Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
You have been diagnosed with schwannoma and that worries you? It makes perfect sense because it's a nerve tumor. However, you should know that tumors are not always dangerous. This is the case of schwannoma.
What is schwannoma? How is it evolving? Can we treat it? In this article, you will discover everything you need to know about this nerve pathology.
Definition of a schwannoma?
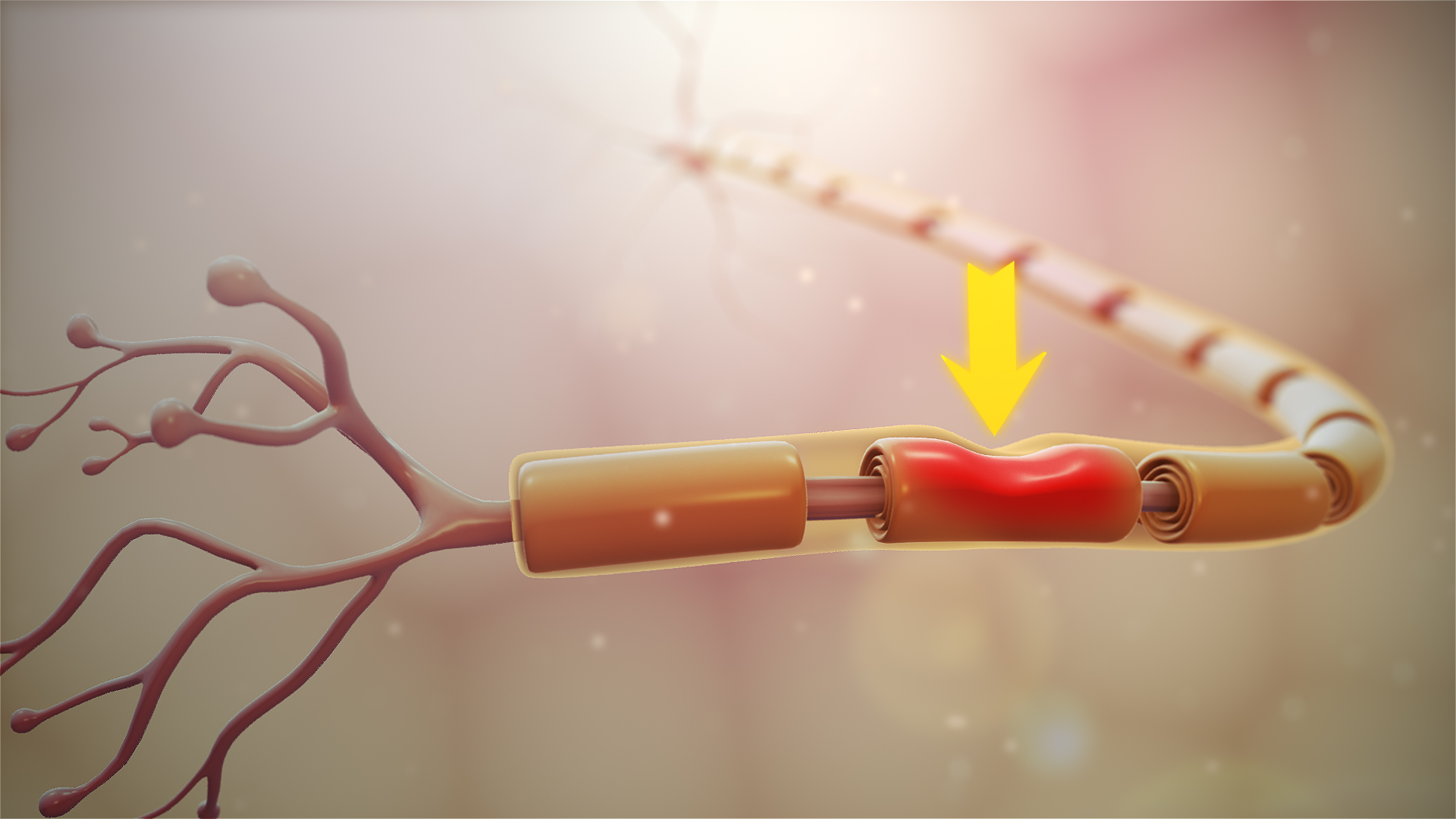
Le schwannoma is a nerve tumor. It develops at the Schwann cell level (cells that make up the myelin sheath covering the nerves). As the nerves spread over different parts of the body, the schwannoma can then manifest itself in various places: central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, rib cage...
Like any tumour, a schwannoma results from a abnormal cell proliferation.
Benign or malignant?
Nerve tumors can be benign or malignant. When the tumors are malignant, that's when we talk about cancer. As for the schwannoma, It's about a benign tumor.
The risk of it turning into a malignant tumor is relatively small. This type of case is very rare (about 4% of cases of schwannoma listed). It is usually seen in people with Von Recklinghausen syndromes. This syndrome is characterized by café-au-lait skin spots.
