There is a narrow space between the pedicles of two vertebrae successive called the conjugation hole. This space allows the passage of spinal nerves coming from each myelomere of the spinal cord. In some cases, this space can narrow and cause pathologies. In this article, we will discuss the definition and the pathologies associated with a narrowing of the lumbar conjugation hole.
Lumbar Spine Anatomy
La lumbar spine is the lower part of the spine. It is made up of five vertebrae, each separated by a disc of cartilage. The vertebrae are linked together by a series of ligaments, and the whole structure is protected by a layer of muscles.
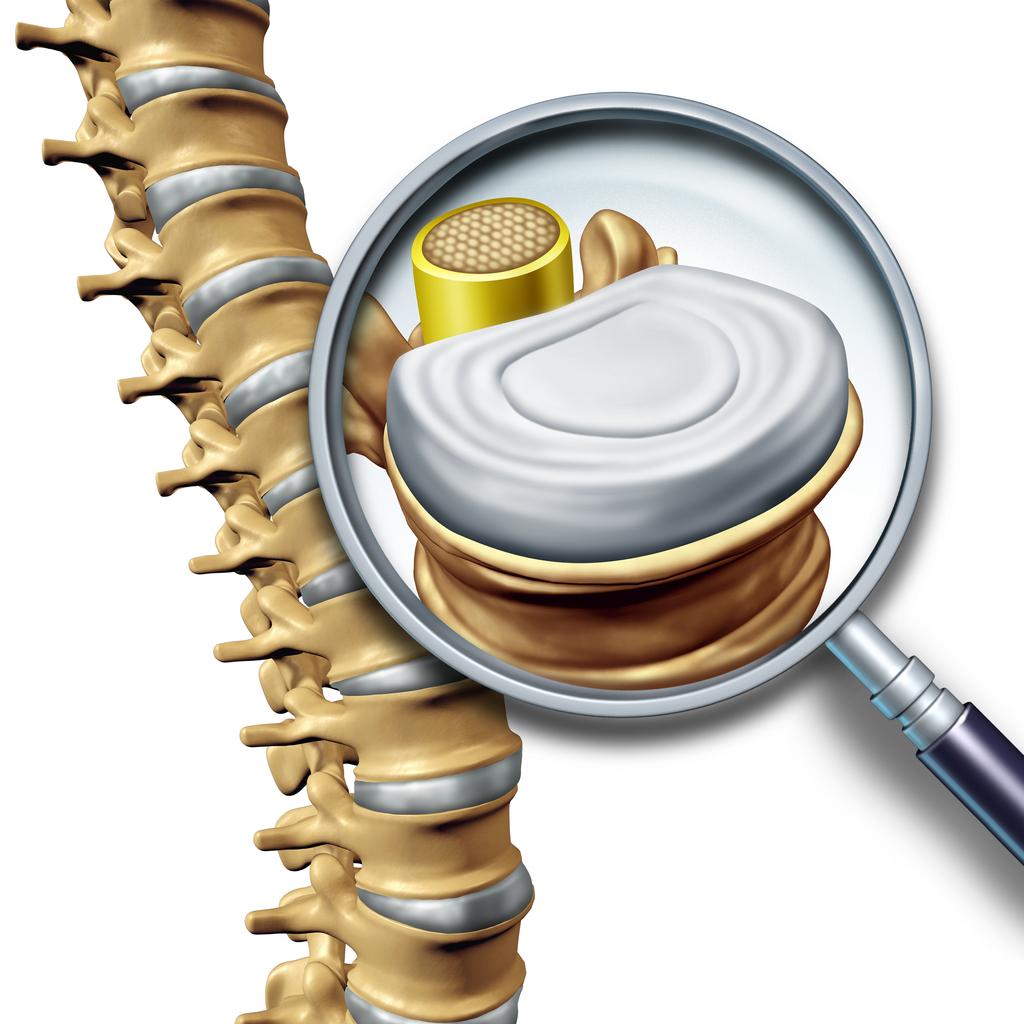
The discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, absorbing the impact of movement and helping to keep the spine flexible. The lumbar spine is also supported by a series of small bones, called facet joints, which allow the spine to move smoothly.
