Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
Uncommon, the transverse myelitis is one of many neurological conditions that can affect the spinal cord. It usually occurs as a result of inflammation of the latter and causes fairly serious motor, sensory and sphincter disorders.
It is estimated that each year, 1 to 5 people in a million suffer from this condition. This figure applies to both children and adults. This article will help you understand what the transverse myelitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and possible treatments to cure it.
Transverse myelitis: definition and anatomy
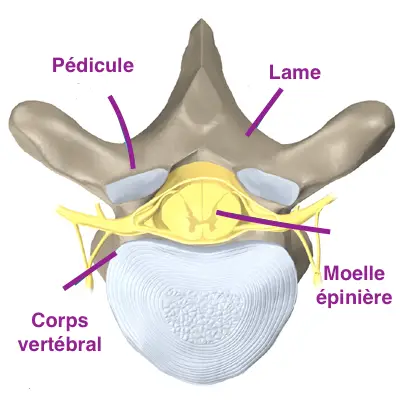
The myelitis » designates any inflammation full spinal cord. It can affect gray matter or white matter. In its acute form, the inflammatory reaction occurs in both areas at the same time.
Word " transverse ', meanwhile, indicates that theinflammation only affectsa part full spinal cord. The affection develops in particular in the region of the sensory-motor and autonomic spinal cords. This is why we count the transverse myelitis (MT) among the inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system.
Generally, the disease sets in in 1 to 3 months. After this period, some patients fully recover, others have more or less significant sequelae. And unfortunately, there are those who are condemned to permanent paralysis.
What causes transverse myelitis?
The causes of transverse myelitis are numerous and difficult to identify. However, in the majority of cases, it turns out that the disease appears following a infection of viral or bacterial origin. The pathogenic germs generally suspected are those responsible for herpes, AIDS, chickenpox, influenza, mumps, smallpox... These can directly infect la spinal cord, which directly causes the transverse myelitis.
In addition, various types of diseases can also be responsible for the symptoms of transverse myelitis. Those are :
- the post-vaccination diseases : they generate immune responses that can lead, in extreme cases, to inflammation of the spinal cord;
- the autoimmune diseases, especially the multiple sclerosis which is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system;
- le syndrome paraneoplastic: combination of myelitis as well as spinal cord cancer. In this case, antibodies produced to fight cancer cells attack those of the spinal cord ;
- the vascular disorders within spinal cord (under the effect of drug abuse, or because of possible malformations,). A insufficient blood flow in the vessels of the spinal cord can also cause a myelitis (following a haemorrhage, or the presence of a clot).
Certain pathogenic germs have a structural characteristic close to that of the cells of the spinal cord. The antibodies produced to eliminate these infectious agents then also attack the cells of the spinal cord. The disturbances caused by this phenomenon on the immune system cause a autoimmune attack on the spinal cord.
La transverse myelitis can also be original idiopathic, that is, without underlying causes. In this case, it often results from an abnormal immune reaction directed at against the spinal cord.
How do the symptoms of this condition manifest?
The manifestations of the signs of transverse myelitis vary depending on the individual affected. Each patient has their own perception of the degree and type of symptoms. The severity of the lesion and inflammation may explain this phenomenon.
The spinal cord contains motor nerve fibers (ensuring the transfer of nerve impulses to the muscles) and sensory nerve fibers (which transmit information from the sense organs to the nervous system). Thereby, TM symptoms can be classified into three types :
- engine : feeling of weakness and numbness in the muscles of the lower limbs in the majority of cases
- sensitive : tingling sensation, pain. Sometimes people with TM experience less heat, pain, and vibration. Sensations of being wrapped in a tight sheath can be felt in the trunk. In addition, the sensitivity to touch of certain parts of the body may increase relatively.
- vesico-sphincter : loss of reflexes, difficulty in retaining urine for example
These TM symptoms develop very quickly and can get worse within 24 hours. It is therefore important to make a diagnosis as soon as possible as soon as one of these signs appears in order to plan the appropriate treatments.
How is transverse myelitis diagnosed?
Le diagnosis of transverse myelitis is based on clinical examination of symptoms. It is recognized by the installation and the rapid evolution of these symptoms.
At the same time, the doctor also looks for a history of neurological syndromes in order to better explain the symptoms that occur.
In addition, in-depth examinations are also carried out to rule out other diseases such as: tumours, herniated disc, narrowing of the spinal canal or stenosis (narrow lumbar canal). A brain scan can for example distinguish myelitis from other diseases such as strokes (cerebrovascular accidents) or brain tumours.
