Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
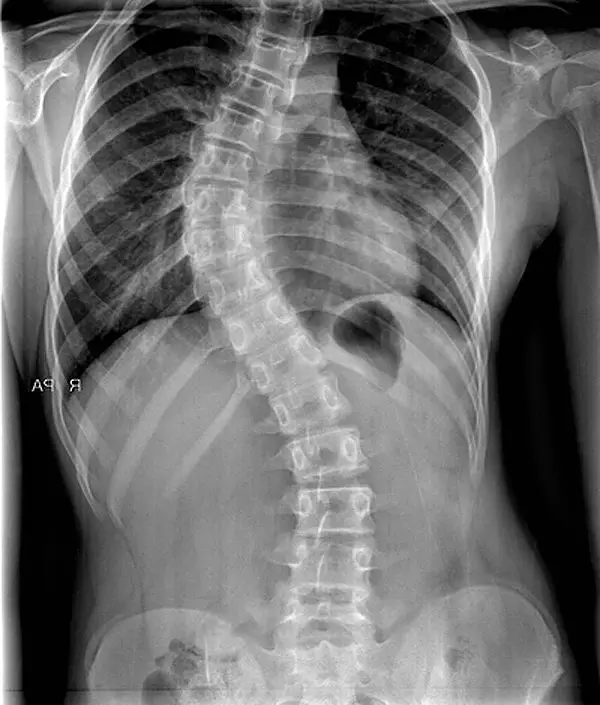
adult scoliosis is a pathology characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. The mild forms cause only simple discomfort, but in more critical situations it is likely to cause more or less intense pain. It can also affect internal organs. This deformation affects 6% of people aged 40, 10% of people aged 65 and 50% of people over 90. Discover in this article all about the adult scoliosis.
Scoliosis, what is it?
Scoliosis means a three-dimensional deformity of the spine or spine. The deviation can be forward or backward; right or left; or in rotation.
La adult scoliosis is similar to that of the child. The only difference is that adult scoliosis is usually symptomatic, which is not necessarily always the case in .
To know everything about the scoliosis in children (including support), see the following article.
The causes of scoliosis
La deformation of the spine can have different origins. There are also two types.
Idiopathic scoliosis
We are talking about idiopathic scoliosis when the cause of the column deformation is unknown.
One observes either a single curvature greater than 10° on the thoracic or thoracico-lumbar or lumbar region, or two curves.
La idiopathic form appears in healthy children and adolescents, since in them traces of pathologies that can cause spinal deformity are not yet observed.
The target age groups are:
- young children (0 to 3 years old);
- children aged 3 to 10;
- adolescents (from the age of 11 until the end of puberty).
This pathology is non-reducible and can have both a moderate and severe form. Its evolution is considerable during the pubertal thrust. It causes spinal and radicular pain and impacts back aesthetics.
Factors that determine idiopathic scoliosis
Although this vertebral condition is not linked to another disease, it remains multifactorial. One of the causes is genetic predisposition. In other words, the disease is present in other family members.
The feminine gender is also a determining factor of this disease. It is more common in girls.
Some specialists have put forward the hypothesis that idiopathic scoliosis is linked to melatonin deficiency. The drop in melatonin causes a signaling defect within the spine.
The specialists (Domenech et al. 2010 and 2011) also carried out an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) examination on patients with scoliosis. They concluded that affected subjects have a different neurological appearance than healthy people.
“De novo” or “degenerative” scoliosis
La degenerative scoliosis is a deformation of the spine about three planes of space. It appears withadulthood (over 50) and is more common in women.
La main cause is a failings (wear) of intervertebral disc associated with muscle loss and ligament weakness. With aging, the spine becomes more fragile. The intervertebral discs that connect the vertebrae between them wear out. Muscles and ligaments relax. To all this can also be added neurological problems or osteoarthritis.
In postmenopausal women, osteoporosis is likely to cause fractures of the vertebrae.
Deformation is often the cause of an overall imbalance leading to a mechanical instability and sometimes neurological signs.
