La Arnold's neuralgia also known as occipital neuralgia ou Arnoldalgia, is a pathology responsible for severe neck pain, due to damage to the greater occipital nerveor Arnold's nerve.
For several years this disease remained unknown to health professionals because of its particular symptomatology evoking no known etiology of neck pain.
Today, thanks to a better knowledge of Arnold's nerve anatomy as well as the advent of themedical imaging, we know almost everything about this pathology.
This article will review the role and interest of medical imaging and more particularly ofIRM diagnosis of Arnold's neuralgia.
What is Arnold's neuralgia?
La Arnold's neuralgia also called occipital neuralgia, is a pathological entity belonging to the group of cervical headache. The latter are characterized by headaches whose origin is in the cervical region, that is to say the neck.
It presents in the form of pain of neuropathic origin, linked to an attack of the arnold's nerve or greater occipital nerve. The latter can be the seat of a compression or an irritation during its course, starting at the level of the nape of the neck and ending along the scalp.
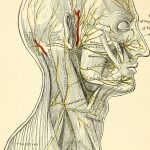
Focus on Arnold's nerve
Le Arnold's nerve (or greater occipital nerve), so named in reference to the German anatomist Friedrich Arnold who described it for the first time in 1834, is a so-called mixed nerve referring to its two components: motor and sensory.
It arises from the posterior branch of the 2nd cervical nerve root, i.e. between the two vertebrae cervical C1-C2 also called the axis and the atlas.
Le arnold's nerve has a complex path. Indeed, it presents several segments and angulations walking through several muscles constituting the framework of the neck.
This particular intramuscular route explains the risk of irritation and entrapment of Arnold's nerve resulting in the characteristic pain of Arnold's neuralgia.
On the sensory plane, greater occipital nerve (NGO) is responsible for the innervation of the cervico-occipital region with an endocranial and exocranial component.
- The exocranial territory corresponds to the cutaneous innervation of the occipital region (back of the skull) to the vertex (top of the skull) and the parietal region.
- The endocranial territory corresponds to the meninges of the occipital region.
On the engine blueprint, the motor fibers innervate the cervical muscles responsible for the mobility of the head: the semispinatus muscle of the head, the inferior oblique muscle, the longissimus of the head, the splenius and the trapezius.
What are the etiologies of Arnold's neuralgia?
La Arnold's neuralgia is the consequence of nerve damage linked to a conflicting situation with the anatomical structures of the neck. Indeed the intimate contact of the arnold's nerve with the bone and muscle elements of the cervical region makes it vulnerable to compression phenomena.
The causes inducing compression of Arnold's nerve leading to the symptomatology of Arnoldalgia are numerous, among others:
- Cervical arthritis, the most common cause of Arnold's neuralgia. Joint degeneration leads to the formation of bone spurs which compress or irritate the nerves occipitals.
- Cervical sprain, related to trauma: Whiplash (whiplash during a car accident), falls on the head, direct trauma to the base of the skull.
- Muscle contraction
- Herniated disc cervical
- Polyarthrite rhumatoïde
- Spinal cord tumor
Although several etiologies have been implicated in the development of Arnold's neuralgia, this pathology remains in the majority of cases without known origin, that is to say idiopathic.
How does it manifest?
La Arnold's neuralgia is characterized by a variety of symptoms. Initially, it manifests as neck pain originating at the base of the neck and radiating to areas innervated by the greater occipital nerve.
The pain is typically chronic, evolving suddenly, that is to say painful phases followed by periods of calm. They are often very intense, induced by head movements.
Other symptoms observed are:
- headaches severe affecting the frontal, orbital (eyes) and temporal region.
- Vertiginous crises in severe pain.
- Feelings of burns or electric shocks in the occipital region.
How to diagnose Arnold's neuralgia?
If you have a persistent pain, it is obviously advisable to consult a doctor who can then make an initial diagnosis following an interrogation and a meticulous clinical examination.
The interrogation
He will be particularly interested in describing the pain reported by the patient.
The characters of unilaterality, paroxysm, frontal or occipital headaches resistant to the usual analgesics (eg paracetamol) as well as sensations of burning and electric shocks in the skull will be systematically sought.
Physical examination
Clinical examination, especially palpation, looks for pain caused by delicate pressure on the course of Arnold's nerve. This is called trigger point ou trigger point. This one is initially on the zone of emergence of the nerve at the level of the second vertebrate cervical.
Additional tests
It should be noted that the diagnosis of Arnold's neuralgia is above all clinical: the prescription of additional examinations is not systematic to confirm it.
Nevertheless, at the end of the consultation, the doctor may possibly consider prescribing it in order to highlight an etiology responsible for the development of nerve damage causing this pathology.
Here are the examinations that may be of interest in the diagnosis of a Arnold's neuralgia :
standard x-ray
It makes it possible to study the bone structures (the vertebrae cervical) which can be the seat of fractures which can compress the 2nd nerve root at the origin of the Arnold's nerve.
CT scan
This examination allows a very detailed study of the bone structures. It will make it possible to search, among other things, for the signs of a Osteoarthritis cervical, primary cause of Arnold's neuralgia.
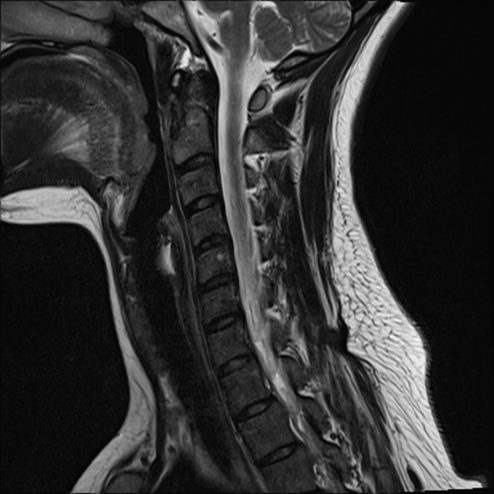
Cervical MRI
It is the radiological examination of choice in the diagnosis of a Arnold's neuralgia. It allows visualization of the anatomical conflict at the origin of the nerve damage thanks to the 3D images it provides.
Benefits of MRI in the diagnosis of Arnold's neuralgia
Cervical MRI is the reference examination in Arnold's neuralgia, due to its high sensitivity and precision.
Thanks to its 3D images, MRI makes it possible to finely detect the nerve damage, thus the various causes of compression of the arnold's nerve (Ex: joint degeneration, spinal cord compression, cervical trauma).
It makes it possible to exclude pathologies describing a symptomatology similar to Arnold's neuralgia, namely a trigeminal neuralgia, migraines, tension headaches or even cluster headaches.
This is a non-invasive examination that does not use ionizing rays that are harmful to health (unlike standard scanners and x-rays).
Procedure
Cervical MRI is like any MRI, a non-invasive, painless examination that does not require prior preparation.
Its contraindications are few and are mainly related to metallic objects inside the body (metallic surgical material in the skull, pacemakers, etc.).
Although completely painless, MRI has certain disadvantages:
- Extended duration : duration of 20 to 45 minutes when the device is locked on its back and completely still. Although this may seem innocuous, it may not be possible for people with claustrophobia, which requires them to undergo an MRI under general anesthesia.
- Noise : The device is very noisy, however people who are phonophobic can use earplugs during the test.
- High cost.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.