A nerve sciatica irritated is not always damaged as such, although it can reproduce sciatica pain. However, the symptoms are often bothersome and limit daily activities.
Le sciatic nerve can it be damaged? If so, what can you do to relieve your symptoms and heal as quickly as possible? We talk about it in this article.
Focus on sciatica
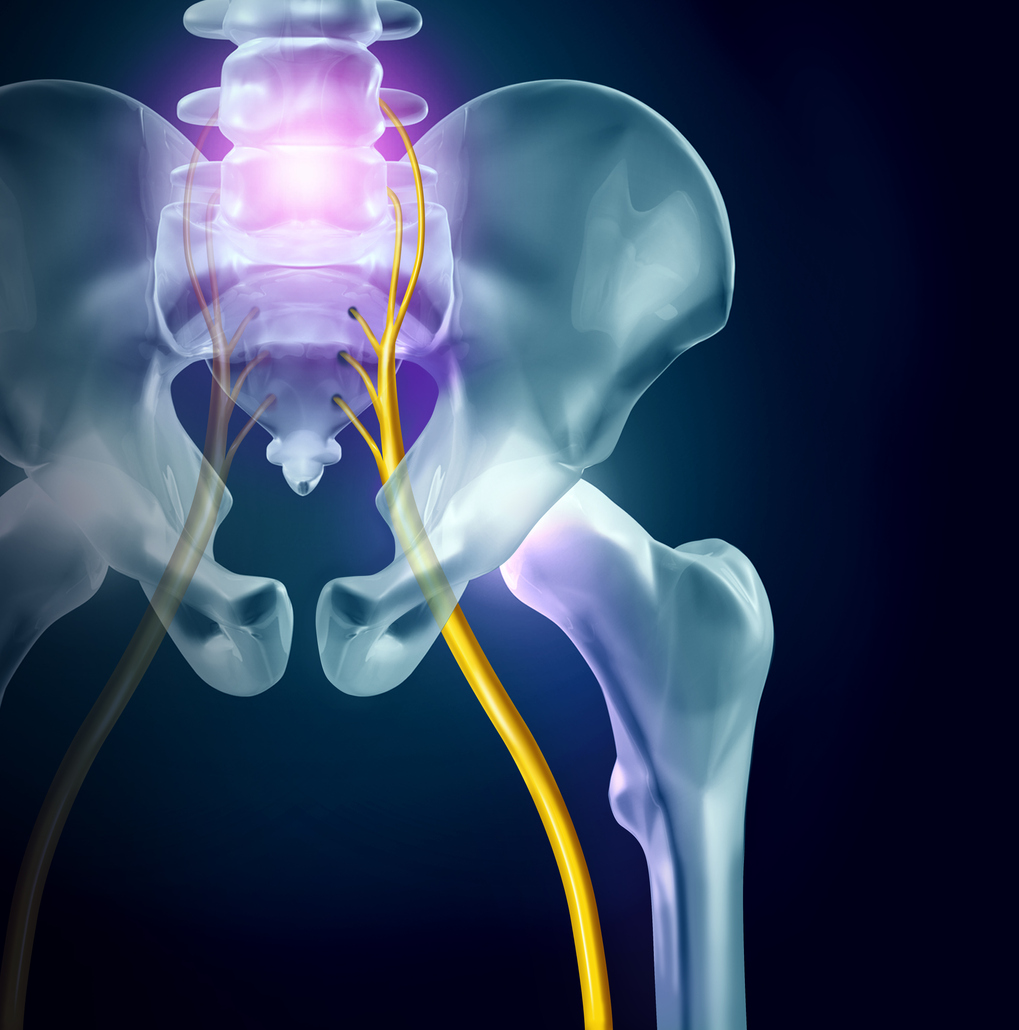
To fully understand how the sciatic nerve can be damaged, it is necessary to refer to its anatomy.
Le sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the human body, extending from the lower back to the feet. It is made up of two main types of fiber: motor fibers and sensory fibers.
The motor fibers control the muscles of the lower leg and foot, while sensory fibers provide information about touch, temperature and pain.
