If one herniated disc can go unnoticed, it can also be responsible for a leg paralysis. Indeed, when the protrusion of intervertebral disc compresses the root of the nerf sciatica consequently, this can lead to motor impairment in the lower limb. In this article, we will explain the link between a herniated disc and paralysis of the leg.
Some notions of anatomy on the spine
To make you understand herniated disc, it is important to remember the anatomy of the spine or spine.
Le spine is a bony arrangement, compound vertebrae juxtaposed which are connected to each other by intervertebral discs. The spine starts from the neck and ends at the pelvis.
At the bottom of the skull, there are 7 chained cervical vertebrae followed by 12 dorsal vertebrae. The spine ends with the 5 lumbar vertebrae (L1, L2, L3, L4, L5) and the sacrum. The latter is composed of 5 triangular vertebrae (S1, S2, S3, S4, S5).
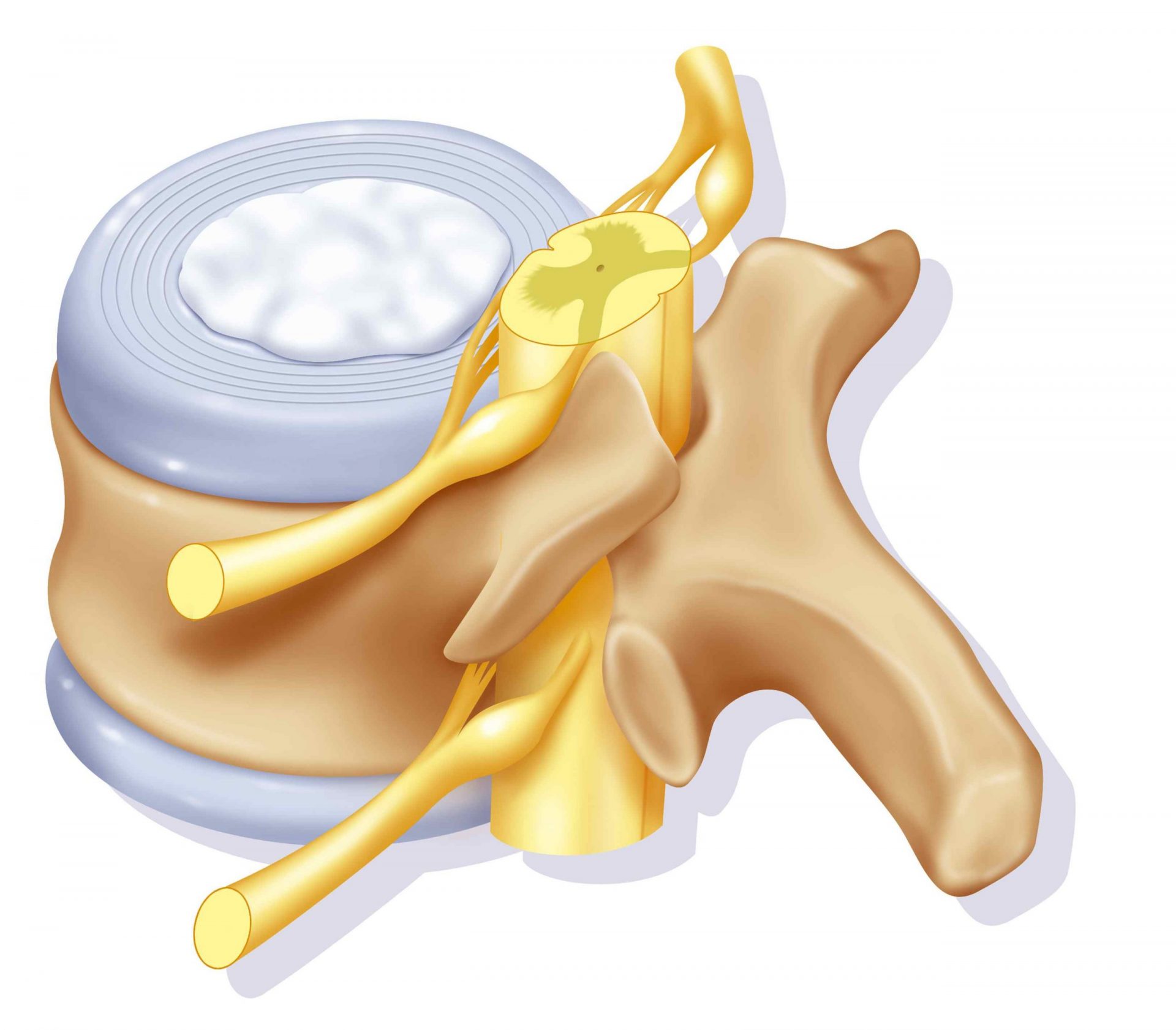
La spinal cord travels along the canal of the spinal column and communicates with the legs through the nerves whose roots are in contact with the intervertebral discs.