Statistics
According to data about the schwannoma, it particularly affects men and women between the ages of 30 and 60. For the Von Recklinghausen syndrome, children are the most affected.
Le schwannoma is also known to cause peripheral nerve tumors.
Indeed, all the peripheral nerves can be affected by this pathology.
Faced with damage to the peripheral nerves, schwannoma is found in 70% of cases..
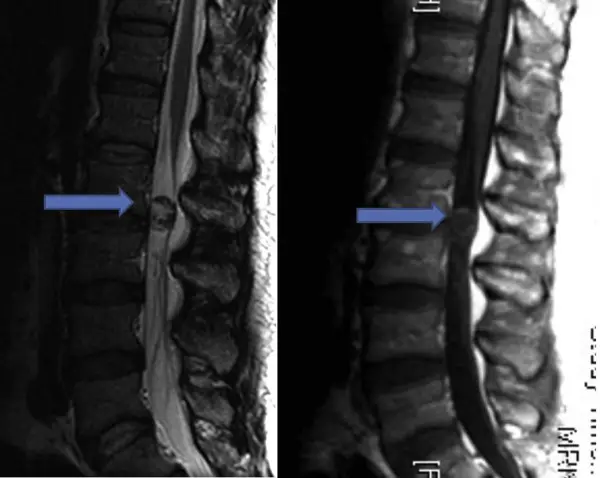
Lumbar schwannoma
When the schwannoma develops on a nerve root located in a root of the Lumbar spine, We are talking about lumbar schwannoma.
This form causes pain in the spine and lumbar region. The nerves therein are nicknamed the nerves of the cauda equina.
Places that may be affected by the spinal schwannoma are numerous: in the cervical region, in the thoracic region and in the lumbar region.
Depending on the area concerned, it can cause the following symptoms respectively: pain in the arms, pain in the chest, sciatic pain, pain in the thighs or on the buttocks.
Like all schwannomas, the spinal neuroma evolves slowly. You may suffer from pain sciatica since a long time. The diagnosis of lumbar schwannoma is only asked much later. This pain can also be felt in the hip, which makes the diagnosis even more difficult.
However, it is necessary to be vigilant with regard to this pathology. If it gets worse, the tumor may completely damage the cauda equina nerves or the spinal cord. You will then be exposed to the risk of motor and sensory paralysis.
Other types of schwannomas
Remember that all peripheral nerves can have a schwannoma. Thus, there may exist different types of schwannoma depending on its location.
Cervical schwannoma
Here, the cervical sympathetic nerve is affected. This tumor is rare and isolated.
It must be suspected in the existence of a mass at the laterocervical level (lateral face of the neck).
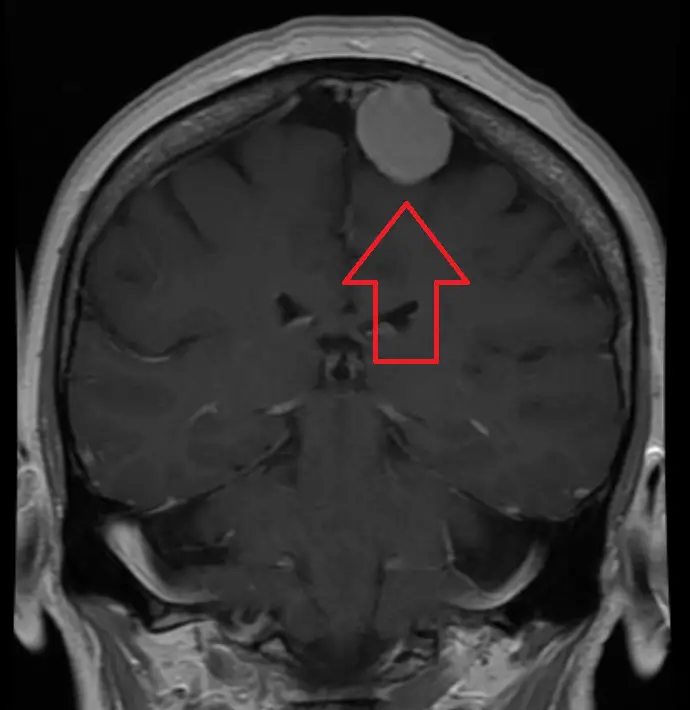
vestibular schwannoma
Also called acoustic neuroma, vestibular schwannoma means a benign tumor that forms in the sheath of the cochleovestibular nerve. This nerve provides hearing and balance.
No risk factor was found in related studies.
As part of a vestibular schwannoma, the person is often subject to a decrease or even loss of hearing.
Schwannoma can also cause other hearing problems such as tinnitus (abnormally loud noises heard in the ear).
As the nerve involved is responsible for balance, the subject may also present certain disorders such as vertigo.
If the tumor grows and manages to compress the facial nerve, it may lead to facial paralysis.
And, in more serious situations, it can even compress the brainstem or brain.
Cardiac schwannoma
Extremely rare, the cardiac schwannoma is associated with a family syndrome of cardiac disorders in half of the cases.
