Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
hip dislocation means a malformation of thehip joint. It can be hereditary or acquired as a result of trauma. Sometimes it interferes with the daily or professional life of some people, because it is very painful and can lead topelvic immobility. In this article, learn how to diagnose and treat a hip dislocation.
Contents
Definition of hip dislocation
Hip dislocation in babies
La hip dislocation is a congenital anomaly of the hip joint. It corresponds to a lack of fit between the two elements of this joint, in particular the femoral head and the acetabular cavity (cavity of the pelvic bone or acetabulum). Under normal conditions, the head of the femur sits in the bone cavity. When the femoral head is found completely outside this cavity, we speak of hip dislocation.
If the treatment of hip dislocation in babies falls behind, this can cause a limp when the child walks.
To know everything about hip dysplasia in babies, see the following article.
In adults
La hip dislocation occurs when the spherical head of the femur protrudes from the articular cavity of the iliac bone (or acetabulum). In an adult, it means a congenital malformation of the hip that manifests itself at a later time.
What can be the causes of a dislocated hip?
hip dislocation may be of mechanical, genetic or hormonal origin. It is largely linked to various factors from birth such as the position of the baby in the uterus, insufficient amniotic fluid or a fetal reaction to maternal estrogen. But, there are also other fairly common causes.
Complication of hip prosthesis
La complication of hip prosthesis is one of the big causes of hip dislocation. This is a classic, very painful complication. We speak of dislocation of the hip prosthesis when the artificial femoral head comes out of the cup (the part which receives the head, on the pelvis side). The (artificial) femoral head and cup assembly form what is called friction torque.
It should be noted that the larger the head of the prosthesis, the more stable and mobile it is (ease of movement). Thus, it decreases the risk of a dislocation.
Trauma
Some traumas can beorigin of this anomaly in the pelvis. This usually happens when the knee and hip are flexed (sitting position) and a strong force hits the knee. It could be a collision with a hard object like a wall, furniture or the dashboard of a car.
The impact that falls on the bent knee pushes the femoral head back and pushes it out of the acetabulum. In this case, we are talking about posterior hip dislocation.
It can also follow a fall from a height such as on a ladder, or following a percussion during a contact sport (American football, rugby, etc.).
Other causes
Some children are born with a dislocated hip (hip dysplasia). This can lead to gait disturbance if not detected before the child begins to walk.
Other factors like age also increase the risk of this deformity. In older people, minimal force can sometimes be enough to cause it.
How does this hip pathology manifest itself?
La hip dislocation is a very painful condition. The person who suffers from it may have great difficulty using the dislocated limb (leg) or the joint in question.
Another frequent sign of this joint pathology is the inequality in the length of the two legs.
- When the femur is pushed back, the affected leg appears shorter than the other and rotates inward.
- When the femur is pushed forward, the leg rotates outward and also feels shorter. The difference in leg length is not as obvious as when the femur is pushed back.
In addition to these symptoms:
- abduction asymmetry;
- limitation of abduction;
- amplitude limitation;
- hip instability.
In case of nerve damage by the pathology, it is possible that the patient feels numbness sensations in a certain part of the foot and ankle.
How is the diagnosis made?
Hip dislocation screening is one of the mandatory examinations at the birth of a newborn. To do this, the doctor uses a technique called Barlow maneuver. It is used to test the laxity of the baby's hip.

Normally, this examination is done systematically until the age of walking and this, in well-defined conditions (relaxed and undressed child, on a hard surface).
