Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
The nerves confer sensitivity and motor skills to every part of the body. This can be innervated by one or more nerves at a time. Damage to a nerve – even just one of them – can disrupt various body functions. In this article, let's take a look at the polyneuropathy. What is that ? What are the different types? How to diagnose it? What are its symptoms? How to treat polyneuropathy?
What is polyneuropathy?
If neuropathy includes all damage to the central and peripheral nervous system, peripheral neuropathy only refers to damage to the peripheral nervous system. The polyneuropathy is one of peripheral neuropathies. It differs from the mononeuropathy by the number of damaged nerves.
La polyneuropathy indicates a damage to several peripheral nerves at once. It is also known as " peripheral polyneuropathy " or " autoimmune polyneuropathy ". It can appear following an inflammation, a rupture or a section of certain peripheral nerves.
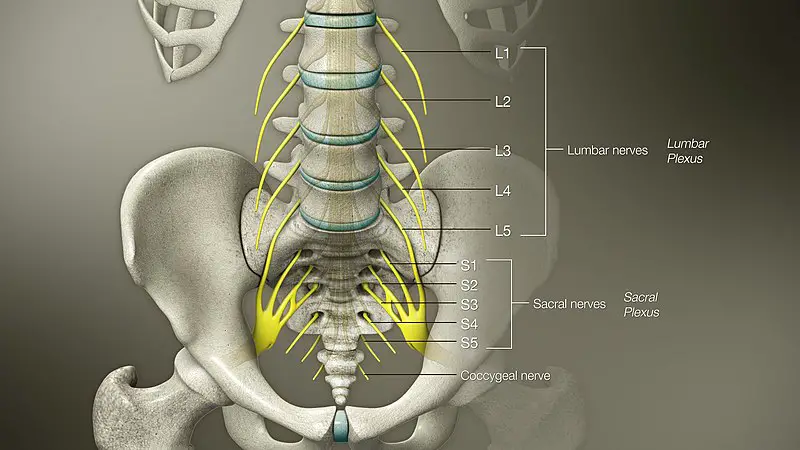
These nerves are called “peripheral” because they do not belong to the central nervous system: neither to the brain nor to the spinal cord. They arise only from the peripheral nervous system. These nerves are responsible for the innervation of different parts of the body: the face, the nose, the eyes, the limbs...
As the peripheral nerves can be sensory, motor or mixed (sensitivomotor), polyneuropathy can also be sensory, motor or sensorimotor. This impairment can therefore impact the sensation of pain or temperature, just as it can impact balance or movement.
What are the different types of polyneuropathy?
There are as many types of polyneuropathy as there are causes of polyneuropathy. Damage to multiple nerves can result from diabetes, alcoholism, certain cancers (such as lung carcinoma), certain genetic conditions (such as Lyme disease and Charcot disease), or certain autoimmune diseases (such as Guillain-Barré syndrome).
Axonal polyneuropathy
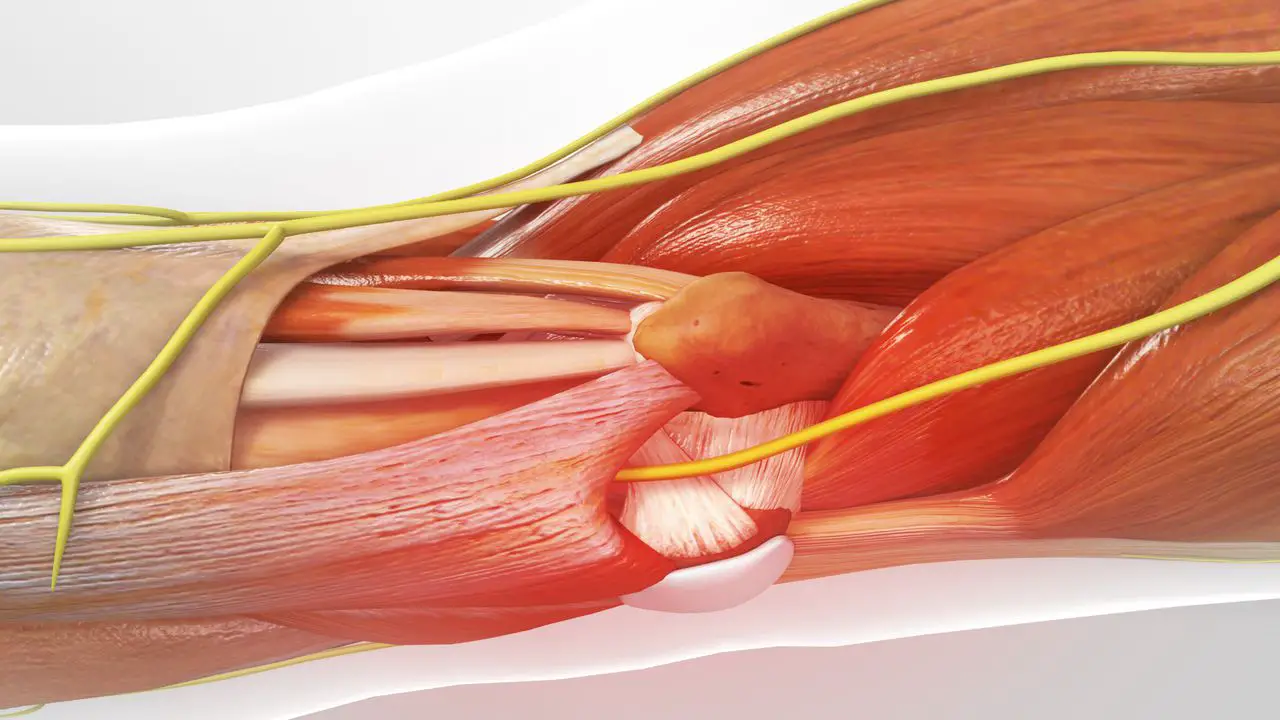