The facet joints are located at the back of each vertebrate and are connected to the vertebrae above and below. Working together, these various structures allow the lumbar spine to move in a wide range of directions while providing support and stability.
Conjugation hole: Definition
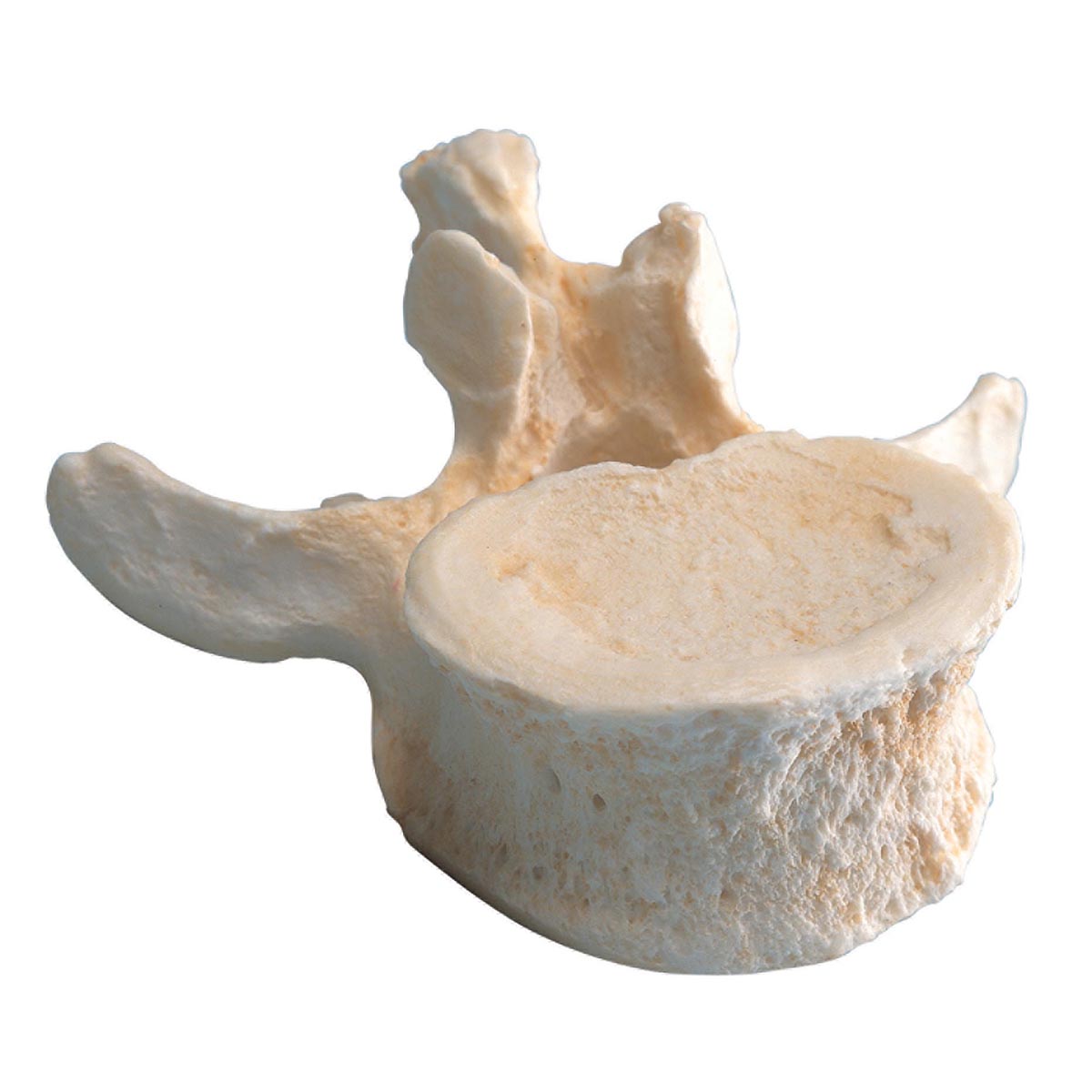
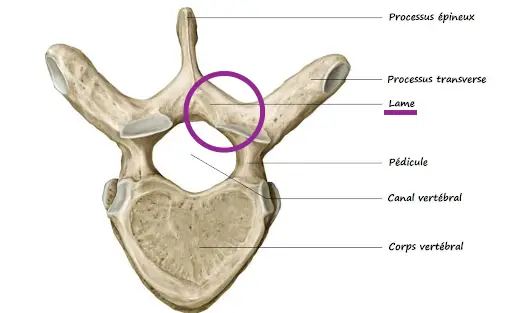
Le intervertebral foramen, also called conjugation hole, designates the space located between the pedicles of two successive vertebrae. There are up to two mating foramina per pair of vertebrae through which spinal nerves from each myelomere in the spinal cord can pass, as well as arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels to their respective organs.