The first stage of development of degenerative scoliosis is disc degeneration. An asymmetrical discopathy develops which results, under the effect of mechanical stress, in the appearance of:
- spondylolisthesis degenerative : sliding of the vertebrae forward;
- rotary dislocation: sliding to the side.
This can sometimes even lead to compression of roots and spinal cord.
She is said " de novo when it occurs on a initially healthy spine and " secondary when it results from the decompensation of a idiopathic scoliosis of the teenager.
In terms of symptoms, degenerative scoliosis is accompanied by various clinical signs (linked to the instability of the spine): back pain, neurological pain (sciatica, cruralgia), postural disorders, difficulty in walking, reduction in walking distance. There may also be pain in the lower limbs caused by the narrowing of the lumbar canal.
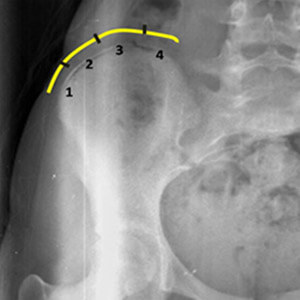
The diagnosis of degenerative scoliosis
Diagnosis of the disease is made by x-rays de l 'entire spine. These imaging examinations make it possible to assess the overall morphology of the spine. The mobile nature of spondylolisthesis is assessed on dynamic views of the face in lateral inclination and in profile (in flexion, in extension and in dog gun position).
An MRI, on the other hand, is useful for measuring the degree of disc degeneration and inflammation of the endplates. You can also ask for the scanner: it provides additional information on the size of the Spinal canal and nerve compression.
What are the main symptoms of scoliosis in adults?
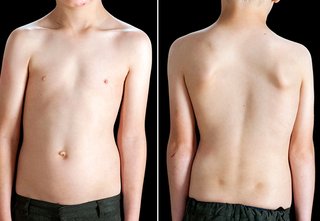
Scoliosis may be asymptomatic for a long time. But, it happens that it is symptomatic in some individuals. It is generally manifested by a deformation of the upper back, which is called humpback. There are also other characteristic signs of this spinal deformity.
Spine pain
About 40% of people with scoliosis have spinal pain. This pain predominates at the lumbar level, but can also occur in the dorsal and cervical (neck) area. It begins with chronic pain and can become very severe if neglected. With increasing pain, the severity of the deformity also increases (in front and in profile).
Sciatica or cruralgia
In a more advanced form of scoliosis, it is common to find a sciatica. It is a neurological pain that is expressed as a burning from the back to the back or the side of the leg and goes to the foot.
To learn more about sciatica and its treatment, see the following article.
La cruralgia manifests with the same type of pain, but it is located in the front (inguinal hollow and anterior aspect of the thigh). The pain is related to the compression of one or more nerves at the level of the Lumbar spine.
To know everything about cruralgia and its treatment, see the following article.
neurogenic claudication
Neurogenic claudication (or intermittent claudication) is none other than fatigue when walking. It occurs after a specified distance or time. We talk about walking distance (5, 10 minutes or 500 meters, etc.).
When walking, some patients report having a feeling of “walking on eggshells”. In fact, the legs lose their strength and can no longer support the body. Sometimes the subject is forced to sit up or lean forward so that he can recover before continuing his journey.
La lameness results from narrowing of the spinal canal (also called Spinal canal) where the nerve roots that innervate the legs and the perineum circulate. It can come from a condition named narrow lumbar canal.
In more severe cases, vesico-sphincter disorders may be added. These result in frequent urinary leakage, fecal incontinence and insensitivity of the perineum (reduced feeling of touch on the buttocks and genitals).
A sagittal imbalance
As you age, the lumbar lordosis (curvature of the lower back inwards) decreases and the thoracic kyphosis (exaggeration of the dorsal curvature over the thoracic area) increases. As a result, the patient finds himself “hunched over”. This is called decompensated sagittal imbalance. In more critical cases, the patient walks with the knees bent to maintain an upright posture.
Respiratory failure
Respiratory failure is a form of complication of idiopathic scoliosis adulthood. It occurs when the thoracic curvature is beyond 100°. We are talking about Cobb's angle and it only occurs in adults.
