Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
The number of people with collagenosis is increasing. It occurs more often in women than in men. Want to know more about this disease? This article is therefore made for you.
Definition
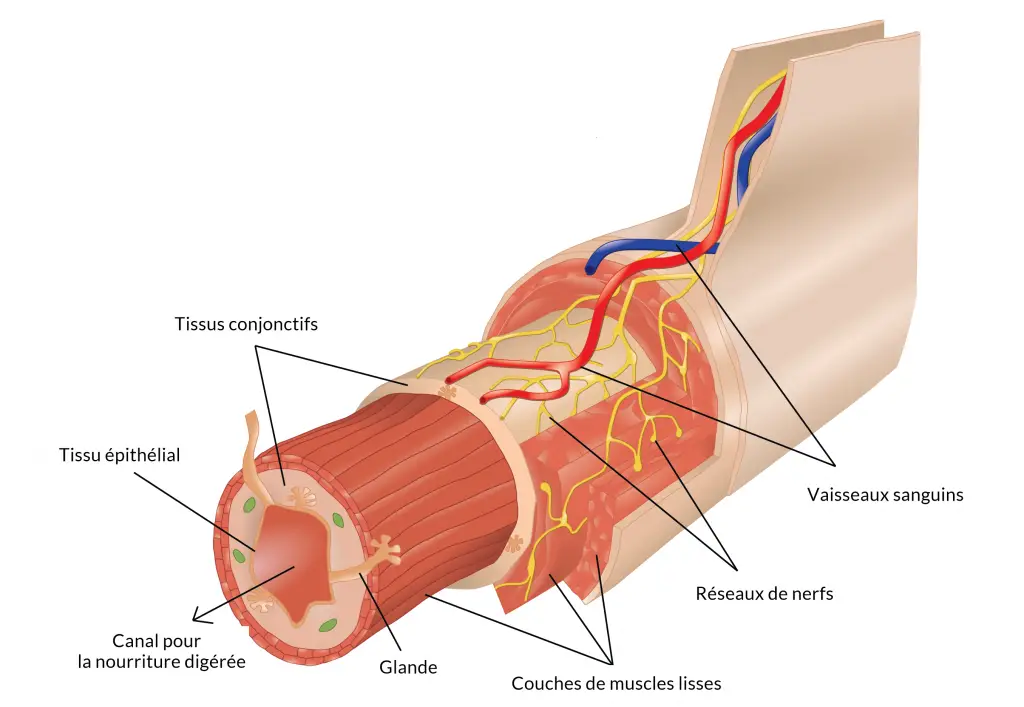
Le collagen corresponds to the protein secreted by connective tissue cells. We are talking about the most abundant protein in the human body. It is thanks to it that each of our organs manages to maintain its flexibility. Indeed, collagen interacts with molecules to form fibers and thus produce a fibrous tissue to prevent the organs from being too rigid.
La collagenosis or connective tissue disease (or even systemic disease) designates all of the autoimmune diseases caused by an abnormal formation of collagen in the connective tissues. These include a hyperactivity of the immune system, a female preponderance and an association with antinuclear antibodies and the dissemination of lesions.
Among the collagenoses, we can cite:
- Scleroderma: this type of collagenosis is characterized by disorders in the skin, heart and digestion.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: it is manifested by disorders in the skin, especially in the face and in the joints and digestion.
- Polymyositis: it is a painful disorder of the muscles, joints and bones.
- Polyarteritis nodosa: it is a diffuse attack of the arteries of the body.
- Sarcoidosis: this type of collagenosis corresponds to damage to the lungs and several other organs.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: this type of collagenosis corresponds to a chronic inflammatory disorder in the joints, in particular in the hands and feet.
- Oculo-urethro-synovial syndrome (OUS): this manifests as painful swelling of the joints, triggered by an infection in another part of the body.
- Spondyloarthropathy: this is what we call all the chronic inflammatory rheumatisms which share clinical manifestations and a common genetic background.
- Horton's disease: this disease is characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels in and around the scalp.
- Gougerot-Sjogren syndrome: this corresponds to a disorder of the immune system which leads to dryness of the eyes and mouth.
- Behcet's disease: it is a rare disease that causes inflammation in the blood vessels.
- Histiocytosis: it is a disease that affects histiocytes, cells derived from white blood cells that defend the tissues in which they are found.
- Periodic illness: it is a genetic disease which is manifested by repeated excesses of fever. These are often accompanied by abdominal and/or joint pain.
- Overload diseases: this concerns genetic metabolic diseases leading to the pathogenic accumulation of a metabolite in the cell.