5 pairs of spinal nerves branch between the lumbar discs and another 5 pairs exit from the sacrum. They meet at the bottom to form a large nerve called sciatic nerve.
Focus on herniated disc
Definition
Often at the origin of a lower back pain, lumbar disc herniation is a protrusion of the lumbar or sacral discs. The protrusion of these discs goes backwards then to the left and will irritate the nerve roots that surround them.
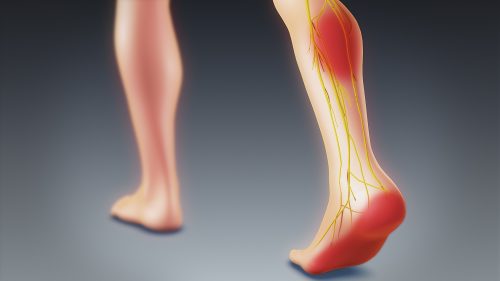
This will induce inflammation of these roots which is responsible for pain in the lower back. This radiates towards the buttock and the leg. It causes unpleasant symptoms on the foot, even paralysis of the leg.
What are the causes of a herniated disc?
The exact cause of a herniated disc remains undetermined, but specialists have nevertheless gathered some biomechanical and environmental causes. Indeed, it can be:
- genetics;
- stress-related;
- osteoarthritis;
- un narrow lumbar canal ou spinal stenosis (video explanation);
- caused by a previous injury;
- the result of repeated efforts and the carrying of heavy loads;
- the consequence of excessive weight;
- the effect of sedentary work;
- abdominal weakness;
- the consequence of bad posture…
How does a herniated disc manifest?
If in some patients, this disease may have no signs in others it is disabling. here are the herniated disc symptoms that we can meet.
- Persistent pain on walking and prolonged standing.
- Pain when sitting and bending forward.
- Appearance of lumbar torsion in case of movement.
- Lower back pain on intense exertion.
- Electric-like pain radiating to the leg.
- Numbness and tingling in the feet.
- Feeling of weakness in the leg.
- Sciatica.
- Cruralgia…
When the situation worsens, the patient evokes the following symptoms.
- Leg paralysis.
- The persistence of continuous pain of mechanical origin.
- Night sweats.
- Weightloss.
- Urinary and fecal enuresis.
Paralysis of the leg during a herniated disc: why?
Nerves are conductors of nerve impulses. They transport information to the brain via the spinal cord, and conversely, the brain sends sensory messages back to the organs or reflex messages to the muscles.
The spinal or spinal nerves have a dual function: a motor function and a sensory role. They are branched anteriorly and posteriorly and unite by a large sciatic nerve which innervates leg muscles.
A herniated disc compresses the lumbar or sacral nerves and irritates them. Then, this irritation radiates to the sciatic nerve. When the nerve is further compressed by the protrusion of the intervertebral discs, it mainly affects the leg. However, if the nerve compression lasts more or less long, the hamstrings weaken more and more and this causes muscle weakness in certain leg muscles.
If the problem persists, it leads to paralysis of the leg. This paralysis does not go alone, often it is accompanied by urinary and fecal incontinence, paresthesias, constant pain...
This is called a crippling disc herniation.
How is a herniated disc diagnosed?
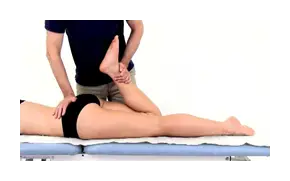
To make the diagnosis, the doctor needs to perform some reflex tests, palpations and clinical examinations.
He first observes posture, then tests sensitivity and range of motion. He then checks muscle strength and leg reflexes. It will also assess nerve conduction and put tension on the sciatic nerve. A neurological examination helps determine the presence of nerve irritation.
A review ofmedical imaging can clarify the presence of a herniated disc or the presence of another bone pathology. Otherwise, it can also be a myelopathy, a cauda equina syndrome, cancer or a narrow lumbar canal…
Treatment of a herniated disc: what to do?
In the presence of symptoms, the patient's condition is considered serious, so it is necessary to consult without delay. In the context of irradiation or tingling of the leg, this is a medical and sometimes surgical emergency. After the herniated disc surgery, it is best to follow physiotherapy sessions specific. It helps to recover as soon as possible.
Otherwise, there are several other ways to treat a herniated disc, moderate physical activity is one of them. Avoid resting as this will cause muscle atrophy and loss of bone density. Sport will promote weight loss, maintain muscle function (via muscle oxygenation) and promote healing.
Physical therapy and massage therapy often work to relieve low back pain and improve function.
For relieve lower back pain, natural methods such as heat or ice help calm them down. It is also possible to take painkillers and anti-inflammatories, but after doctor's approval.
Projects
Herniated disc and sport: do they go together?
https://www.lombafit.com/hernie-discale-a-z/
https://www.lombafit.com/hernie-discale-et-sport/