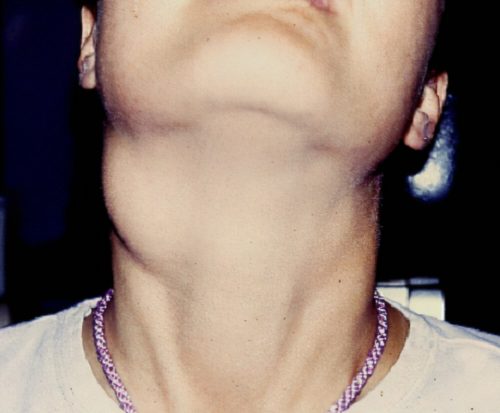
The neck cyst or cervical cyst is a pathological entity affecting the cervical region and grouping together several diseases of different origins. In the vast majority of cases, the cervical cyst is benign, but some complications, such as malignant degeneration, can occur due to the long silent nature of this condition.
In this article, we are going to discover together what is a cervical cyst, its causes, its clinical symptoms as well as the different therapeutic means that its management requires.
Cervical cyst or neck cyst: what is it?
Un cyst appears as a cavity filled with liquid, air or a semi-solid substance. It can be found in any region of the body, and it can be benign or malignant.
Le cervical cyst ou neck cyst is an entity that can include many pathologies.
A good part of the cysts of the neck are of origin congenital, and their development generally remains independent. However, sometimes complications occur such as fistulas, infections or malignant degeneration.
The causes of the cervical cyst
The most accepted theory as to the etiology of cervical cysts remains at present the congenital cause, although the exact mechanisms are still poorly understood.
Indeed, in recent years, research has shown that cysts develop from the beginnings of the branchial arches (embryonic formations appearing during the development of the neck and head). Thereby :
- The embryonic remains of the cervical sinuses would form the lateral cysts.
- The non-germination of the thyroid duct would lead to medium cysts.
The hypothesis of a genetic predisposition is also proposed but not yet confirmed.
Types of cervical cyst
The cervical cysts can be found in the lower or upper part of the neck, they can be lateral or medial, deep or on the surface of the skin.
So, neck cysts are usually divided into lateral, middle and dermoid formations, which makes it possible to distinguish:
- Thyroid cysts ou thyroglossal duct cysts in the mid-cervical:
These are usually benign formations located on the front of the neck. They can be the cause of dysfunctions of the thyroid gland leading to hypo or hyperthyroidism.
- Second branchial arch cyst ou tonsilloid cyst in the lateral cervical:
It is a cyst which forms during embryonic life from the epithelial cells of the brachial pouches and which evolves silently for years.
- Epidermoid (dermoid) cysts:
It is a benign and rare mass formed by the elements of the skin (keratinized epithelium, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, etc.) that evolves gradually and can cause difficulty in breathing, eating or speaking when its volume increases. .
Cervical cyst: Clinical manifestation
Cervical cysts can remain inconspicuous for a long time before appearing at a variable age in the form of a swelling.
The circumstances of discovery are of two types:
The recent appearance of a cervical mass mobile, painless, of elastic consistency and/or of a fistulous orifice chronic skin more or less in an inflammatory context, or the occurrence of a inaugural complication revealing a cervical cystic swelling such as an acute pharyngeal infectious episode.
The symptoms are strongly related to the size of the cysts. Thus, large cysts manifest more quickly and with a more or less noisy clinical picture depending on the degree of compression of the vasculo-nervous formations, and on the occurrence or not of superinfection which may be the cause of a pain, An redness and possibly a fistulization next to the cyst with flow of a purulent liquid.
The evolution towards a abscess is plausible unlike the risk of cancerization which is extremely rare.
Le midline cyst has a particular characteristic which is its displacement during swallowing, when it is located at the root of the tongue and it is voluminous, it can be the cause of swallowing and speech disorders.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis of certainty of cervical cysts remains to this day quite difficult, because on the one hand the pathology remains poorly explained and the data concerning it are rather poor and on the other hand, because their clinical pictures present many similarities with others. other infectious and tumor pathologies of the neck.
The examination carried out in first intention to the discovery of a tumefaction on the level of the neck is cervical ultrasound, it makes it possible to specify the cystic nature of the lesion and to specify its localization.
A cytopuncture fine needle under ultrasound control can also be proposed in order to carry out an anatomopathological study of its content to determine the benign or malignant origin of the swelling.
Cervicothoracic computed tomography with injection of contrast medium (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are examinations that the doctor also performs to specify the topography and the size of the cyst, the course of the fistula, its relationship with the surrounding tissues and the vascular-nervous structures and possibly the thyroid attack.
Finally a opacification of the fistulous path under scanner can be performed before a surgical resection procedure. Its realization must nevertheless be done at a distance from an episode of superinfection.
Being still a poorly understood entity, it is important to eliminate the different differential diagnoses of the cervical cyst in order to adopt the best strategy for its management.
The main other causes of cervical masses are represented by:
- cervical lymphadenopathy sometimes revealing cancer of the upper aerodigestive tract or thyroid cancer, particularly in children.
- Lymphoma or an infection like tuberculosis, the Toxoplasmosis or cat scratch disease...
- thyroid goiter can be evoked when the swelling is in the medial compartment.
- Laryngocoele which is a dilation realizing at the level of the structures located in the larynx called ventricles of Morgagni pockets filled with air, it mainly concerns adults and generally appears at a distance from laryngeal surgery.
- Lipomas, parotid swellings of tumoral origin and vascular and nerve tumors can also be the cause of these cervical swellings, particularly when they are located in the lateral compartment.
Cervical cyst: what management?
When the diagnosis of the cervical cyst is confirmed, more or less short-term surgical management is immediately proposed in order to reduce the risks of infections, phlegmons, abscess and cancerization. Indeed, there is no room for alternative treatments such as drug treatments, homeopathy or a simple puncture of the cyst.
However, revelation of the cyst by an infectious context remains the only indication for an initial drug treatment based on a antibiotic therapy broad spectrum.
The middle cyst is removed during an operation performed under general anesthesia.
It consists of a horizontal incision at the level of the neck, then removal of the cyst, the persistent duct as well as part of the hyoid bone to reduce any risk of recurrence.
If a fistula is discovered during the operation, its path is “stained” with methylene blue in order to visualize it clearly and remove it.
Tonsilloid cysts are also subject to complete resection during surgery under general anesthesia.
Given its lateral location of the cyst, the intervention may prove to be more delicate. Indeed, the presence of important vascular structures makes this excision slightly more complicated.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.