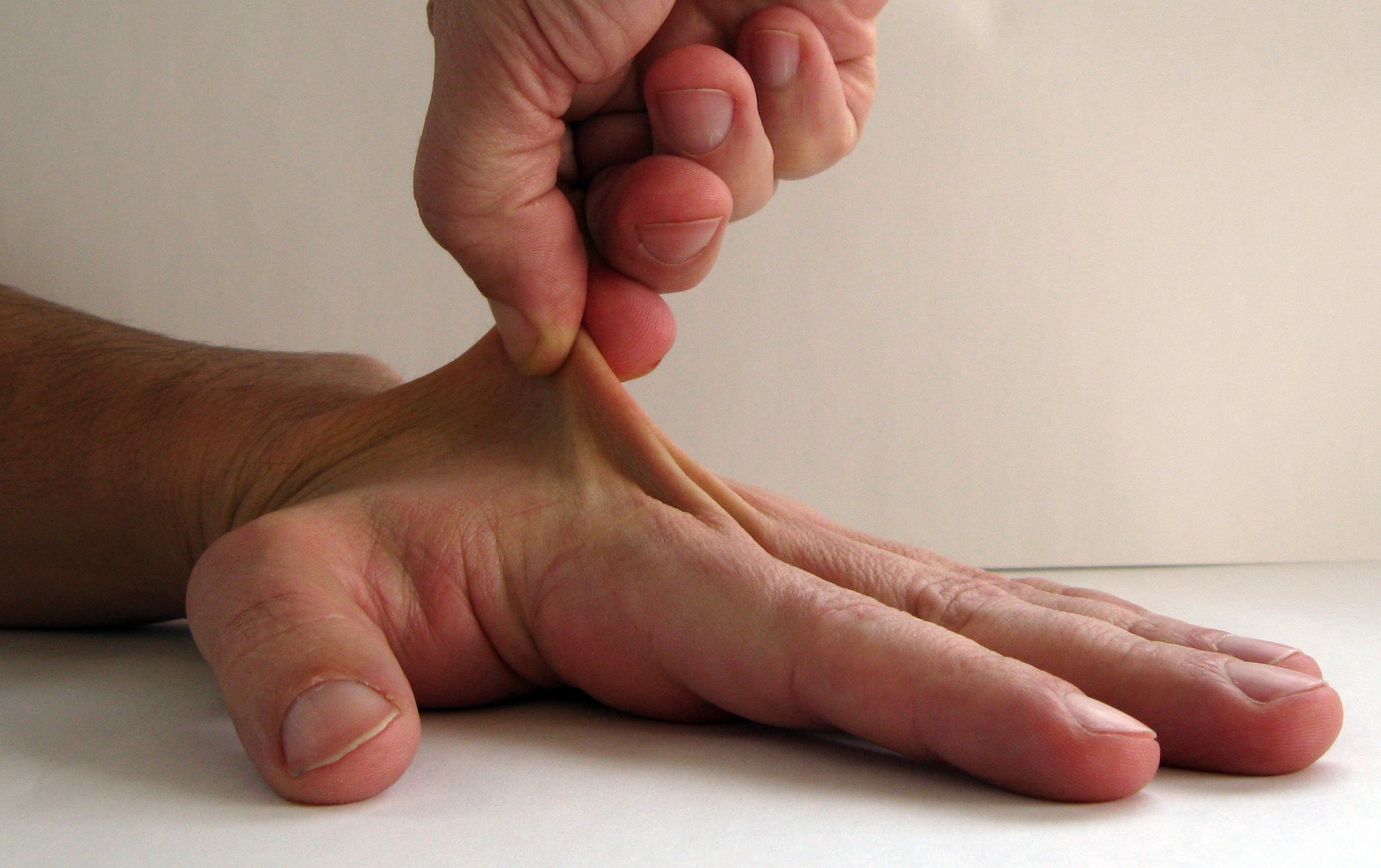
- Elastic tissue disease: it is a rare inherited disease of the elastic connective tissue which generally results in abnormal flexibility of the joints, very elastic skin and weakened tissues (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome).
Causes
Until now, the origins of collagenosis are not yet recognized. However, immune system disorders suggest an autoimmune cause. Indeed, the body creates abnormal antibodies, directed against the own constituents of its cells. This is why these abnormal antibodies are called autoantibodies or antinuclear.
These diseases favor the meeting between certain antigens of the histocompatibility system (HLA), or in certain families more frequently affected, this is what explains the favoring role ofa genetic factor.
