Un spondylolisthesis is a condition of spine which can cause pain and disability. If you have this condition, it's important to get the recognition and support you need.
In this article, we are going to talk about the spondylolisthesis and what you can do to get the help you need.
Spondylolisthesis: definition
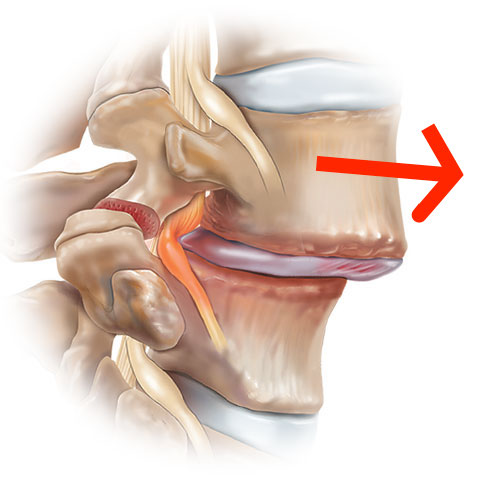
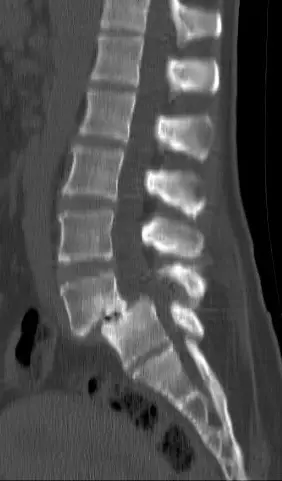
Le spondylolisthesis is a condition characterized by the forward displacement of a vertebrate on another. This phenomenon occurs most often in vertebrae lower parts of the column, because the lower part of the column is naturally more mobile than the other areas.
The levels at which the spondylolisthesis can occur are usually located between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebra (L4-L5) or between the 5th lumbar vertebra and 1st sacral vertebra (L5-S1). In both cases, a vertebra slips and moves forward, relative to the vertebrae around it.
This can cause a number of symptoms, depending on the severity of the condition. However, if you think you are suffering from a spondylolisthesis, it is important to see a doctor or other healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Le spondylolisthesis can be treated by various methods, depending on the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include exercises, physical therapy, and surgery. With proper treatment, the spondylolisthesis can be managed effectively.
Causes of spondylolisthesis
Le spondylolisthesis is a condition in which a vertebra in the spine slips out of position and presses on the underlying vertebra. There are several possible causes of spondylolisthesis, which can be congenital or acquired:
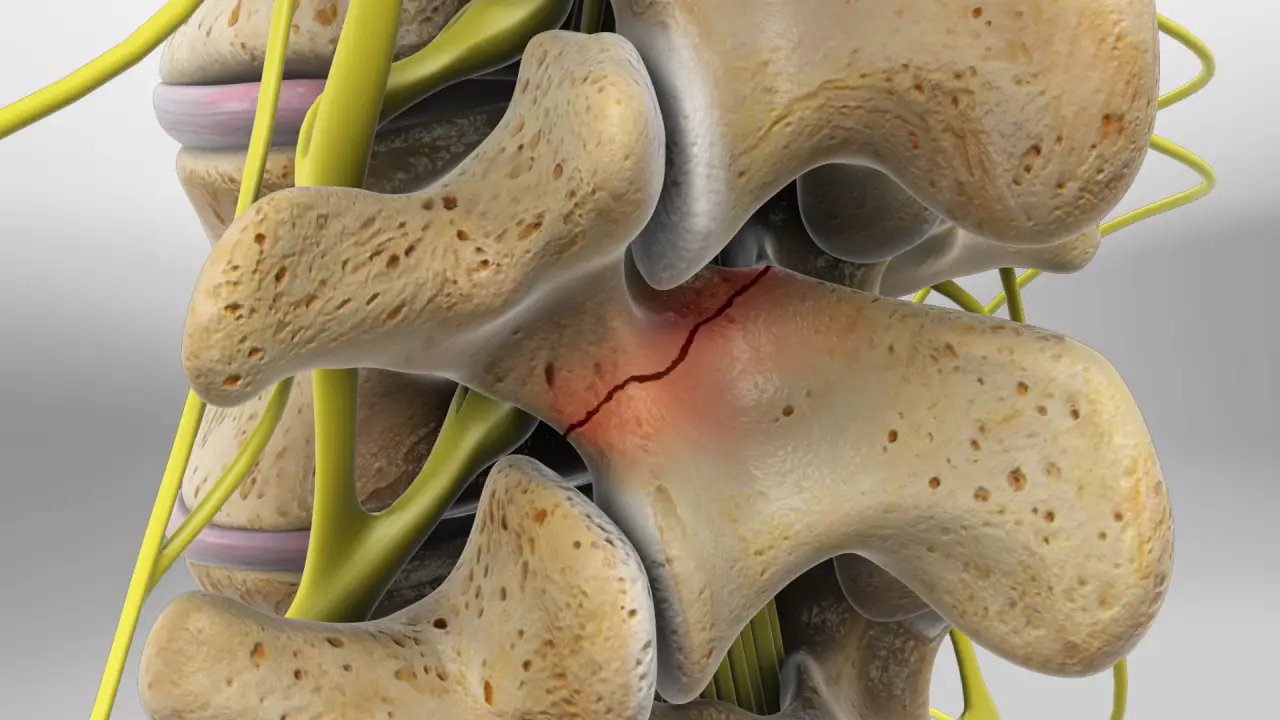
Congenital : This spondylolisthesis derives from a lack of ossification of the vertebral isthmus and is defined as a spondylolisthesis by lysis of the isthmus.
