Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
La spinal cord and the brain form the central nervous system. The latter is covered and protected by three brains. From outside to inside, we find the dura mater, thearachnoid and the pia mater. The dura mater is the superficial layer that protects the brain. It also allows the separation of bones and nerve structures present in this part of the body.
An infection between the meninges or the membranes that line the central nervous system can cause a swelling of the epidural space. This phenomenon is called epidural abscess ". We talk about it in this article.
The epidural abscess in a nutshell
THEepidural abscess results in a collection of pus in the epidural space. This pus can be present either between the dura mater of the brain and the nervous system, or between the dura mater of the spinal cord and the adjacent bone.
Spinal epidural abscess or spinal epidural abscess
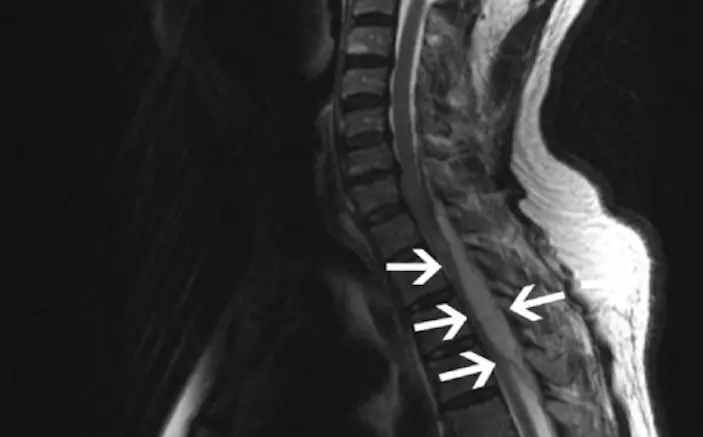
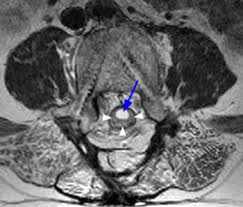
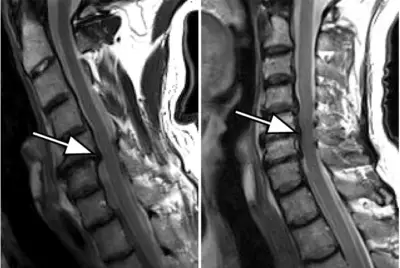
When the pus is present somewhere along the spine, we are talking aboutepidural spinal abscess (ESA) or spinal epidural abscess. The abscess may extend over several floors. Infection occurs through the blood (hematogenous route) or from a nearby focus.
The presence of pus can mechanically compress the spinal cord, but this is found in rare cases. In addition, it is completely reversible if you receive adequate treatment in time. It is indeed a neurological emergency requiring prompt treatment.
Epidural intracranial abscess
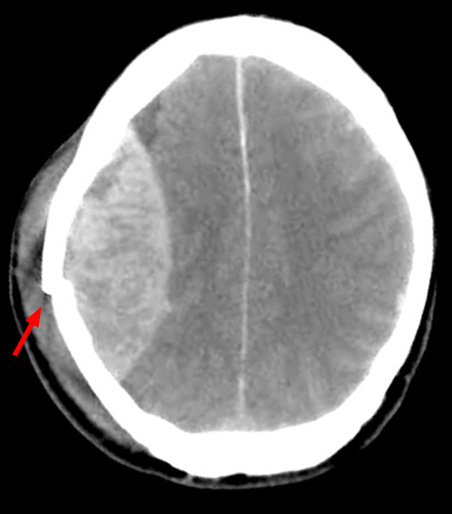
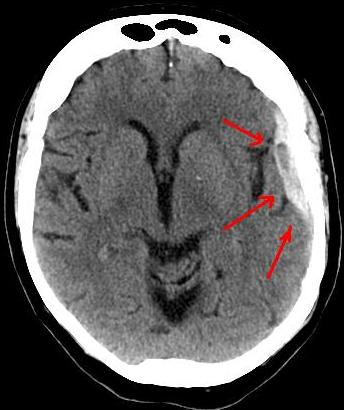
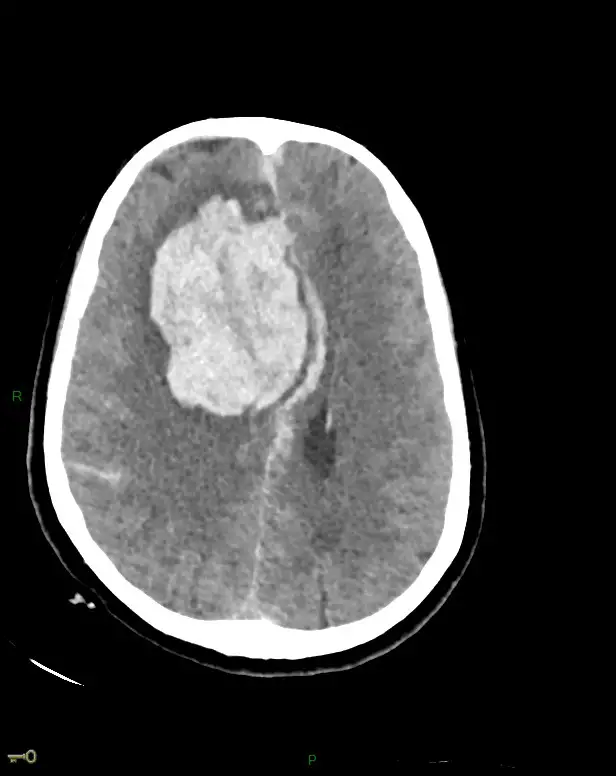
We are talking aboutepidural intracranial abscess (AIE) when the swelling is located between the skull and the brain. When pus lodges there, the adhesion of the dura mater to the skull becomes tight. This will limit its extension. In the same way, it causes a dangerous increase in intracranial pressure. An EIA is also a neurosurgical emergency.