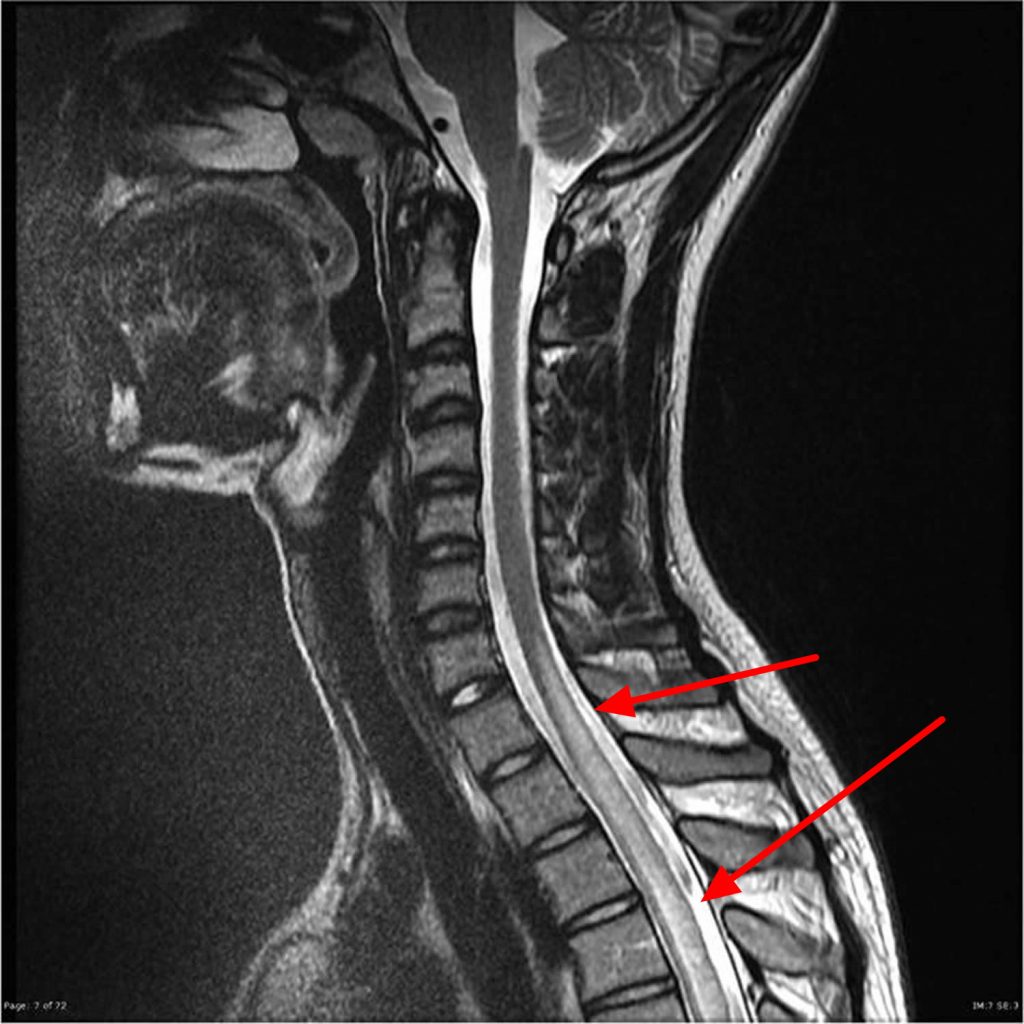
Regarding theIRM (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), it is useful to confirm the diagnosis. The positive result shows a white spot affecting more than half the width of the spinal cord.
If the images are ambiguous, we proceed to myelography. To do this, a puncture is first made in the patient's neck or lower back. Then, a contrast medium or stain is injected into theenvelope surrounding the spinal cord. Finally, the x-rays are taken while tilting the patient up and down. This way the stain flows properly and traces the outline of the spinal cord.
If these images do not show massive lesions in or around the spinal cord, it could therefore be transverse myelitis.
If the results are not yet conclusive, a lumbar puncture could give information about the existence of inflammation or an abnormal immune reaction. To do this, we make a spinal fluid collection to analyze protein and white blood cell levels.
For a more in-depth analysis of the cause of transverse myelitis, other analyzes may be necessary such as blood tests. They will be able to determine the evolution of the disease and give leads on the treatments to be considered.
How to treat transverse myelitis?
Le transverse myelitis treatment varies depending on its cause.
- D’infectious origin, antibiotic, antiviral or antiparasitic treatment is required (depending on the infectious agent).
- If it is a system malfunction immune, the doctor usually recommends treatment with high-dose corticosteroids.
- Personalized plasma exchange can be done for more efficiency. This alternative makes it possible to eliminate the molecules responsible for the autoimmune reaction against the spinal cord.
- La rehabilitation (kinesitherapy or physiotherapy) are also necessary to treat the sequelae of transverse myelitis.
Since symptoms worsen rapidly, treatment should be as soon as possible in order to limit the damage.
Sources
- https://www.chu-lyon.fr/myelite-transverse
- https://www.docteurclic.com/maladie/myelite.aspx
- https://www.concilio.com/neurologie-myelite-transverse/
- Joanne Lynn in "Transverse myelitis: symptoms, causes and diagnosis", 2016