A herniated disc secondary to a kick is extremely rare, but it should not be overlooked. If you have fallen and you feel pain in your neck, arm, lower back and leg, consider a herniated disc. Depending on its location, it can be a source of neurological deficit and various complications. Discover in this article all the concepts you need to know, including gravity.
What is a herniated disc?
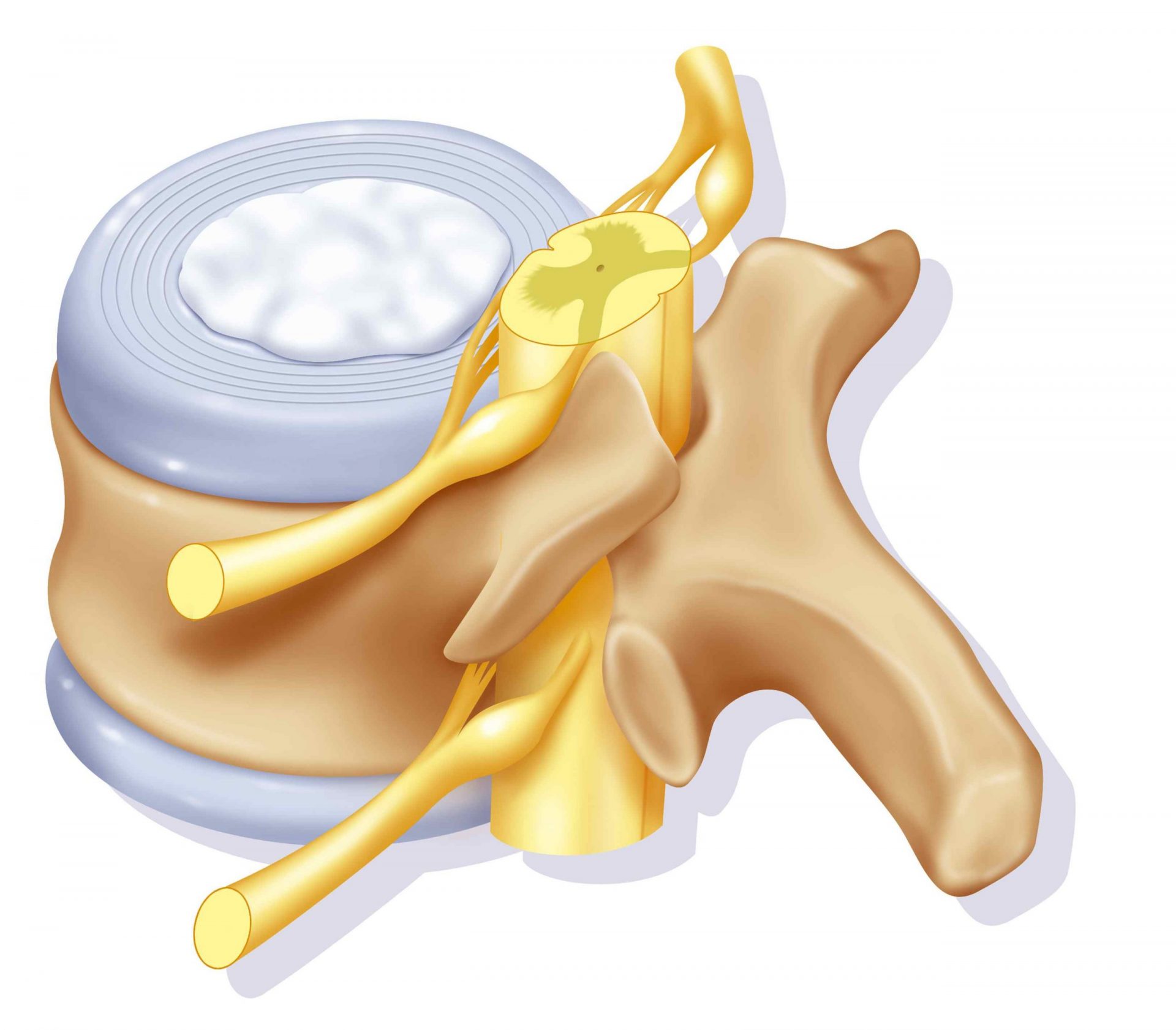
La herniated disc is the protuberance of a portion of a disc between two vertebrae. It can be located between the vertebrae, at any level (cervical, dorsal, lumbar).
Normally, the intervertebral discs give flexibility to the column and act as shock absorbers in the event of an impact. The outer layer of the disc, called annulus fibrosus, is hard and flexible and may become pushed out from the inside of the soft, gelatinous-looking disc, called nucleus pulposus.
