Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
The pelvic fractures are potentially serious. They are associated with a high mortality rate between 5 and 15%, even up to 50%. As the basin contains several noble organs (vascular, nervous, digestive, urinary and genital), a lesion in this region can cause immediate complications that can be fatal. In this article, we tell you all about the pelvic fractures.
Definition and types of pelvic fracture
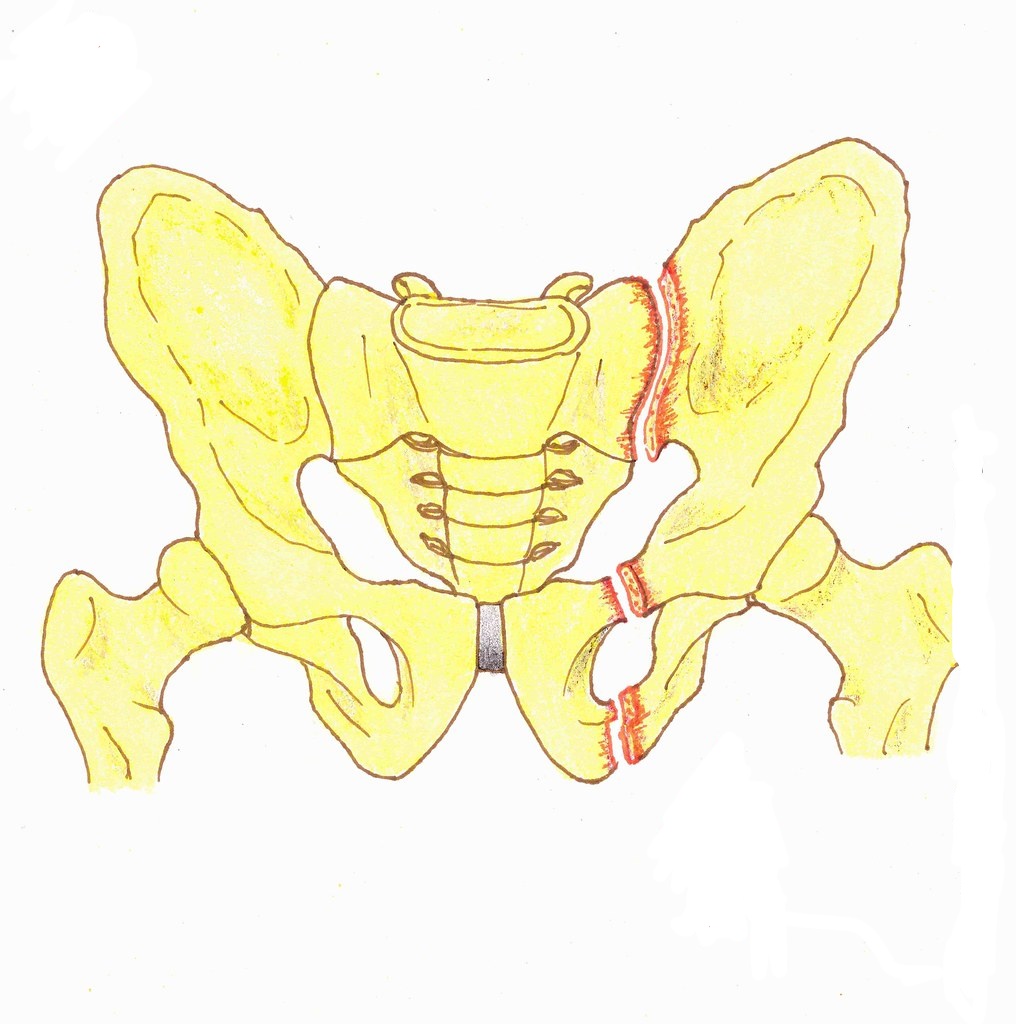
Le basin , is made up of 3 bone structures : I'iliac, sacred and pubis. It has several joints dedicated to the mobility and standing position :
- the hip joint (the coxo-femoral joint);
- the sacroiliac joint;
- the pubic symphysis.
The pelvic fractures can affect each of these bones, with more or less complex lesions. They can also affect nearby vessels, nerve roots or organs.
Those are frequent fractures with a varying severity. This ranges from benign partial fractures to major forms breaking the continuity of the pelvic ring. For these forms, the mortality rate is very high. The pelvic ring fractures represent 1,5% de l 'all osteo-articular fractures.
Pelvic fractures are classified into 3 main types.
- Stable lesions with respect for the organs of the small pelvis: these are fractures of the iliac wing, the ischium, the sacrum or the coccyx, without repercussions on the function of the lower limbs and walking abilities.
- Partially stable lesions with rotations of the fracture segments, but with respect for the organs of the small pelvis.
- Unstable lesions with complete rupture of the pelvic ring, with damage to the organs of the small pelvis. We typically find vascular lesions, nerve lesions (lumbar plexus et sciatic nerve), urinary lesions (ruptured bladder, urethral injury) and skin lesions.
Causes of pelvic fractures
Most pelvic fractures occur as a result of high kinetic energy trauma. These traumas include:
- road and traffic accidents (context of polytrauma, in nearly 75% of cases);
- accidents at work, which are seen above all in construction workers, most often following a fall from scaffolding;
- sporting accidents such as jump mountaineers;
- war accidents in mine explosions for example;
- defenestrations for the purpose of suicide or recklessness;
- earthquakes ;
- landslides causing pelvic crushes and members.