The foramina are located laterally to the vertebral bodies and therefore do not communicate with the vertebral canal. Each foramen is bordered superiorly and inferiorly by articular processes, through which pass the zygapophyses which articulate with those of the adjacent vertebrae.
The pedicles and laminae form the posterior wall of the foramen, while its anterior edge is formed by the vertebral body and its costal processes. The foramina are larger in children than in adults due to the process of ossification of the growth plates. In adults, their size varies according to the level of the spine, being larger at the lower levels.
Causes of narrowed lumbar foramen hole
Several pathologies can cause narrowing of the lumbar conjugation hole. These include:
- Lumbar osteoarthritis : It is a degenerative joint disease. It causes breakdown of the cartilage between the vertebrae, which can lead to the formation of bone spurs. These bone spurs can narrow the foramen and compress the nerves running through it.
- Disc degeneration: The discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers and help keep the spine flexible. Over time, these discs can degenerate, lose their water content and become thinner. This can lead to the formation of bone spurs which narrow the foramen and compress the nerves.
- Herniated disc : A herniated disc occurs when the outer layer of the disc tears and the inner layer bulges out. This can compress the nerves that pass through the foramen and cause pain.
- Narrow lumbar canal : The lumbar canal is the space inside the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes. In some people, in fact, the lumbar canal is narrower than average. This can lead to compression of the nerves and cause pain.
- Spondylolisthesis (video explanation): Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which one of the vertebrae slips out of alignment. This can narrow the lumbar foramen and compress the nerves. The most common symptom is pain in the lower back. Other symptoms may include leg pain and difficulty walking.
Symptoms associated with the constricted foramina at the lumbar level
Symptoms of lumbar foramen narrowing depend on the underlying condition, level of inflammation, and extent of nerve damage. Typically, symptoms include lower back pain and potential neurological signs such as:
- Paresthesias (tingling, numbness or burning);
- Weakness ;
- Muscular atrophy.
In the most severe cases, the spinal cord can be damaged, which constitutes a medical emergency. Patients with symptoms of spinal cord injury such as:
- Incontinence;
- Paralysis;
- Or the loss of feeling.
Should seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of narrowing of the lumbar foramen hole
The diagnosis of foraminal stenosis begins with a clinical assessment. The doctor will take a complete medical history and perform a physical examination to assess symptoms. They will also ask about any previous injuries or conditions that may be causing or exacerbating the current problem.
However, imaging studies are often needed to support the diagnosis and identify affected anatomical levels and structures. The most commonly used imaging modality for this purpose is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
MRI can assess the narrowing of the lumbar foramen, as well as any other changes in the surrounding structures. In some cases, computed tomography (CT) may also be used.
CT is less sensitive than MRI for detecting foramen narrowing, but it can be useful for evaluating bony changes or calcifications. Once lumbar foramen narrowing is diagnosed, treatment can be undertaken.
Lumbar conjugation hole: What to do?
The treatment of narrowing of the lumbar conjugation hole depends on the underlying condition, severity of symptoms, and presence of neurological deficits. In general, treatment options include:
- Conservative treatment : It includes a combination of rest, physical therapy and pain medication. Physical therapy (physiotherapy) can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine and improve range of motion. Painkillers can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Invasive treatment: It includes injections of steroids or other drugs into the foramen or surrounding areas. Surgery may also be needed to decompress the nerves.
- Alternative treatments : These include acupuncture, massage and chiropractic care. These modalities can help relieve pain and improve range of motion.
Patients with narrowing of the lumbar conjugation hole should consult a medical professional to determine the best course of treatment. In most cases conservative treatment is effective. However, in some cases, invasive or alternative treatment methods may be necessary. Surgery should only be considered as a last resort.