The axon is a nerve fiber that forms a kind of electrical cable with other fibers. The network that these fibers allow to pass a signal so that an organ or a muscle can function. This type of polyneuropathy thus indicates theinflammation of the axon.
Demyelinating polyneuropathy
Myelin is the substance responsible for the protection and nutrition of nerve fibers. This is the layer that sits above the axon. It allows the transmission of information between neurons. Therefore, the demyelinating polyneuropathy indicates damage to the myelin of several nerves. L'damage of these myelin can disturb the passage of nerve impulses.
On the surface, the myelin presents receptors similar to those of an agent foreign to the body such as a bacterium. Sometimes the nervous system is attacked by the immune system because it confuses these two receptors. This is generally the case with Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Sensory polyneuropathy
La sensory polyneuropathy only means the deterioration of peripheral sensory or sensorimotor nerves.
Diabetic polyneuropathy
In the majority of cases, diabetes is the main cause of peripheral nerve damage. The diabetic polyneuropathy is characterized by inflammation due to increased blood sugar levels over a prolonged period of time. It can also occur in case of diabetic microangiopathy. This results in damage to the small blood vessels that must supply the nerves and their axons.
In unbalanced diabetics, this type of polyneuropathy appears rapidly. On the other hand, in balanced diabetics, the inflammation is only triggered after 10 or 15 years.
Alcoholic polyneuropathy
In the long term, alcohol consumption can also be responsible for peripheral polyneuropathy. Indeed, the nerve cells degenerate little by little in the event of regular intake of alcohol. Over time, they may lose their function. It is the sensitivity that is mainly impacted in case alcoholic polyneuropathy. However, if the axons are also affected, it can lead to motor complications.
It should be noted that polyneuropathy can also be caused by taking certain medications.caments. This is particularly the case with anti-tuberculosis drugs or drugs used in chemotherapy.
How to diagnose polyneuropathy?
