La multiple sclerosis corresponds to an inflammatory pathology called autoimmune, touching the central nervous system. Recognized as the leading neurological cause of non-traumatic disability in young adults, the diagnosis of SEP is essentially based on cerebral MRI.
But what about cervical MRI ? Can she diagnose multiple sclerosis? Answers in this article.
What is multiple sclerosis?
La multiple sclerosis ou SEP is defined as a chronic inflammatory disease of autoimmune origin. It affects the central nervous system, in other words the encephalon (brain, cerebellum and brainstem), the spinal cord and peripheral nerve roots.
First described in 1868 by Jean-Martin Charcot, it now affects around 120 people in France, with an average of 000 new cases detected each year. The average age of diagnosis is between 3 and 000 years old, and there is a predominance of involvement in women.
Multiple sclerosis is currently considered the leading cause of severe non-traumatic disability in young adults.
It is a disease that usually progresses through spurts interspersed with periods of remission. However, it sometimes happens that its evolution is continuous and gradual.
The mechanism behind multiple sclerosis is a demyelination of axons. Indeed, the axons are extensions of the neurons which are surrounded by a sheath formed by a substance called " myelin », this sheath has the role of protecting and isolating nerve fibers while increasing the speed of propagation of nerve impulses.
During multiple sclerosis, the immune system attacks, for reasons still unknown, the myelin-producing cells called " oligodendrocytes and destroys them. This results in a demyelination of nerve fibers and the absence of myelin sheath leads to impaired conduction of nerve impulses.
Since the central nervous system is the place of command for intellectual, cognitive, sensory and motor functions, its impairment therefore results in multiple symptoms secondary to the anomaly of these functions.
Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for multiple sclerosis. The proposed treatments, based on immunoregulators and immunosuppressants, only allow a spacing and a reduction of flare-ups, thus slowing down the progression of the disease.
It nevertheless happens that encouraging therapeutic advances in terms of the development of a treatment that can improve the evolution and prognosis of this pathology are under development.
Clinical diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a slowly progressing disease. Indeed, many patients present during their lives transient symptoms that are not immediately related to this pathology. This is called the " latency phase ". This phase can last from 1 year to 20 years, it is characterized by demyelination that does not cause clinical manifestations.
When the clinical signs begin to appear, the disease then becomes " license and the disease begins to evolve either continuously and progressively, or by flare-ups interspersed with periods of remission.
Multiple sclerosis attacks are characterized by dissemination in time and space. This means that they affect different organs and occur at different times..
The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is currently based on a bundle of clinical and paraclinical arguments.
The clinical manifestations encountered in multiple sclerosis are very varied. All of its symptoms generally evolve in a context of permanent fatigue, so we find:
- Personalized motor disorders: telltale signs of the disease in 40% of cases, it may be monoparesis, paraparesis or more rarely hemiparesis. This manifestation can range from discomfort such as heaviness, muscle cramps or fatigue on exertion to more complete paralysis. In the extreme paraplegia with abolition of reflexes may occur.
- Personalized sensitivity disorders:revealing the disease in 20% of cases, these disorders include paresthesias, hypoesthesias and even anesthesia. But also, pain or feelings of electric shocks during certain movements.
- Vision problems:falling within the scope of retrobulbar optic neuropathy, these manifestations reflect damage to the optic nerve, they include a decrease in usually unilateral visual acuity accompanied by periorbital pain increased during movement of the eyeballs.
- Disorders related to the impairment of cranial nerves : such as facial paralysis, decreased hearing acuity (hypoacusis) or facial neuralgia.
- Disorders due to cerebellar and vestibular involvement: including light-headed gait, ataxia, dysarthria and vertigo.
- Genito-sphincter disorders: include sexual impotence in men, retention or, on the contrary, urinary incontinence.
- Cognitive disorders: such as concentration difficulties and memory problems are found after a few years of progression of the disease. In the extreme, dementia can occur.
Paraclinical diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
Confirmation of the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis requires the performance of certain paraclinical examinations, namely:
Lumbar puncture
It allows a biological and immunochemical analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid, it highlights the presence of inflammatory signs and an abnormal synthesis of immunoglobulins (antibodies) in the latter.
Before its realization, it is nevertheless necessary to make sure that there are no contraindications such asintracranial hypertension and this by performing a fundus and/or a brain scan.
The study of CSF must systematically be done simultaneously with that of the patient's serum taken on the same day in order to make a comparison.
The measurement of evoked potentials
The evoked potentials are electrical potentials which make it possible to study the variations in the electrical activity of the nervous system following a stimulation of external visual, auditory, sensory or motor origin.
It makes it possible to evaluate the quality and speed of conduction of nerve impulses in the motor, sensory, hearing or vision pathways.
Regarding MS, the visual evoked potentials are the only ones used to confirm the diagnosis. Indeed, a slowing down of transmission of nerve impulses at the level of the optic nerves is generally observed.