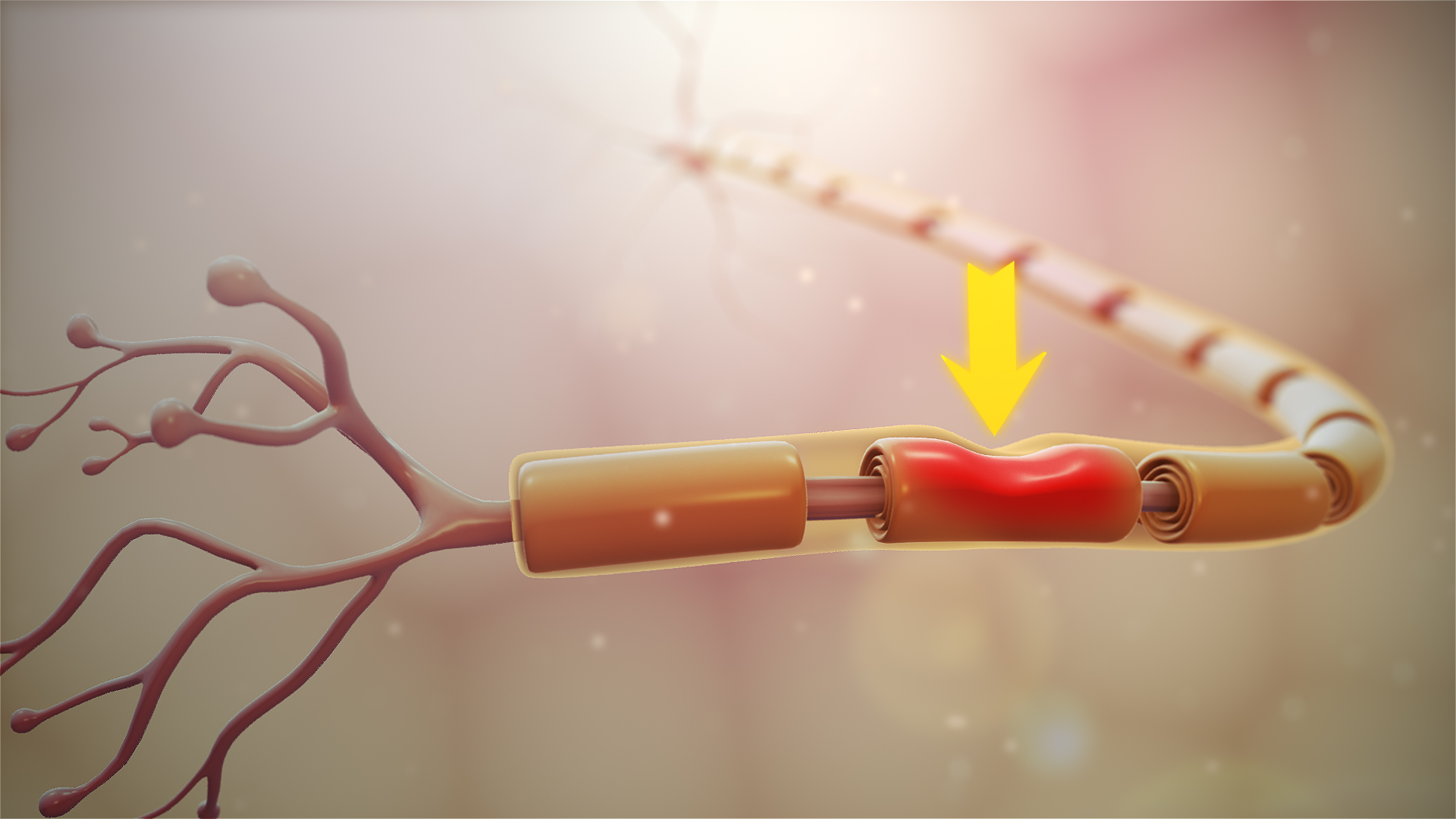
Le sciatic nerve is surrounded by a tough sheath of connective tissue, which protects it from damage. However, if this sheath is inflamed or irritated, it can put pressure on the nerve, causing pain that radiates down the leg.
Depending on where it is irritated, the sciatic nerve will cause significant pathology.