A herniated disc occurs when a disc cracks or breaks and part of the gelatinous core breaks out. This mechanism occurs during a trauma as a fall on the back.
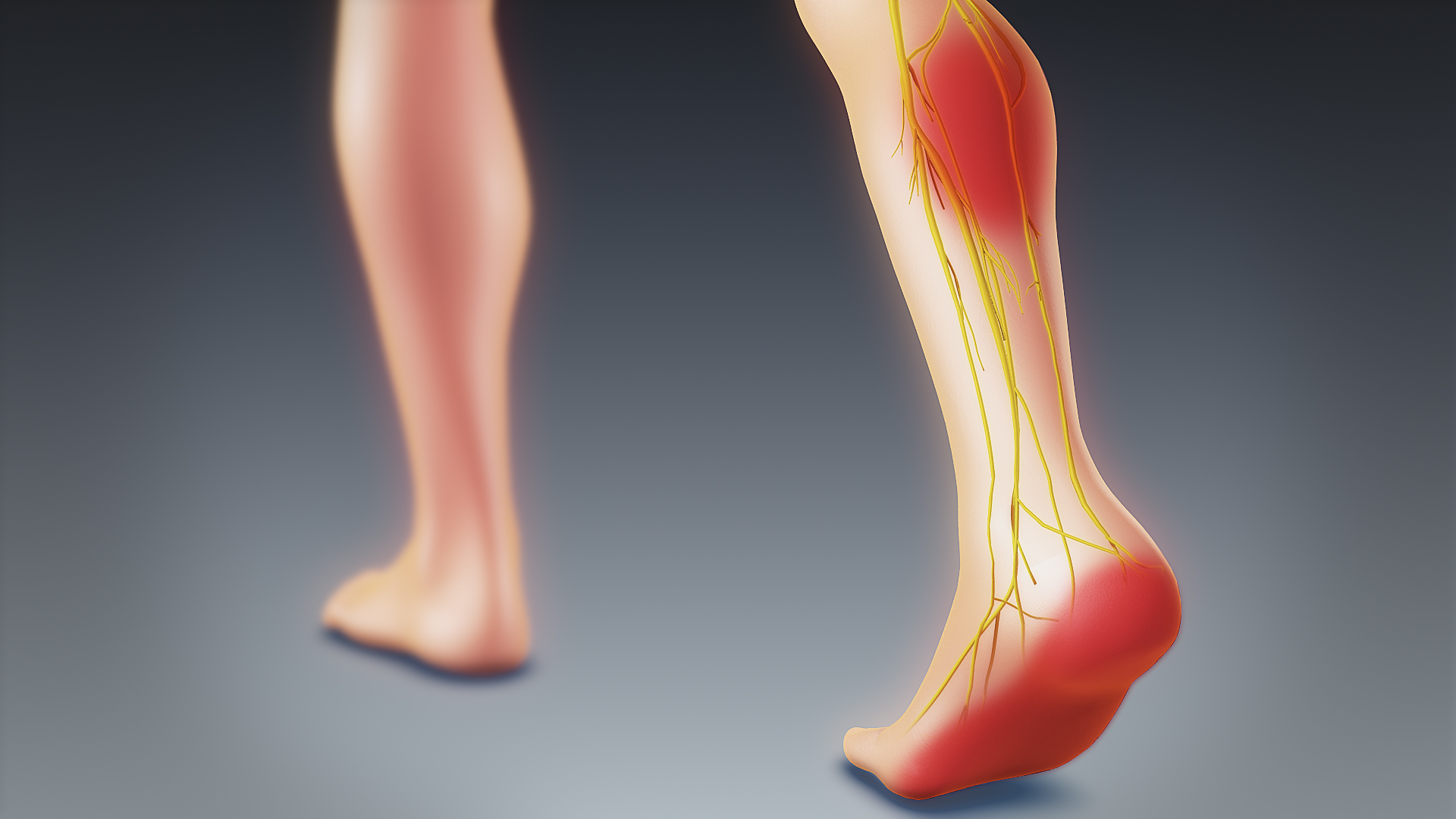
As a result, the spinal canal which contains the spinal cord will gradually shrink. We then speak of spinal compression or central. In other cases, it is the nerve roots that will end up cramped and be more or less compressed. It's here peripheral compression.