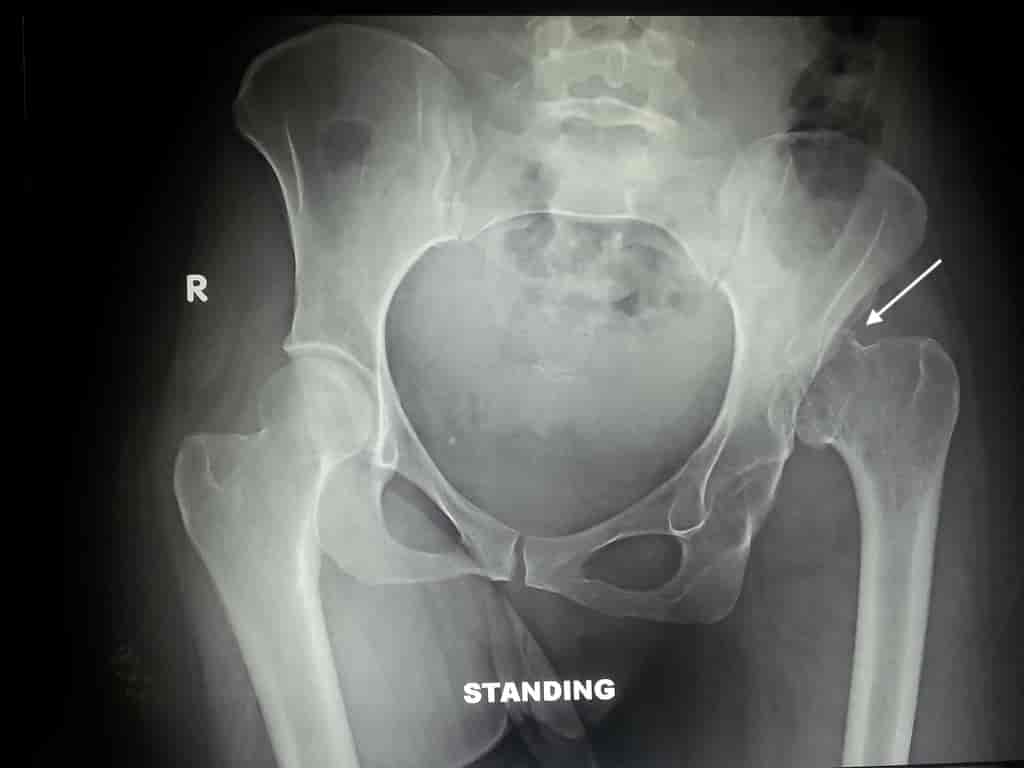
Sometimes, the dislocation of the pelvis does not manifest itself until adulthood. Thus, the diagnosis is more complex and requires X-ray or ultrasound. An X-ray examination can identify and confirm the diagnosis. It can also detect other fractures.
As for ultrasound, it consists in measuring the acetabular bottom thanks to a dynamic coronal section or rather an external coronal section. The latter is carried out with a high frequency probe. This is a dynamic monocut practiced by positioning the back horizontally and the hip flexed in adduction. Normal conditions are:
- acetabular bottom less than 6 mm;
- difference between the two legs, less than 1,5 mm.
What are the treatments for a hip dislocation?
Treatment of a dislocated hip aims mainly to put the head of the femur back in its cavity as well as the mobility of the hip. There are different treatments depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease.
In general, the treatment is orthopedic and can be done at home. These are methods that stabilize the hip and promote the development of the acetabulum.
For toddlers, the treatment requires the use of certain "accessories" such as the abduction cushion and the Pavlick harness. It is the doctor who chooses the appropriate tool depending on the condition of the baby. But in any case, these treatment tools are all aimed at keeping the legs apart.
For an adult, treatment consists of a closed reduction as soon as possible. For this, there are a few techniques.
- Allis' Technique
- The Captain Morgan Technique
- rocket launcher technique
These techniques require a sedation and muscle relaxation. The patient should lie down.
If these different approaches are not effective, a surgical treatment. This type of treatment consists of pelvic osteotomy. This allows to restore a good adaptation of the head of the femur and the acetabulum. Following the operation, the patient must wear a cast from the waist down to the toes for several weeks.
Healing time
Healing time after hip dislocation varies depending on the type of treatment used. Among other things, the wearing of treatment tools for the baby must be followed systematically. It is according to the state of the child that the doctor decides to stop the treatment.
In the majority of cases, the healing of a dislocated hip ranges from a few weeks to a few months.
Sources