Pathologies associated with the sciatic nerve
The pathologies of sciatic nerve can occur anywhere along this long nerve, and can range from mild discomfort to complete paralysis of the affected leg. Some common ailments include:
- Sciatica: It is the most common type of pathology of the sciatic nerve. This is pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve, from the lower back to the foot. The main cause of sciatica is herniated disc. In this case, the sciatic nerve is irritated at the level of the spine.
- Piriformis syndrome : This condition occurs when the piriformis muscle, which is located in the region of the spine, is damaged or contracted. As the sciatic nerve is close to the piriformis muscle, this can lead to compression of the sciatic nerve and cause pain.
- Tumor of the spine: A tumor that grows on the spinal cord or in the Spinal canal can compress the sciatic nerve and cause pain.
- Trauma : A traumatic back injury can damage the sciatic nerve anywhere along its course, and cause characteristic symptoms.
THINGS TO DO
Treatment for sciatica is multi-factorial, and depends on its underlying cause. It is important to consult a health professional to clarify the diagnosis and guide the treatment.
Conventional treatments
The following are typical modalities prescribed to treat the symptoms of sciatica:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be helpful in reducing pain. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatories can also help reduce swelling and relieve you of pain. sciatica.
- Lumbar extension taken from the McKenzie method can quickly help relieve pain in specific cases. An often prescribed exercise is the lumbar extension. To perform this exercise, lie on your stomach and raise your body until you feel a slight tension in your lower back. Hold this position for 3 seconds and repeat ten times.
- Stretching in the buttocks can relieve muscle tension there, and thereby reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve. For example, lie on your back (on a mat) with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Place one hand on your affected leg and slowly pull your knee toward your chest until you feel a slight stretch in your buttocks. Hold this position for 30 seconds, then repeat 3 times.
- In addition to stretching the glutes, another effective treatment for relieve your sciatica is the neural slip of the nerve sciatica. This exercise involves lying on your back, grabbing the back of your symptomatic thigh. Then, the leg is gently moved up and down to tension the sciatic nerve, and improve nerve conductivity.
- Strengthening exercises for the trunk, abdominals and glutes will stabilize the lumbar region and the pelvis. This will activate blood circulation and indirectly reduce stress on the sciatic nerve, allowing an optimal environment for its healing.
- Manual treatments from a qualified therapist (such as a physio or osteo) will reduce tight muscles, manipulate problematic vertebrae, and reduce pressure on the damaged sciatic nerve.
Other alternative treatments
Applying an ointment or cream to the affected area can help relieve pain and inflammation. Besides traditional medicine, take a grandmother's remedy, such as garlic cloves, tea with miel or cider vinegar, can also relieve your sciatica temporarily. Note, however, that these alternative methods are not unanimous from a scientific point of view.
Finally, doing breathing exercises and meditation can help relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can find pain relief from sciatica.
Sciatica: when to worry? (and consult urgently?)
Although it is generally harmless, there are situations where sciatica comes from serious causes. When the sciatic nerve is really damaged (as a result of severe compression), it sometimes requires urgent medical intervention.
So here are the warning signs a cas de acute sciatica which can point to a more serious cause:
- A elective pain which concerns a vertebrate (well objectified during the clinical examination with digital pressure).
- Personalized neurological symptoms such as paresis (muscle weakness of the inner limb), the paresthesia (tingling, numbness, tingling, etc.), the sphincter disorders (urinary or faecal incontinence), thesaddle anesthesia or hypoesthesia (total or partial loss of sensitivity)... Especially when these symptoms are intense.
- Personalized persistent pain ou progressively worsening.
- Pains not relieved by rest (non-mechanical looking).
- Un antecedent de cancer (orientation towards a tumoral cause, in particular a bone metastasis of distant cancer).
- A profound asthenia, emaciation unexplained, a perte of appetite and / or deterioration of general condition (direction towards a malignant cause).
- A notion of trauma recent (orientation towards a vertebral fracture).
- A bilateral involvement (can point to a narrow lumbar canal).
- A fever ou feverish state (referral to an infectious cause such as spondylodiscitis, osteomyelitis, epidural abscess...).
- The presence of certain factors such as Addiction (intravenously) and immune deficiency.