If you feel a hip pain, the first cause you need to think about is the sciatica. But, pain emanating from this region can also have another origin such as gluteus medius tendonitis.
La gluteus medius tendonitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the gluteus medius muscle particularly affecting athletes.
After reading this article, you will be able to find out what gluteus medius tendonitis is, its different causes, its symptoms and how long it lasts.
Anatomical reminder
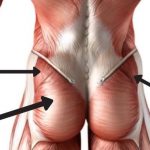
Also called the gluteus medius, the gluteus medius muscle is one of the muscles that make up the gluteus. It is located on the outer side of the hip and plays a key role in stabilizing the pelvis and trunk, especially when walking.
It also plays a role in the abduction and external and internal rotation of the thigh.
It is a muscle constituting the superficial plane of the muscles surrounding the hip joint. It inserts at the level of the external iliac fossa above and ends by inserting below through a tendon on the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter which is at the upper and lateral part of the femur.
Definition of gluteus medius tendonitis
The tendon is an anatomical structure that attaches a muscle to a bone. When the latter is the seat of inflammation, we speak of tendonitis.
La gluteus medius tendonitis thus represents the inflammation of the tendon attaching the gluteal muscle to the greater trochanter.
It is generally due to significant and repetitive stress on the muscle, thus putting it under excessive tension. It is a pathology frequently encountered in some athletes practicing running, figure skating on ice, skiing or martial arts because of repeated support on one foot.
It can nevertheless be secondary to trauma, a metabolic disease affecting the muscles or a tumor cause.
It is more frequent in women because of their pelvis which is wider and therefore more subject to muscular stress, and in the elderly in whom it is often associated with other lumbar pathologies.
Other factors such as the tabagisme (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) and the obesity also seem to play an important role in the appearance of this pathology.
Finally, it is important to emphasize that in the long run, this pathology can tend towards chronicity and become quite disabling on a daily basis.
La gluteus medius tendonitis is manifested by so-called pain exquisite and occurring when the gluteus medius muscle is solicited. This pain can be felt at the level of the hip or the posterior and/or external part of the buttock.
It radiates to the outer face of the thigh and can go to the foot, sometimes simulating sciatica. It is often triggered by prolonged standing, climbing stairs or running.
It happens that gluteus medius tendonitis causes lameness. Especially when the pain becomes permanent.
The diagnosis of gluteus medius tendonitis is typically clinical. A simple physical examination can highlight the pain, identify its origin and eliminate other causes.
Sometimes a radiography and scan may be requested to assess the extent of the lesion.
To know everything about gluteus medius tendonitis, see the following article.
How long does it last ?
The time required for the healing of gluteus medius tendonitis depends on the one hand on the seriousness of the lesion and on the other hand on the earliness and the quality of its management.
When the inflammation is not severe, healing may require three to six weeks.
On the other hand, when the attack is more widespread and more serious, the duration can extend over several months (six to eight months on average), it even happens that it becomes chronic and never fully recover.
There are different determining factors for the healing of tendonitis which are the factors accelerating the healing and the factors which slow it down.
Factors accelerating healing
Rapid healing of gluteus medius tendonitis depends on multiple factors and comprehensive care.
- Consultation and early diagnosis:
It is important not to neglect hip pain and to consult a health professional as soon as possible so that the problem is detected and taken care of quickly.
- Good medical follow-up:
The role of the healthcare professional should not be limited solely to diagnosis but go beyond this with rigorous and appropriate follow-up of the lesion. The latter will not only determine the best therapies but will also direct you towards a physiotherapist (physiotherapist) which will play an important role in mobilizing the hip and reducing pain.
- Appropriate treatment:
In addition to resting the gluteus medius muscle, medical treatment is usually prescribed by the doctor, it is represented by painkillers type nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and sometimes, corticosteroid injections.
From the almost complete physiotherapy is also essential in the management of gluteus medius tendonitis. She uses analgesic modalities to relieve pain, therapeutic exercises, and daily advice.
- physical exercise
A suitable physical exercise program must be put in place to allow good muscle and tendon strengthening.
- The role of a healthy diet:
Tendinitis being a inflammation, the rapid reduction of the latter also passes through thefood. Indeed, a consumption of vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage or spinach which are rich in antioxidants reduces inflammation and therefore speeds up healing.
It is also advisable to consume foods rich in protein (eggs, dairy products) which strengthen the muscles and help rebuild them after tendonitis, as well as increasing the intake of vitamins (especially vitamin C) and minerals such as zinc, magnesium and potassium.
Factors slowing healing
As healing can be accelerated by some factors, it can also be slowed by others, including:
- La tobacco consumption as well as caffeine which contributes to bone loss by binding to calcium;
- La alcohol intake which maintains inflammation and prolongs its duration;
- La overweight and muscular which can aggravate the attack;
- Un too much rest : although it is part of the care, prolonged rest can be the cause of muscle weakness due to the non-solicitation of the latter;
- A high consumption of sugar : can slow muscle healing and reduce immune defenses while prolonging and maintaining inflammation.
Prognosis
The course and prognosis of a gluteus medius tendonitis depend essentially on the precocity of the care and the quality of the latter.
Thus, when the patient benefits from adequate treatment, gluteus medius tendonitis has a fairly good prognosis and generally progresses towards complete recovery.
However, when the lesion is neglected and the recommendations and treatments are not taken seriously, the disease can become chronic and very disabling on a daily basis, in particular due to the pain and lameness it can cause.