment.
The treatment of chordoma
Due to the rarity of this tumour, you must go to a neurosurgical center with sufficient experience in this disease.
It should be noted that this tumor does not respond to chemotherapy. However, the role of the latter as well as those of other targeted therapies remains to be studied.
Surgical treatment of chordoma
In chordoma, the surgery is the first-line treatment. It consists of the removal of the bone tumor.
But it is not uncommon for the chordoma not to be completely removed, despite repeated operations. This occurs especially in case of advanced metastasis or in case of damage to important anatomical structures.
Treatment of chordoma with prontotherapy
For reduce the risk of chordoma recurrence, prontotherapy is suggested as a complement to surgical treatment. It is a radiotherapy technique which consists in irradiating the tumor cells, with proton beams, without impacting the peripheral healthy tissues.
Life expectancy: What are the chances of survival?
The prognosis after a chordoma takes into account several factors, namely:
- the age of the patient;
- the type of chordoma;
- the size, location and spread of the bone tumor;
- the chosen treatment;
- the extent of excision...
Life expectancy people diagnosed with chordoma is now seven years old. This statistic is based on the median survival rate, which means that half of people diagnosed with a chordoma will live more than seven years and the other half will not.
The 5-year survival rate, or the percentage of people who live at least 5 years after their diagnosis, is 68%.
The 10-year survival rate, or the percentage of people who live at least 10 years after diagnosis, is 40%.
While these statistics may seem grim, it is important to remember that they are based on averages and do not take into account individual circumstances.
With advances in treatment and detection, these numbers may improve in the future.
Factors favorable to the appearance of Chordoma
The favorable factors for this disease are a family history of the disease, as well as previous exposure to radiation.
Factors that affect life expectancy are:
- The location of the tumor
- The spread of the tumor to other parts of the body
- The age and general state of health of the person
There are several treatment options for chordoma, which can extend life expectancy and improve quality of life. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Clinical trials are also an option for some people with chordoma. These trials test new treatments that may eventually become standard care options.
Factors unfavorable to the appearance of Chordoma
Recurrent factors after treatment include:
- The type of surgery performed
- Whether or not the tumor is completely removed during the operation
- The dose of radiotherapy
- The chemotherapy used
If you chordoma recurrence, it is important to consult a multidisciplinary team experienced in the management of this disease. She will be able to develop a treatment plan that will give you the best chance of controlling your disease in the long term.
Sources
https://www.chordomafoundation.org/learn/comprendre-le-chordome/