What causes an epidural abscess?
In general, there are more cases of CSA than EIA. Indeed, epidural abscesses often appear in the thoracic or lumbar regions.
An epidural abscess is due to the presence of an underlying infection. This can be:
- at a distance such as endocarditis, a furuncle or a dental abscess;
- contiguous as in the case of vertebral osteomyelitis, retroperitoneal abscess or pressure ulcers.
The origin of this infection is not found in almost 1/3 of the cases. In the remaining cases, the presence of bacteria, fungi or parasites is identified. Usually we find the Staphylococcus aureus,Escherichia coli or mixed anaerobic germs in question.
In rare cases, thecollection of pus in the epidural space is linked to bacteremia (transport of the bacteria in the blood) resulting from:
- medical instruments;
- a dental procedure;
- injection drug use.
It also rarely happens that it is linked to a tuberculous abscess of the dorsal spine (Pott's disease).
It should be noted that this type of abscess almost never develops in the subdural space (between the dura mater and the arachnoid). On the contrary, a subdural hematoma may be the source of the infection.
Risk factors for epidural abscess
There are many risk factors for CSA:
- diabetes ;
- AIDS;
- cancer ;
- trauma;
- spine surgery ;
- recent blood infection;
- alcoholism;
- intravenous drug use…
With regard to EIA, we find these risk factors:
- history of sinus or ear infections:
- head injuries;
- head surgery.
What are the symptoms of epidural abscess?
The abscess symptoms vary depending on the location of the swelling.
Symptoms of an Epidural Spinal Abscess
If you have a spinal epidural abscess, you may notice these signs:
- bowel problems;
- bladder problems such as urinary incontinence or difficulty urinating;
- lumbar pain with sometimes radicular irradiation;
- fever accompanied by malaise, tremors or anorexia;
- vomiting;
- weakness and difficulty when moving;
- paresis of extremities (partial loss);
- more rarely paralysis.
Symptoms of an intracranial epidural abscess
On the other hand, if you suffer from an intracranial epidural abscess, you will notice these symptoms:
- severe headaches;
- nausea ;
- vomiting;
- fever ;
- lethargy (deep, continuous sleep);
- pain at the swelling.
Consequences of an epidural abscess
Spinal cord compression can cause:
- un cauda equina syndrome (neurological damage to the lower back);
- paraplegia (paralysis of the lower limbs);
- quadriplegia (paralysis of all limbs of the body).
Sphincter disorders and sensory deficits may also appear depending on the size and site of the lesions.
How to make the diagnosis of epidural abscess?
See a doctor if you suffer from:
- persistent back pain;
- headache associated with fever;
- fever accompanied by vomiting.
The consultation becomes essential if you suffer from paralysis or serious weakness. This can reflect significant nerve damage that can sometimes become permanent.
To establish the diagnosis, the doctor performs imaging tests such as a CT scan or an MRI. If necessary, other examinations can be carried out.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
In case of unexplained back pain, the doctor directly prescribes an MRI. It is an examination of choice which makes it possible to highlight the presence of a discusses (flaming disk).
La presence of a discitis makes it possible to make the difference between a spinal epidural abscess and an abscess of a metastatic tumor. In general, abscess formation occurs after inflammation of the intervertebral disc. Whereas in the setting of a metastatic tumor, the disc is intact. It is the closest bone that is destroyed.
The use of a contrast product, such as gadolinium, makes it possible to specify the diagnosis.
Myelography
La myelography can be an alternative to MRI. It's a spinal cord test. This examination must be followed by a computed tomography (CT) which makes it possible to detect the abscess.
An x-ray scanner
In 2/3 of patients, a simple X-ray scan may show osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone and bone marrow) or osteitis (inflammation of bone tissue). This examination is not systematically prescribed.
blood cultures
Once the abscess is discovered, the doctor takes samples to find the source of the infection. Blood culture is also necessary for diagnosis in order to highlight the germs present in the blood.
A lumbar puncture
La lumbar puncture is contraindicated, especially in cases of ASE. If the abscess causes a complete obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid, the lumbar puncture risks triggering a spinal cord herniation. It can also cause an intrathecal (subdural) infection.
What is targeted treatment for epidural abscess?
Usually, epidural abscess requires two types of treatment.
Drug treatment of epidural abscess
Drug treatment is based on taking antibiotics. The doctor prescribes strong antibiotics. You need to take it for 4 to 6 weeks, or even longer in case of osteomyelitis.
Surgical treatment of epidural abscess
In addition to intensive antibiotic therapy, you must also undergo surgery. It consists of draining the abscess. It will allow relieve pressure on the brain or spinal cord.
Le abscess drainage is especially recommended if you have neurological deficits such as paresis.
For ESAs, several laminectomies may be necessary in case of extension of the abscess on several floors. They allow to decompress the spinal cord by surgically cutting one or more spinal blades.
Sources
https://www.symptoma.fr/fr/info/abces-epidural
https://www.netinbag.com/fr/health/what-is-an-epidural-abscess.html