When we talk about the subject of sciatica, we generally think of the shooting pains for which it is responsible. This disease, which affects both the elderly and young subjects, can sometimes prove to be very debilitating and disabling in certain individuals. But how long does sciatica last?
At least, after how long do the symptoms of sciatica fade?
This article answers these questions and also deals with the aspects of sciatica (causes, symptoms and circumstances of discovery), as well as the various therapeutic approaches allowing its cure.
Reminder: What is sciatica?
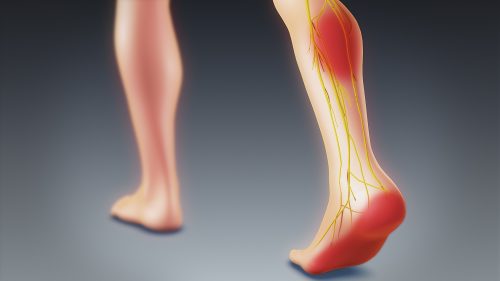
Sciatica or sciatalgia defines pain that manifests along the course of the sciatic nerve, the main nerve of the lower limb for which it provides sensory-motor innervation.
The sciatic nerve is the largest and longest nerve in the body, so it can cause severe pain, sometimes even resistant to analgesics.
Sciatica presents a path at the level of the lower limb well traced, going from the lumbar region, passing through the buttock, the posterior part of the thigh and the knee, to finish in the leg and the foot:
- Either through the outer part of the calf, the back of the foot and the big toe, when it is L5 sciatica,
- either by the posterior side of the calf, the heel, the sole of the foot ending at the level of the last three toes, in the case of S1 sciatica.
In general, only one lower limb is affected by sciatica, it is however possible that it affects both legs.
To learn all about sciatica, see the following article: https://www.lombafit.com/sciatique-a-z/
Causes of sciatica
Various reasons can cause sciatica; it can occur suddenly following a violent effort, a sneeze or a wrong gesture. As it can develop gradually following an accumulation of microtrauma or a degenerative pathology of the spine such as disc herniation.
The main conditions that can be responsible for sciatica are:
herniated disc
It is the main cause of sciatic pain. THE herniated disc occurs when part of the intervertebral disc comes out of its natural cavity and compresses the roots of the sciatic nerve. Sustained physical effort or certain contact sports can be the cause. In addition to sciatica pain, the hernia can cause lower back pain, resulting in lumbosciatic pain.
La spinal stenosis (narrow spinal canal)
It is a reduction of space inside the spine due to wear and tear on its structures. This results in compression of the sciatic roots. Sciatica can occur on one or both lower limbs, at rest or on exertion.
This stenosis is more common in people over the age of 60, and is usually the result of osteoarthritis.
A trauma
It happens that sciatica is secondary to trauma causing a fracture of a vertebra and/or the pelvis or a spinal collapse, the risk of developing a chronic sciatica increases with the severity of the injury.
Cancer
Whether primary such as a tumor in the spine or pelvis or secondary through metastases, cancer can be the cause of compression of one or more roots of the sciatic nerve.
Inflammatory sciatica
More rarely, so-called sciatica of inflammatory origin can be seen, it is generally sciatica secondary to spondylodiscitis (spinal infection mainly due to tuberculosis).
Sciatica symptoms
The symptoms encountered during sciatica obviously include pain along the path of the sciatic nerve. But it is also accompanied by other signs indicating more or less its seriousness, namely:
- Paresthesias at the level of the lower limb felt by the patient as numbness, tingling, tingling or a feeling of electric shock;
- muscle weakness accompanied by cramps and heaviness in the lower limb.
- Partial or complete paralysis with the impression of letting go of the knee, impossibility of walking on the tip or the heel of the foot.
How long does sciatica last?
It is very difficult to accurately estimate the duration of sciatica because it depends on different factors.
Nevertheless, with a good rest and a well conducted treatment, the average duration is about three to six weeks. The factors mentioned in the infographic influence healing time. It should also be noted that sciatica can however recur in the absence of a good basic treatment and the necessary precautions.
Can she pass on her own?
When sciatica is mild, it heals spontaneously in nearly half of cases. An effective rest associated with the taking of analgesics or rehabilitation generally makes it possible to obtain a remission of the pain within four to six weeks.
However, depending on the cause, sciatica can persist and limit daily activities. In these cases, more drastic measures should be considered. We think in particular of infiltration and surgery in extreme cases.
How does she stop?
The mechanisms making it possible to obtain a remission of the pain are represented on the one hand, by a reduction in the irritation of the nerve, indeed the fact of reducing the intensity of the efforts makes it possible to decrease the tension exerted on the sciatic nerve and thus the resulting irritation.
And on the other hand, by a cessation of the inflammation which occurs at the level of the nerve root thanks to the action of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or physical therapy (analgesic modalities, massages, mobilizations, electrotherapy, exercises , etc).
Support: What to do?
The management of sciatica is based on a well codified treatment combining medical treatment, rehabilitation and sometimes surgery.
Medical treatment
Used first and systematically, its main purpose is to reduce or even eliminate pain. It combines first-degree analgesics (paracetamol, NSAIDs) with muscle relaxants and sometimes even class III analgesics (morphine and opium derivatives). Its duration is about four to six weeks.
If oral treatment fails, patients are sometimes offered lumbar cortisone injections. Whether with or without radiological control.
Re-education
Contrary to old dogmas, specialists currently recommend a gentle and gradual resumption of sporting activity instead of absolute rest.
Physiotherapy is also a considerable help in the management of sciatica.
Indeed, by implementing stretching and muscle strengthening exercises, the physiotherapist helps to correct the patient's posture in addition to reducing pain by performing massages or other manual techniques.
Warm wraps as well as electrotherapy can also help relieve pain, although these passive modalities should ideally be combined with active approaches to achieve optimal results.
Surgical treatment
In case of failure of drug treatments or worsening of the clinical picture, recourse to surgery becomes a necessity.
The main purpose is to release and relieve the compressed nerve root. For this, it is possible: to surgically remove the part of the intervertebral disc at the origin of the herniated disc or to remove it percutaneously.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.