This is the Carney complex. There are various skin and mammary (breast) tumors.
The sick person also shows signs of heart failure such as dyspnea and heart rhythm disturbances.
A study looked at the effect of cell phone radiation on the hearts of rats. After an exposure of 9 hours per day and for two successive years, the researchers objectified the development of a particularly rare cardiac schwannoma. 2 to 6% of males became carriers.
Other schwannomas
The other types of schwannoma mainly concern the skin: the plexiform schwannoma and melanotic schwannoma.
We also find the retroperitoneal schwannoma.
Le melanotic schwannoma falls under a Carney complex. The name melanotic is taken from markers found in tumor cells. They show melanocytic differentiations. The patient also has abnormalities in endocrine hormones.
As to plexiform schwannoma, he is asymptomatic. The tumor is solitary. It is a small nodule. But, its size will gradually increase.
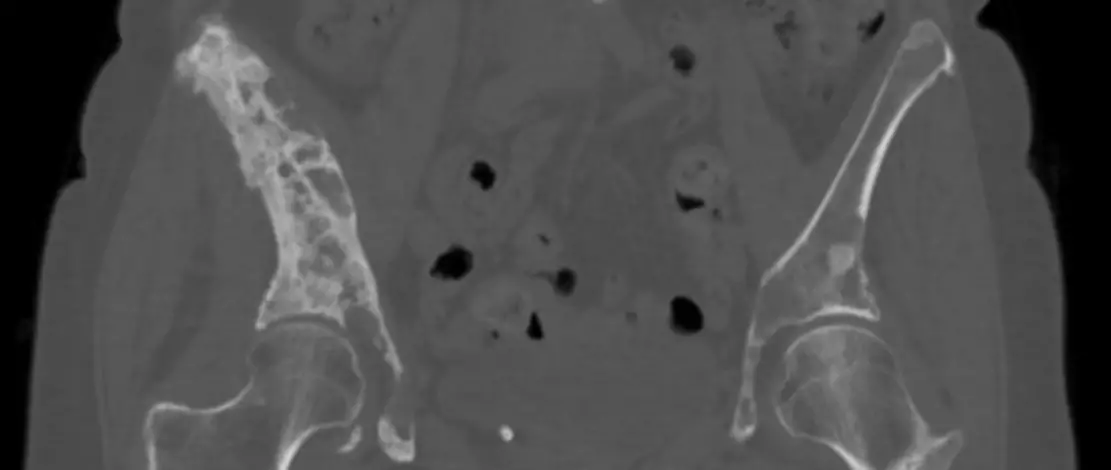
Le retroperitoneal schwannoma causes lower back pain. Other pains will be felt following the compression of the neighboring organs by the tumour.
How is a schwannoma diagnosed?
Le diagnosis of a schwannoma specifically depends on the type. The symptoms will then be cardiac, cutaneous, auditory or sometimes marked by lumbar pain.
But, in general, people with schwannoma still experience sensory disturbances. Some patients explain it as a " shock ».
Personalized motor disorders may also appear. The specific sign is the presence of tingling on the extremities of the limbs.
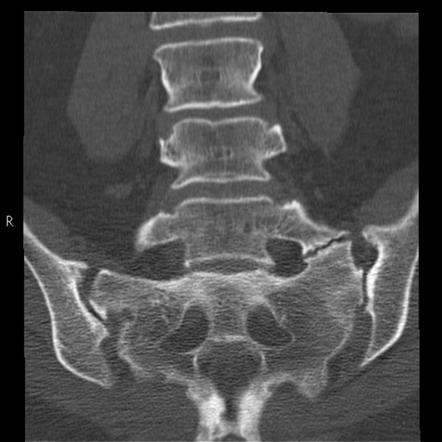
However, all these symptoms only guide the diagnosis. The examination needed to confirm this is magnetic resonance imaging or MRI.
Other examinations such as cardiac ultrasound or CT scan can also be carried out depending on the type of schwannoma suspected.
To be sure of the non-cancerous origin, doctors usually request an anatomopathologic analysis of the tumor following a biopsy.
What treatments are available for a schwannoma?
The schwannoma treatments are based on the surgery. Removing the tumor preserves nerve function. The goal is to avoid compression of other nearby organs.
To do this, the surgeon will remove part of the affected nerve with the tumor by performing a radiosurgery.
For malignant tumors, treatment is based oncomplete removal of the nerve affected by surgery. But this is supplemented by chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Those are the neurosurgeons who are the specialists of this pathology. Their opinion is essential if you have a schwannoma.
Conclusion
Le schwannoma is a benign tumor found in peripheral nerves and cranial nerves. Conclusion diagnosis is not clear because of his slow evolution. Moreover, the signs presented are not really typical. They only direct the doctor. Despite its benignity, it must be treated fairly quickly to preserve nerve function and avoid compression of other organs. If you present the symptoms of a schwannoma, consider consulting a neurosurgeon for better care.