Apart from these symptoms, be aware that adult scoliosis can lead to many disorders such as asymmetry of the trunk, loss of autonomy and strength, muscle sensitivity as well as digestive problems.
Possible treatments for adult scoliosis
The treatment of scoliosis is based on symptomatic treatment. It can be either simple monitoring and orthopedic treatment, if the curvature of the spine is not significant.
In addition, if the curvature is more substantial, surgery may be possible.
Conservative treatment
In the context of scoliosis, conservative treatment always has its place. It corresponds to medical treatment, rehabilitation (physiotherapy) and conservative orthopedics (wearing a corset). It is suitable for adults as well as teenagers.
Wearing a corset
Le corset is a medical device that helps to support the spine to reduce the risk of curvature related to scoliosis. The choice of the type of corset depends on the importance of the deformation of the spine.
Made to measure by molding the body, this device adapts perfectly to the morphology of the patient.
In adults, the brace eases scoliosis pain, restores the balance of the spine and limits the evolution of the pathology.
To know the different types of braces used in the treatment of scoliosis, see the following article.
Physiotherapy
The exercises offered in physiotherapy improve muscle tone, flexibility and strength. They also act on the deformation of the spine and help to better control pain and improve posture.
The surgical operation
La adult scoliosis surgery is indicated when the discomfort felt with the symptoms becomes disabling and affects the patient's activities of daily living.
Intervention is also advised when conservative treatments fail or when the disease is more serious. In this type of surgery, the work stoppage can last up to a year or more.
Before proceeding with thescoliosis surgery, the patient must carry out a series of examinations in order to be able to make an exhaustive assessment of the disease and to secure the conditions for carrying out the operation.
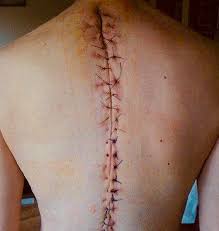
The surgery first consists of aligning the vertebrae from the front and restoring the profile of the spine.
It then intervenes in the fusion of the vertebrae between them. This is carried out by a bone graft making it possible to weld the vertebrae on a certain number of floors. The replacement of intervertebral discs is necessary sometimes (disc prosthesis).
What sports are prohibited for scoliosis?
You wonder if the practice of sport is prohibited for scoliotics? So the answer is no. On the contrary, physical activities and especially sports that solicit the back muscles (like the rhomboids) and the trunk are strongly recommended.
According to health professionals, playing sports for at least 180 minutes a week promotes scoliosis treatment. Although there are sports that are compatible with this pathology, there is still prohibited sports.
Among the sports at risk are collision sports. These sports disciplines could theoretically damage the spine and aggravate scoliosis.
In addition, when the pathology is associated with myalgia or low back pain, it is preferable to dispense with the following sports:
- weightlifting;
- acrobatics;
- le golf ;
- the horse riding ;
- high-speed racing;
- rugby, soccer;
- javelin throw or shot put;
It should be noted that these sports do not represent an absolute contraindication. Indeed, it is possible to practice these sports if the muscles and the body can support the required load. A health professional can guide you if you ever want to practice a contact sport in the presence of scoliosis.
Is scoliosis an occupational disease and a disability?
A occupational disease is the consequence of more or less prolonged exposure to a risk during a usual and professional activity.
Nowadays, only sciatica and radiculalgia by herniated disc appear in the table of occupational diseases of the general scheme (RG) or the agricultural scheme (RA) of the Social Security. So no, the scoliosis is not an occupational disease.
In addition, the crippling disease is a set of health disorders that affect vital internal organs (respiratory failure, heart or kidney failure, joint disorders, etc.). According to this description, as scoliosis is a joint pathology, it can thus be considered as a disabling disease. It is estimated that 10% of people with scoliosis all suffer from disability.
References
https://rachis.paris/pathologies-problemes-de-dos/scolioses/scoliose-adulte/
https://www.sofcot.fr/patients/actualites/tout-savoir-sur-la-scoliose-de-ladulte