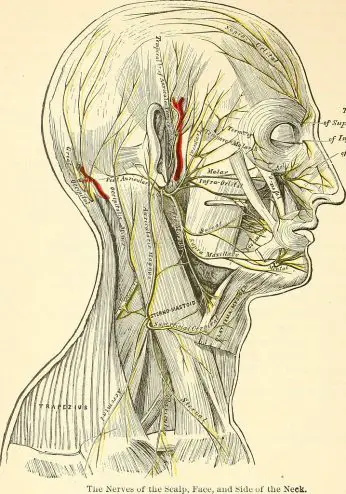
For better control of Arnold's neuralgia, it is important to have a good knowledge of the anatomy of the arnold's nerve also called greater occipital nerve.
To do this, this article will discuss the anatomy of Arnold's nerve, its course, its functions as well as all the conditions causing its damage.
Arnold's Nerve Anatomy
Le arnold's nerve ou greater occipital nerve is a nerve at the base of the skull (base on which the brain rests) which emanates from the spinal column, at the level of the posterior branch of the 2nd cervical nerve root, i.e. between the two cervical vertebrae C1-C2, also called the atlas and axis.
It is the largest of the posterior branches of the cervical nerves (average 3 mm in diameter).
Its direction is ascending (like those of the occipital nerves C1 and C3) while the other branches C4 and C5 follow a path either horizontal or descending.
It was first described in the year 1834 by a German anatomist, Friedrich Arnold.
Path
Le arnold's nerve presents an ascending course of the spinal column, where it originates to end at the level of the skull, more precisely at the scalp where it will give ramifications or nerve branches.
Particularly complex because it has several segments and angulations, Arnold's nerve successively crosses the three muscles: inferior obliques of the head (or large oblique), superior oblique of the head (or small oblique) and rectus abdominis, responsible for the different head movements.
This particular intramuscular course explains the risk of irritation and compression of Arnold's nerve leading to the characteristic pain of Arnold's neuralgia.
Features
Arnold's nerve is an even so-called mixed nerve, that is to say, it fulfills a double function, sensitive et driving force, with a predominance of sensory nerve fibers.
On the motor level, it gives nerve branches to the semispinatus capitis muscle (extension and inclination of the head), to the inferior oblique muscle (ipsilateral rotation of the C1-C2 joint), to the longissimus capitis (extension and ipsilateral tilt), splenius (ipsilateral extension and rotation), and trapezius.
At the sensory level, it innervates exo and endocranial territories:
- the exocranial territory includes the occipital region (back of the head) up to the vertex (top of the head), the lower parietal region, and to a lesser extent the frontal, supra-orbital regions, as well as the back of the pavilion of the 'ear.
- the endocranial territory includes the meninges (membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) of the occipital region.
Arnold's nerve pathologies
Its sinuous course comprising intra- and inter-muscular portions particularly exposes Arnold's nerve to the phenomena of compression and stretching.
Arnold's neuralgia testifies to the nerve pain resulting from the irritation of Arnold's nerve.
Some factors are known to be responsible for this suffering, including:
- Arthrose : joint degeneration causes a decrease in mobility of the neck, which promotes inflammation between the vertebrae and the underlying muscles. Knowing that Arnold's nerve passes through this region, he can also see himself suffering from this inflammatory condition.
- Trauma : car accident (whiplash), high-amplitude contact in athletes (such as hockey and football players), falls to the head, and direct blows to the base of the skull.
- neuropathy
- Muscle contraction
- Herniated disc cervical
- Polyarthrite rhumatoïde
Clinically, Arnold's neuralgia classically results in a pain neuropathic acute, sitting in the territory of the nerve triggered by the mobilization of the neck.
In the vast majority of cases, this pathology is idiopathic (without known cause) and benign, although it is responsible for significant discomfort.
It is important to note that some diseases can be confused with Arnold's neuralgia. Other causes of cranial and facial pain include migraines, tension headaches (describing a tight feeling around the head) or cluster headaches.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.