The lesions are most often severe and displaced. They usually appear in young people, with a male predominance.
The simple lesions, little displaced, concern rather the elderly population, essentially female, following a low energy trauma.
Apart from high-energy trauma, there areother risk factors to a pelvic fracture such asosteoporosis or cancer.
Symptoms of Pelvic Fractures
Most of the time, this type of fracture is observed in a young victim of a road accident.
The injured person complains of a severe pain at the level of pelvic region. Depending on the bones or joints affected, the pain may be in the pubis, in agroin or in the buttock.
Concretely, the practitioner awakens pain in the iliac region by mobilizing the coxo-femoral joints. It also causes it by compressing the iliac wings and spreading the iliac wings.
One can also find gait disorders, even a complete incapacity à mobilize the lower limbs ou to move.
Depending on the severity of the associated lesions, the patient may present:
- signs of genitourinary and/or gynecological injuries : blood in the urine (haematuria), anuria, vaginal bleeding, bleeding from the urethral meatus, scrotal or perineal hematoma;
- signs of vascular complications: retroperitoneal hematoma manifested by abdominal bloating;
- signs of bowel damage: abdominal or pelvic pain, rectal bleeding, perforation, etc.;
- neurological damage: loss of motor skills and sensitivity of the lower limbs, urinary incontinence or urinary retention…
Diagnosis of pelvic fractures
Le diagnostic a broken pelvis initially based onphysical examination. It consists of examine the hip joints and palpate the pelvis, looking for:
- by pelvic asymmetry with elevation of a iliac crest and lower limb shortening ;
- by exaggerated external rotation of two lower limbs which is seen in the large pubic disjunctions;
- an abdominal bloating by a retroperitoneal hematoma.
Un imaging workup is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis. It consists first of all in carrying out AP and three-quarter (3/4) x-rays of the pelvis. These x-rays will then be supplemented by a scanner (possibly with 3D reconstruction) in order to clearly visualize the fracture lines and/or possible bone displacements.
Depending on the context, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a CT angiography can specify the associated vascular or cartilaginous lesions and assess the condition of the intra-articular soft tissues.
Treatment of pelvic fractures
Depending on the stability, involvement and location of the fracture, the treatment will be surgical or functional. It should be noted that the therapeutic indications are based on a precise lesion assessment.
The purpose of the treatment is to maintain the vital prognosis of the injured. The treatment also fights against orthopedic and visceral complications caused by severe fractures.
La physiotherapy is strongly recommended for find the walking functions and lower limb stability.
Orthopedic treatments
Orthopedic treatments may vary depending on the severity of the fracture.
- Functional treatment: it consists of rest the fractured pelvis. This treatment lasts for 6 weeks. It is indicated in case of stable fractures.
- Hanging in a hammock : the pelvis is contained in a sheet and raised above the bed. This position is maintained for 6 weeks. This treatment is indicated in case of pubic disjunction.
- Continuous transosseous traction in the axis of the limb : its aim is to gradually obtain a satisfactory reduction of a vertical fracture. It lasts for 4 to 6 weeks.
Consolidation time and immobilization time
If the fracture is stable and not displaced, a simple rest bedridden from 6 to 8 weeks enough to obtain a good consolidation.
Re-education
In all cases, a re-education is necessary after the initial immobilization phase. It can last several months. It is passive at first, but will be active later.
Its purpose is tosoften the joints of the lower limb (hip, knee, ankle and foot) as well as the joints of Lumbar spine. It also aims to avoid decubitus complications through nursing and physiotherapy.
surgery
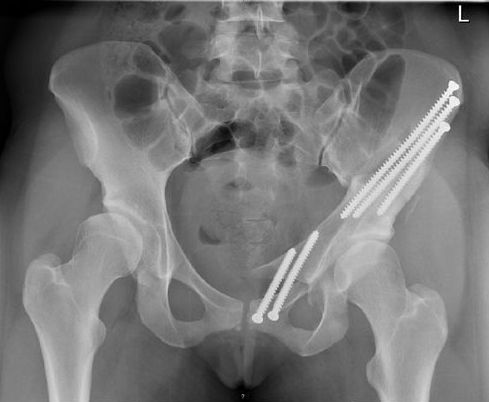
In case of displacement or unstable lesion, surgical treatment is considered.
Most of the time, the treatment is based onosteosynthesis. It is more precisely a reassembly of the fragments of a fractured bone by means of metal plates and screws. Depending on the case, the surgeon can use an external fixator.
Complications
The complications of a pelvic fracture are numerous.
- Immediate complications: cutaneous, nervous, vascular, intestinal, urinary or gynecological lesion.
- Secondary complications: phlebitis, sepsis if the treatment was surgical
- Late complications: hip osteoarthritis, shortening of the lower limb, obstetric complications in women, disjunction of the pubic symphysis which can cause persistent pain, etc.
Projects
https://www.msdmanuals.com/fr/professional/blessures-empoisonnement/fractures/fracture-du-bassin
https://www.revmed.ch/view/578594/4584646/RMS_idPAS_D_ISBN_pu2008-46s_sa03_art03.pdf