They are mainly due to a lack of ossification of the growth plate of the isthmus (pars interarticularis), which creates a separation between the vertebral body and the posterior arch, which no longer move together during trunk movements.
The vertebral body thus slides over the one below. It occurs most often at L5-S1 (in the lysis of the isthmus of L5) and can be identified as low or high dysplasia depending on the degree of bone damage it causes on the vertebral bodies.
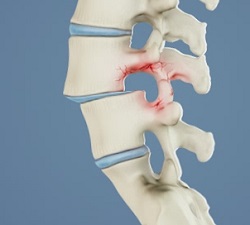
Acquired : It is rather these spondylolisthesis which appear as a result of vertebral osteoarthritis and which will classify in the phase known as the unstable phase of the degenerative cascade of the vertebral metamer.
In this case, the spondylolisthesis occurs as a result of wear and tear of the articular masses and intervertebral disc, which gradually become hypermobile and generate less resistance in the vertebral joints, which leads to instability.
They are never accompanied by a isthmic lysis and are almost always associated with arthritic compression of neural structures, which results in herniated discs, ductal stenosis and spondylodiscarthrosis.
Symptoms of spondylolisthesis
Symptoms of spondylolisthesis depend on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, there may be no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may include the following:
- Back pain;
- Pain in the legs;
- muscle weakness;
- Limited mobility;
- Numbness or tingling in the legs.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor or other healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
the spondylolisthesis can often be successfully treated with a combination of exercise, stretching, and weight loss. Surgery is only recommended in severe cases where other treatments have failed
Spondylolisthesis, occupational disease?
There is no definitive answer to the question of whether the spondylolisthesis is an occupational disease. If the spondylolisthesis can be caused by congenital factors, it can also be acquired later in life.
However, certain occupations and sports may increase the risk of developing a spondylolisthesis due to increased strain on the spine. These include the following professions in particular:
- Manual work : Jobs that involve lifting, twisting, or other strenuous activities can put pressure on the spine and can eventually lead to a spondylolisthesis.
- Contact sports: Participation in contact sports such as football or hockey can also lead to spondylolisthesis due to the high impact nature of these activities.
- Ballet and gymnastics: The constant stretching and stress on the spine required for ballet can also lead to a spondylolisthesis.
Occupations that involve heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, or twisting and bending of the spine are considered potential risk factors for spondylolisthesis.
Is spondylolisthesis recognized as an occupational disease? Currently, only the sciatica and radiculalgia by herniated disc are registered in the tables of occupational diseases of the general scheme (RG) or the agricultural scheme (RA) of the Social Security. This means that spondylolisthesis cannot be considered an occupational disease.
However, there are ways to have your spondylolisthesis recognized as an occupational disease (explained in this article). It is recommended to discuss with your doctor to determine the options available to you if ever your low back pain limits the practice of your profession (work stoppage, professional reclassification, etc.).
Prognosis of spondylolisthesis
The prognosis of spondylolisthesis depends on the severity of the condition. In most cases, the spondylolisthesis can be successfully treated with a combination of exercise, stretching, and weight loss.
Surgery is only recommended in severe cases where other treatments have failed. With early diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis of spondylolisthesis is generally good.
However, if the condition is left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as nerve damage and paralysis.
In severe cases, surgery may be required to stabilize the spine and prevent further damage.
The success rate of surgery is high, but it is important to note that there is a risk of complications such as infection and blood clots. With proper treatment, the majority of people with spondylolisthesis can enjoy a good quality of life.