Compression of the disc on the nerve roots is the cause of different symptoms. If it is at the level of the roots at the lumbar level, it is responsible for a sciatica ou lumbosciatica (attack at the level of L5 or S1) and cruralgia (affected at the level of L4). More rarely, when the hernia is at the cervical level, a cervico-brachialgia. Thus, the pain felt in the limbs depends on the compressed roots and their path. Besides these well-known symptoms of herniated disc, many others exist, such as:
- la paresthesia which is manifested by tingling or tingling sensations;
- la dysesthesia which is a disturbance of sensitivity. It can go as far as a complete loss of sensitivity or anesthesia. The area affected depends on the affected root;
- the possibility of loss of muscle strength partial or complete;
- the sphincter disorders which are rare, but possible in some herniated discs.
What about herniated disc secondary to a fall ?
Is that bad ?
To the extent that the symptoms mentioned above appeared to you, after a sudden action, a shock or a kick, it is still necessary to suspect a likelihood of a herniated disc. Although this is a relatively rare.
In the majority of cases, it should not not really be reaction. So, you don't have to worry too much. Indeed, the pain related to herniated discs fade spontaneously after about 4 to 6 weeks.
However, it is not because the evils are attenuated that one should lower one's guard. And if the sudden resorption of pain hid complications ?
When should you worry?
Indeed, like all diseases, there are always more complicated cases. This is explained by the fact that everyone does not necessarily react in the same way to a disease. Since each organization has its specificities.
In addition, the conditions, frameworks and effects of falls are not always necessarily the same. A fall on a few stairs, a stumble will not have the same effects as a fall from the top of a slope of a few meters. So there will be cases where you need to worry more like the case when the following signs present themselves:
- the persistent back pain and become unbearableOr handicapped ;
- you become feverishand you lose weight without other obvious reasons;
- After the fall, your ailments come together incontinence whether urinary or fecal, or on the contrary of the retention (which translate a paralysis bladder);
- a limb impotence: you have difficulty moving your legs, for example;
- a decrease and loss of reflexes at the level of the lower limbs: while you walk, you feel a release and you fall automatically.
These are the main signs of severity as well as complications against which you have to worry.
They are to be feared since they reflect a lserious lesion of the spine and trauma cervical. If they are not dealt with as soon as possible, they could get worse more and jeopardize the vital prognosis of the patient. This can be immediate or delayed, in relation to the respiratory and cardiovascular complications that could be linked to it.
So, in summary we have to worry if there is:
- chronicity (this is especially common in people who are overweight, depressed and chronically stressed);
- neurological impairment: neurological deficit, paralysis (irreversible);
- if the patient is particularly vulnerable (as in the case of older people, for example).
What to do in the event of a herniated disc after a fall?
See a doctor
If you suspect a herniated disc due to a fall, you must first consult a doctor. The latter will perform various clinical and paraclinical examinations to confirm the diagnosis.
At thephysical examination, the practitioner insists more particularly on painful areas and on the back (flexibility, mobility, looking for signs of nerve root damage).
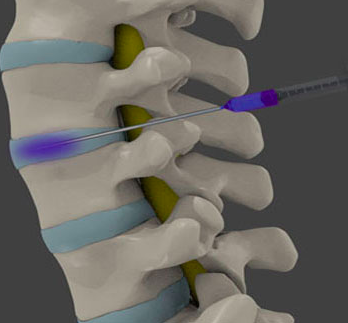
While at theexam paraclinical, he will prescribe an MRI or CT scan to determine the location and confirm the cause.
CT myelography is prescribed only when more details of the spinal cord and adjacent bones are needed.
Sometimes electrodiagnostic tests are done to examine the nerves, muscles, and to identify the affected spinal nerve root.
Follow non-drug treatments
Simple measurements can be used to ease the pain, as : the application of cold (ice packs, etc.) or hot (hot water bottle…), the repos strict in bed (for 5 days) in a comfortable position.
If the patient sleeps in the supine position, a cushion can be placed under the knees.
On the other hand, if the sleeping position is in lateral decubitus, a pillow should be placed under the head and between the knees. It is also necessary to flex the hip in this position.
Following drug treatments
The analgesics (paracetamol, etc.), NSAIDs (ibuprofen, etc.), corticosteroid injections and muscle relaxants are the most prescribed by doctors.
They not only relieve pain, but also gradually resorb the hernia. In 90% the results are good.
Opt for surgical treatment
It is indicated only as a last resort and only in case paralyzing, hyperalgesic hernia without any apparent efficacy of drug treatments.
Do physiotherapy and practice some exercises at home
Physical therapy will relieve symptoms and improve function. It will include in particular analgesic modalities such as massage or electrotherapy, and will integrate adapted and progressive therapeutic exercises.
Projects
https://www.vidal.fr/maladies/appareil-locomoteur/hernie-discale/symptomes-complications.html