Patients with collagenosis include female rate higher than male. This discrepancy explains the involvement of theestrogen (a hormone present in women) in this disease. Which then means that the period of pregnancy (a period of high hormonal impregnation) can also promote a flare in female patients.
Symptoms of the disease
No part of the body is devoid of connective tissue, so collagenosis or systemic disease can attack any organ. Hence, the symptoms of this disease can affect:
- The joint;
- The skin ;
- The heart ;
- Lungs ;
- Kidneys ;
- The nervous system ;
- Blood vessels ;
- The digestive system
In general, collagenosis progresses in flare-ups. They are associated with an inflammatory syndrome and can vary either from one patient to another, or from one degree to another. Here are some examples:
- Low-grade fever (mild fever)
- Abatement
- Chronic fatigue
- Decreased performance
- Difficulties of concentration
- Sun and light sensitivity
- Alopecia
- Sensitivity to cold
- Nasal / oral / vaginal dryness
- Skin lesion
- Weight loss
- Joint pain
- Inflammatory muscle pain (myalgia)
- Inflammatory joint pain (arthralgia).
It should be noted that when it is a case of connective tissue disease or undifferentiated collagenosis, the patient does not present any symptoms other than joint pain and fatigue. However, in the opposite case, i.e. in case of overlap syndrome, the patient will present with much more significant symptoms.
Diagnostic
To prevent the disease from affecting several organs, a diagnosis is essential. If the medical practitioner suspects collagenosis on the basis of the anamnesis, it is then necessary to carry out a screening assessment including: the search for an inflammatory syndrome, a blood count, a creatinine assay and an analysis of the urinary sediment, or even a C4 assay. Indeed, the diagnosis is based on two things:
- On the patient's antecedent story
- And on his clinical examination.
The presence of antinuclear antibodies in the blood of patients means that it is imperative to establish a diagnosis. However, it is also important to emphasize that the presence of these auto-antibodies in the blood does not always mean that one suffers from collagenosis.
Sometimes it is necessary to go through a tissue sample to perform a biopsy. For this, it is necessary to seek the advice of a specialist to confirm the diagnosis and find the treatment that corresponds to it.
Treatment
Autoimmune disease often suggests multidisciplinary care. That is to say, it will be necessary to consult a specialist for each organ affected and also to consult other health professionals such as a pharmacist, a dietician, a nurse, a physiotherapist, a psychologist.
The objective of this treatment is to control the progression of the disease and to reduce it to the minimum possible. The treatment obviously varies according to the type of collagenosis diagnosed and also according to the organs affected.
Connectivity support includes drug treatments and non-drug treatments.
Drug treatments
Drug treatments include symptomatic treatment and disease-modifying treatment.
Treatment of symptoms of collagenosis
The treatment of symptoms aims to reduce or even eliminate flare-ups and relieve pain by restoring order to the dysfunction of all the affected organs. For this, the corticosteroids are the most requested. Due to their rapid and potent efficacy, corticosteroids are used as a first-line anti-inflammatory for collagenosis. If collagenosis affects an organ such as the kidney, lung or brain, treatment may involve the use of an oral or injectable immunosuppressant in high doses.
However, the corticosteroid dose will vary depending on the damaged organ and the extent of its damage. When an organ such as the heart, kidney, lung or nervous system is affected by collagenosis, specific treatment will be necessary.
You can also take analgesics and/or anti-inflammatories in case of severe joint or muscle pain.
Basic treatment
Basic treatment is divided into 3 types:
- Synthetic background treatment (or chemical) such as hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, leflunomide, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide.
- Biotherapy or biomedicine, including rituximab and belimumab.
- cell therapy, this type of treatment brings together delicate interventions such as the autografting of peripheral stem cells.
Non-drug treatments and associated protections
Sport, physiotherapy and occupational therapy play an important role in the management of connectivitis. Indeed, the benefits of physical activity for certain diseases, including systemic diseases, cannot be estimated.
Physiotherapy, on the other hand, serves as support for successful physical activities without pain. Finally, occupational therapy helps us to understand the mechanisms of the disease, to know the place of each type of treatment (medicated or not), and to live daily with collagenosis. Basically, these treatments are effective in the fight against weakening of muscles, stiffness of joints, skin lesion, muscle pain,…
Protection against the sun or the cold is often necessary. It is also necessary to avoid taking tobacco in order to prevent flare-ups of the disease and reduce the aggravation if the lungs are affected.
Psychological support is sometimes useful to learn to live with the disease and to manage the stress that results from it. Indeed, stress promotes flare-ups of systemic disease.