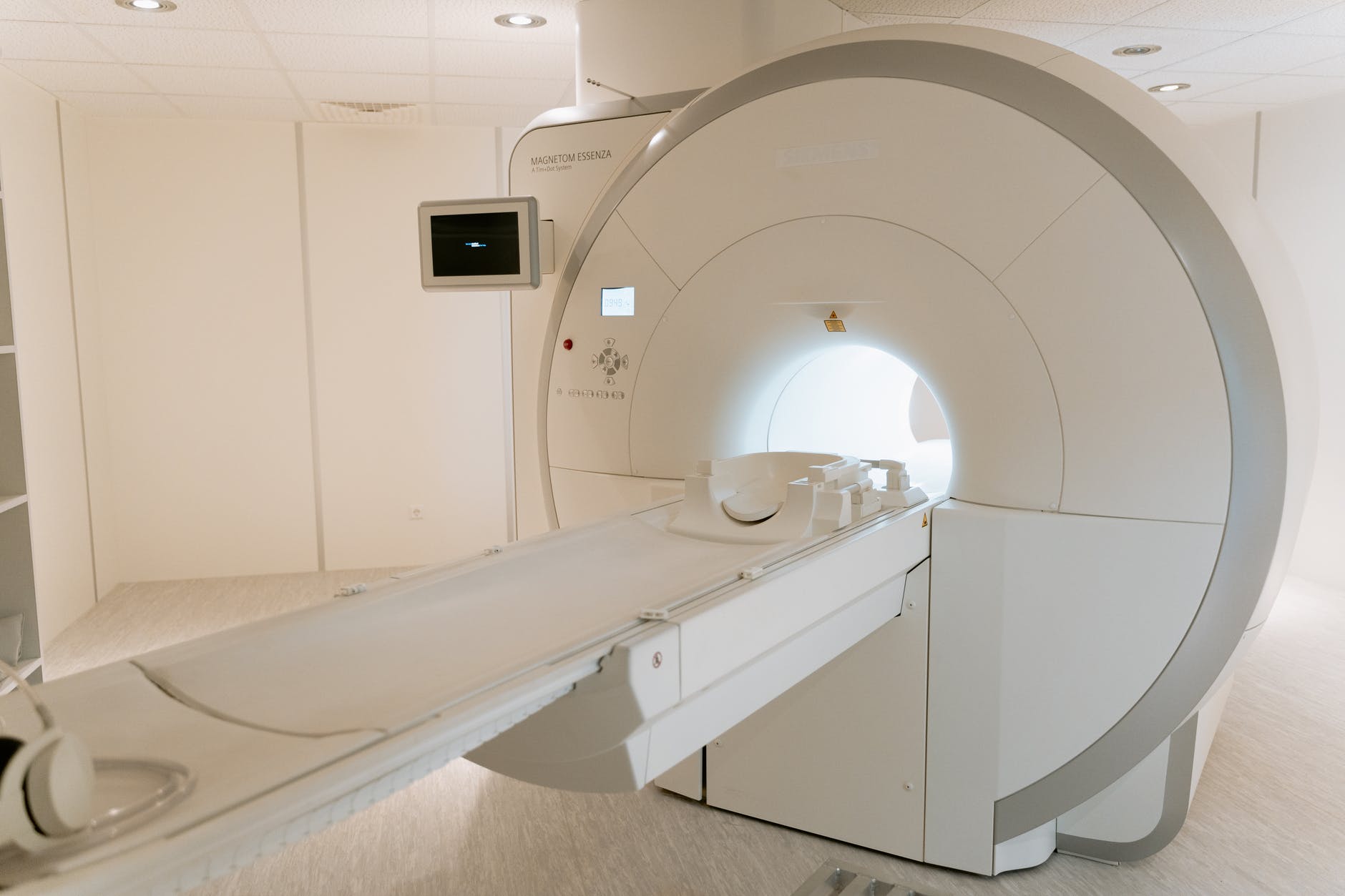
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
THEBrain and spinal cord MRI represents the examination of choice in the diagnosis of MS, it makes it possible to highlight the presence of inflammatory plaques in the central nervous system.
These plates are called injury ", they take the appearance of white spots named " hypersignals » or black say « hyposignals ».
These lesions are generally located in the periventricular white matter, more particularly in the brainstem and in the marrow, especially the cervical one, hence the interest of using a Cervical MRI.
Role of cervical MRI in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
In general, the first imaging examination indicated in multiple sclerosis is cerebral MRI. It nevertheless happens, in certain patients, that no brain lesions are found because the plaques have only formed in the spinal cord and more particularly in the cervical area.
It is in this situation that theCervical MRI finds all its interest.
However, it should be emphasized that cervical MRI alone is not enough to confirm the diagnosis, nor to monitor the disease.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.