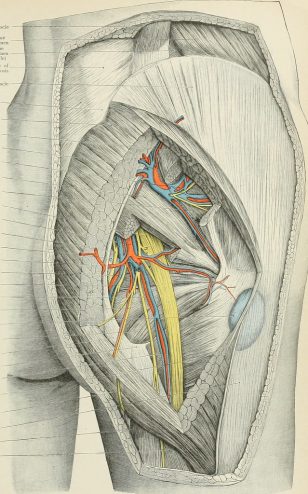
The upper and lower gluteal or gluteal nerves are exclusively motor nerves originating from the plexus lumbosacral. Recall that the latter is formed by the ventral branches of the spinal nerve roots of L4 to S4.
The gluteal nerves originate in the lumbosacral region. They come out of the pelvis through an orifice called “greater sciatic foramen”. They then cross the piriformis muscle before giving branches intended for the motor innervation of the gluteal muscles.
Superior gluteal nerve
Le superior gluteal nerve (or upper buttock) is a motor branch from the lumbosacral plexus which arises from the posterior divisions of the nerve roots L4, L5 and S1.
On its way, the superior gluteal nerve crosses the large foramen sciatica in company the artery and superior gluteal vein.
It then passes over the piriformis muscle to divide into two motor branches:
- There’s nothing quite like a upper branch intended for the innervation of the muscle gluteus medius.
- There’s nothing quite like a lower branch intended for the innervation of the small gluteus muscle and tensor fascia lata.
The superior gluteal nerve in brief:
- Origin: lumbosacral plexus L4 to S1.
- Branches: upper and lower.
- Function : gluteus medius innervation.
- Important concept: it crosses the large sciatic foramen (vulnerability to trauma).
Inferior gluteal nerve
Le inner gluteal nerve also arises from the lumbosacral plexus, specifically from the posterior divisions of the anterior nerve roots L5, S1 and S2.
After leaving the pelvic cavity via the greater sciatic notch, it passes below the piriformis muscle and terminates giving motor branches for the innervation of the gluteus maximus muscle.
The inferior gluteal nerve in brief:
- Origin: lumbosacral plexus L5 to S2.
- Branches: branches for the gluteus maximus muscle.
- Function : motor innervation of the gluteus maximus muscle only.
- Important concept: it passes below the piriformis muscle (possible irritation or compression by the latter during piriformis syndrome).
Gluteal nerve pathologies
The achievement of superior gluteal nerve is quite rare. It is mainly observed during pelvic fractures (particularly those located at the level of the large sciatic foramen where the superior gluteal nerve runs) or other buttock trauma.
On the other hand, damage to the inferior gluteal nerve are more frequent. They are mainly represented by piriformis syndrome.
Le « piriformis syndrome » is a condition characterized by compression and irritation of the sciatic nerve, but also inferior gluteal nerve by the piriformis muscle.
This syndrome is sometimes referred to as « pseudo-sciatica », as it is often misdiagnosed as a sciatica given their very similar clinical pictures, in particular with buttock pain.
This syndrome can also manifest as weakness of the gluteus medius muscle especially noticeable during hip abduction (moving the leg away from the axis of the body).
In addition, the patient suffering from compression of the inferior gluteal nerve secondary to a piriformis syndrome may present with waddling gait aimed at compensating for the motor failure of the gluteal muscle.
Reference
[1] P. Bauer, “Piriformis (pelvic pyramidal) muscle syndrome for the use of proctologists”, in foot, 2001, vol. 1, p. 9
[2] “Superior Gluteal Nerve – an overview | Science Direct Topics”. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/superior-gluteal-nerve (Accessed July 6, 2022).
[3] M. Diop, B. Parratte, L. Tatu, F. Vuillier, A. Faure, and G. Monnier, “Anatomical bases of superior gluteal nerve entrapment syndrome in the suprapiriformis foramen”, Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, flight. 24, no 3, p. 155-159, 2002.
My name is Katia, I am specialized web editor in writing medical articles. Being passionate about medicine and writing, I set myself the goal of making medical information accessible to as many people as possible, through the popularization of even more complex scientific concepts.