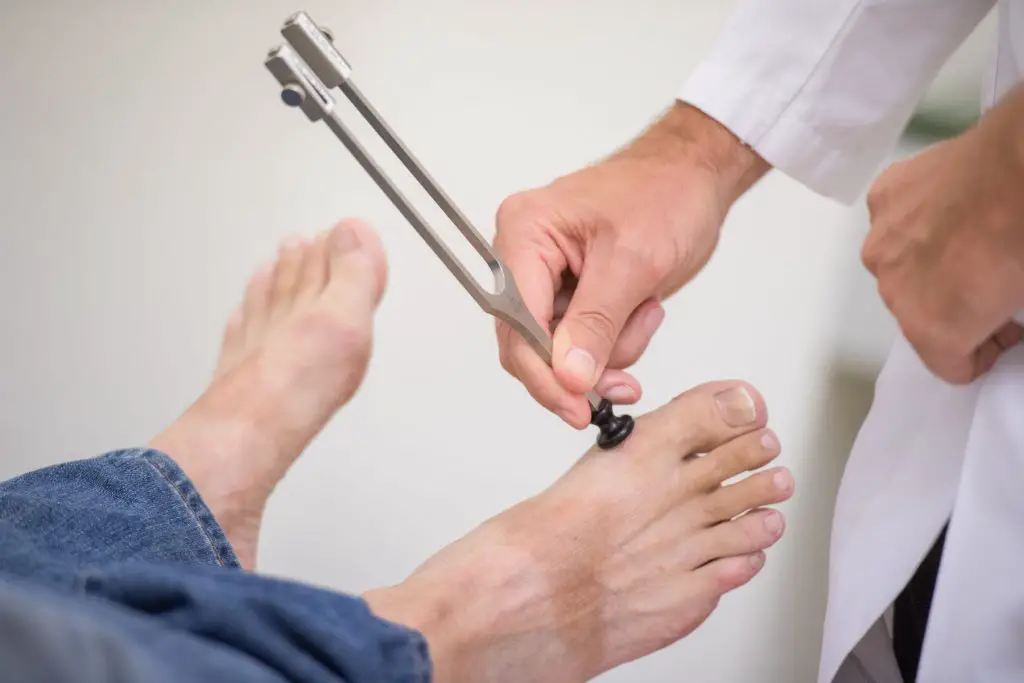
For diagnose polyneuropathy, the neurologist carries out an interrogation followed by a series of examinations. Thanks to the interrogation, this one can know the personal and family antecedents of the patient. As for the examinations, they allow the doctor to look for all the signs presented by the patient.
In general, the practitioner studies the electrical transmission of nerve impulses using an electromyogram (EMG), accompanied by a study of nerve conduction velocity (VCN). It also happens that he has recourse to other biological examinations such as the dosage of hormones or vitamins.
Depending on the results, the specialist may order a skin or muscle biopsy, a lumbar puncture or laboratory tests for further clarification in the diagnosis. Likewise, other specific examinations can be carried out if an infectious cause is suspected.
A differential diagnosis must often be made, as the signs of cerCertain diseases of the central nervous system can mimic those of polyneuropathy. These include numbness or weakness in the lower limbs. A differential diagnosis is also necessary to distinguish it from myopathy (neuromuscular disease).
What are the symptoms of polyneuropathy?
The symptoms are numerous and may vary from patient to patient depending on the affected nerve.
In the event of degradation of sensory nerves, the main signs of polyneuropathy are tingling, pain, a decrease or even loss of sensation. This happens especially in the case of sensory or diabetic polyneuropathy. Hypersensitivity may also be observed in some cases. It is this which causes intense pain at the slightest touch.
On the other hand, if the motor nerves are affected, the symptoms can be:
- Cramps ;
- difficulty walking;
- amyotrophy (decreased muscle volume);
- paralysis (of the face or limbs depending on the damaged nerves).
In terms of mixed nerve involvement, it is possible to see all of these signs in the same patient.
The symptoms of a polyneuropathy progress gradually. If the tingling begins to be felt in the toes, it will progress to reach the legs. Without treatment, damage to peripheral nerves can lead to limb amputation.
Likewise, a decreased sensitivity of nerve fibers who take care of the innervation of the heart can expose to serious cardiac risks. The patient may have a heart attack without even realizing it.
What is the treatement ?
Le polyneuropathy treatment is only symptomatic. In other words, we mainly treat the cause of the disease.
To soothe the pain, the doctor may prescribe:
- antiepileptics (gabapentin is the most effective);
- antidepressants;
- anti-inflammatories;
- painkillers (morphine analgesic).
In case of Guillain-Barré symptoms, plasmapheresis treatments are prescribed to eliminate antibodies in the blood. This type of treatment can also be associated with the administration of immunoglobulins.
For polyneuropathies of infectious origin, treatment may vary depending on the type of infection. While some patients can take corticosteroids, others will be treated with immunosuppressants.
Polyneuropathy requires neurological examinations regular. The evolution of the disease must be closely monitored by a neurologist. It is advisable to see the specialist at least once a year.
Sources
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0248866387801078