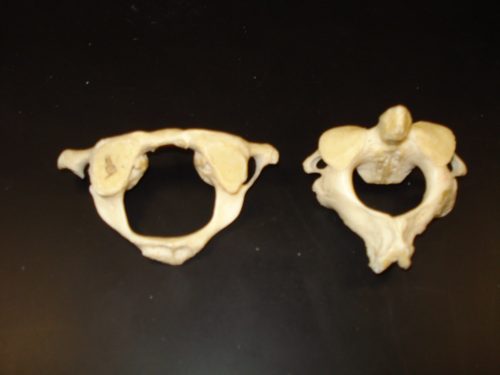
Did you know that theatlas is the first cervical vertebra in your spine? It owes its name to the god Atlas, who is said to have supported the world on his shoulders. L'atlas is responsible for maintaining your head!
One of the most important structures of theatlas and the ligament transverse. This ligament helps stabilize and protect your neck. In this article, we will discuss the anatomy of the ligament transverse and its importance for spinal health. Stay tuned !
Transverse ligament of the atlas: what is it?
Le ligament transverse of'atlas current is a ligament essential to support the weight of the head on the spine. This fibrous and strong band crosses the ring of theatlas and attaches to the odontoid process.
Le ligament transverse stabilizes the position of the head on the spine and prevents excessive movement that could damage delicate neurological structures. A ligament injury transverse can lead to serious problems, such as instability of the head on the spine and displacement of the odontoid process.
Treatment usually consists of immobilization of the head and neck, followed by physical therapy to regain range of motion. Surgery may also be required in some cases.
Role of the atlas and the ligament
THEatlas is the first cervical vertebra and supports the head. L'atlas has a unique anatomy among vertebrae, as it lacks a spinous process and has specialized joints that allow a wide range of head movement.
THEatlas is held in place by the ligamentum Nuchae, which attaches to the posterior surface of the neck and skull. L'atlas also has two transverse processes, which serve as attachment points for the muscles of the neck.
The main functions of theatlas are to support the head and protect the brainstem. L'atlas is essential for maintaining balance and allowing the head to move freely in all directions. Without it, our ability to move our head would be severely limited.
The role ofatlas is to support your head, your skull resting on it. L'atlas is C-shaped and rests on the odontoid process (also called “dens”), which rises from the second cervical vertebra (the axis). Together these bones form a joint called joint atlantoaxial, where they are connected to ligament nuchal, a band of tough tissue that runs along the spine.
Le ligament transverse current is a ligament important that supports the weight on the head. It's a ligament strong and fibrous which crosses the ring of theatlas and attaches to the odontoid process.
Pathologies associated with the atlas
Several pathologies can affect theatlas and ligament transverse. These include:
- Atlantoaxial instability: This situation occurs when theatlas and axis are not properly aligned. This may result in displacement of theatlas on the axis, which can in turn compress the spinal cord or cause other neurological problems.
- Fracture of the odontoid process : The odontoid process is a small, peg-shaped part. A fracture of this bone can occur during a fall or other trauma to the head and neck. This can cause severe pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the joints of the spine. This can lead to pain, stiffness and deformation of the spine.
- La Scheuermann's disease : This is a condition that affects the growth of the vertebrae. It can cause abnormal curvature of the spine and lead to pain and health problems.