Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
What is a dorsal hernia and how to treat it? Is it more serious than other types of herniated discs? How to diagnose it?
This popularized article explains everything you need to know about this condition that is sometimes responsible for back pain.
Definition and anatomy
To better understand the dorsal hernia, it is necessary to revise certain notions of anatomy which will allow you to better identify the structures concerned.
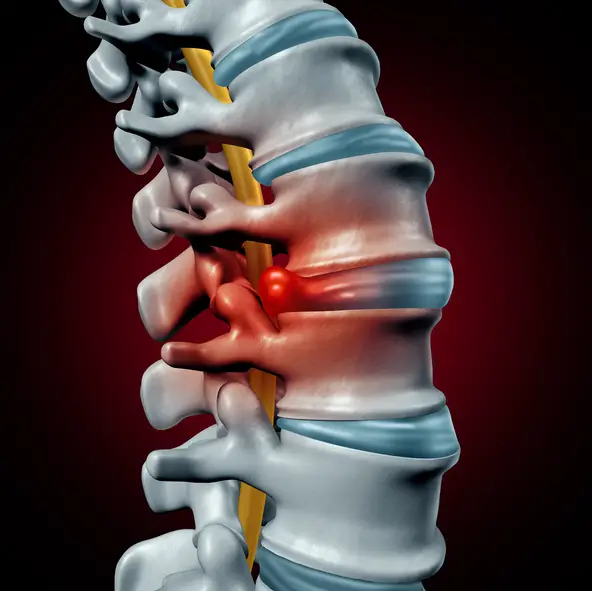
Le dorsal spine (also called dorsal column, thoracic spine or thoracic spine) is composed of 12 vertebrae juxtaposed. Between each vertebra there is a intervertebral disc. This is composed of a gelatinous nucleus surrounded by a fibrous ring.
There’s nothing quite like a herniated disc occurs when the fibers of the annulus fibrosus surrounding the disc are cracked, and the gelatinous nucleus migrates to the periphery. The deformed disc can therefore irritate surrounding structures (spinal cord, spinal nerves, nerve roots, ligaments, etc.) and cause symptoms.
To know everything about herniated disc, see the following article.
In the dorsal region, there is very little space around the spinal cord. Thus, a herniated disc at this level can be more serious than hernias located at the cervical or lumbar level. In some cases, a back hernia can even cause weakness in the muscles below the waist, even going as far as paralysis.
Fortunately, herniated discs in the thoracic region are not as common as in the lumbar spine.
Diagnostic
Diagnosis of dorsal hernia is made by medical imaging. Although x-rays or CT scans can provide relevant information related to the intervertebral discs, it is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that is the test of choice for diagnosing this condition.
On the other hand, it must be understood that the MRI will not provide a complete picture of the condition of the patient with a dorsal hernia. This is because this condition may be asymptomatic in some individuals, primarily due to the body's gradual adaptation to disc changes.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor (or other healthcare professional) will perform an additional clinical examination, often before even prescribing imaging. This examination will include questions on the medical history, as well as clinical tests (strength, reflexes, sensitivity, trunk movements, etc.) to exclude serious damage and observe the functional repercussions of the dorsal hernia.
Symptoms of the disease
As mentioned, back hernia symptoms will vary from person to person, and will even be non-existent in some. Essentially, they depend on the pressure exerted on the surrounding spinal nerves, and the degree of inflammation caused.
Here are the symptoms encountered in people with back hernias:
- Trunk pain that spreads down one leg (or both)
- Numbness or tingling of the lower limbs
- Muscle weakness in certain leg muscles (or both)
- Leg spasticity
The location and type of symptoms encountered depend on the spinal nerve(s) irritated, as well as the degree of tearing of the intervertebral disc. In addition, damage to the spinal cord will greatly influence the prognosis. Indeed, a central attack constitutes a medical (and even surgical) emergency.
If you observe any of the following symptoms, you should consult your doctor immediately. This could be related to spinal cord injury:
- Bilateral pain and paresthesias
- Loss of sensitivity in the area of the genitals
- Urinary or fecal incontinence
To find out more about serious spinal injuries, see the following article.
Treatment
The treatment of dorsal herniation does not differ from conventional disc herniation.
He will start with conservative approaches including medication, kinesitherapy (physiotherapy), osteopathy, etc. Of the natural products are sometimes recommended, although they are not supported by solid scientific evidence.
If symptoms persist despite well-conducted conservative treatment, more invasive approaches will be considered. One thinks, for example, of infiltration and surgery.
To learn about all the treatment approaches related to herniated disc, see the following article.