Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
Tailbone pain is not uncommon. It can occur following a fall, be related to pregnancy, or sometimes occur without any particular reason. As many daily gestures and postures put pressure on the coccyx, the discomfort can greatly limit the quality of life.
Where does coccyx pain, also called coccydynia, come from? How to know if the coccyx is broken? In terms of treatment, what to do when you have pain in the coccyx?
This article covers everything you need to know when you have tailbone pain, and want to understand your condition in order to find adequate solutions.
Anatomy and role of the coccyx
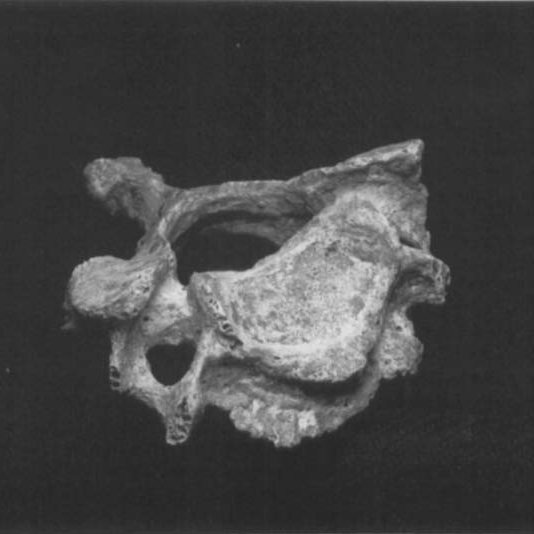
The coccyx is located at the very bottom of the spine, below the sacrum. It has a triangular shape and is composed of 3 to 5 lowercase vertebrae individual.
These bones fuse in adulthood to form the coccyx, although the fusion may be partial in some individuals. In this case, the coccyx is made up of 2 (or more) separate bones.
The coccyx serves as an anchor for several muscles, tendons and ligaments in the pelvic region. For example, muscle gluteus maximus, an important thigh extensor, has one of its origins in the coccyx.
In addition to its role in fixing the muscles, the coccyx also plays an important role in supporting the spinal cord. THE terminal filum, a fibrous tissue that serves as an extension of the spinal cord, attaches to the coccyx and uses this bone as an anchor for the spinal cord.
In a seated position, the coccyx helps the two seat bones of the pelvis to support the weight of the body, much like a tripod.
Finally, in women, the coccyx moves posteriorly during childbirth to leave more space for the head of the fetus.
Why do my coccyx hurt? (causes)
Coccyx pain is common. Women are five times more likely than men to develop coccydynia. Adults and adolescents suffer from it more often than children. In addition, obese people are three times more likely to develop coccyx discomfort compared to those with a "normal" weight (according to BMI).
Here are some potential causes of tailbone pain:
- Fall
- Pregnancy
- Vaginal postpartum
- Prolonged and/or repetitive sitting (especially on a hard surface)
- Degenerative changes
- Repetitive movements (such as cycling, rowing, running, etc.)
- overweight, or drastic weight loss
- Weight too low (in lean people)
- Hemorrhoids
- anal fissure
- Straighten
- Infection or abscess (rare – sacrococcygeal or pilonidal cyst)
- Tumor and cancer (rare)
You may have tailbone pain, and cannot correlate your symptoms with one of the causes mentioned above. Indeed, the exact cause of coccyx pain is unknown in a third of cases.
Coccyx pain during pregnancy
Coccyx pain usually appears in the last three months of pregnancy, or after childbirth. It is most often caused by the relaxation of the pelvic ligaments (around the pelvis). Indeed, the body releases a hormone called relaxin during pregnancy; its role is to make the joints more flexible and flexible to allow the growth of the baby and the delivery.
This ligamentous laxity can cause a slight deviation of the spine, or even a slight displacement of the joint between the sacrum and the coccyx, which is synonymous with pain.
In addition, the pelvic floor muscles could work harder to compensate for joint instability caused by relaxin. As these muscles are anatomically connected to the coccyx, repeated contractions of greater intensity (to stabilize the pelvis) could cause pain in the coccyx.
In addition, the expansion of the abdomen changes the center of gravity and posture, leading to increased pressure on the lower back and tailbone. As the baby can also exert additional pressure on the coccyx, certain positions (such as prolonged sitting or standing) could be painful.
Finally, issues such as constipation or lack of exercise can also contribute to tailbone pain.
Coccyx pain and cancer
Many people with coccyx pain fear that it is cancer. This is all the more true when the symptoms have appeared for no particular reason, and when they worsen over time. Cancers that can cause pain in this area include:
- chordoma
- prostate cancer
- colorectal cancer
- bone metastases
- spinal tumor
- etc.
It should be noted that these are rare cases, and that coccyx pain comes most of the time from benign causes. If you ever observe any of the following signs and symptoms, it is best to consult your doctor without delay:
- Blood in the stool or urine
- Urinary or fecal incontinence
- Burning sensation during urination or ejaculation
- Sudden onset erectile dysfunction
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chronic fatigue
- Constipation or recurrent diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Loss of sensation and significant weakness in the legs
How do I know if I have a broken tailbone?
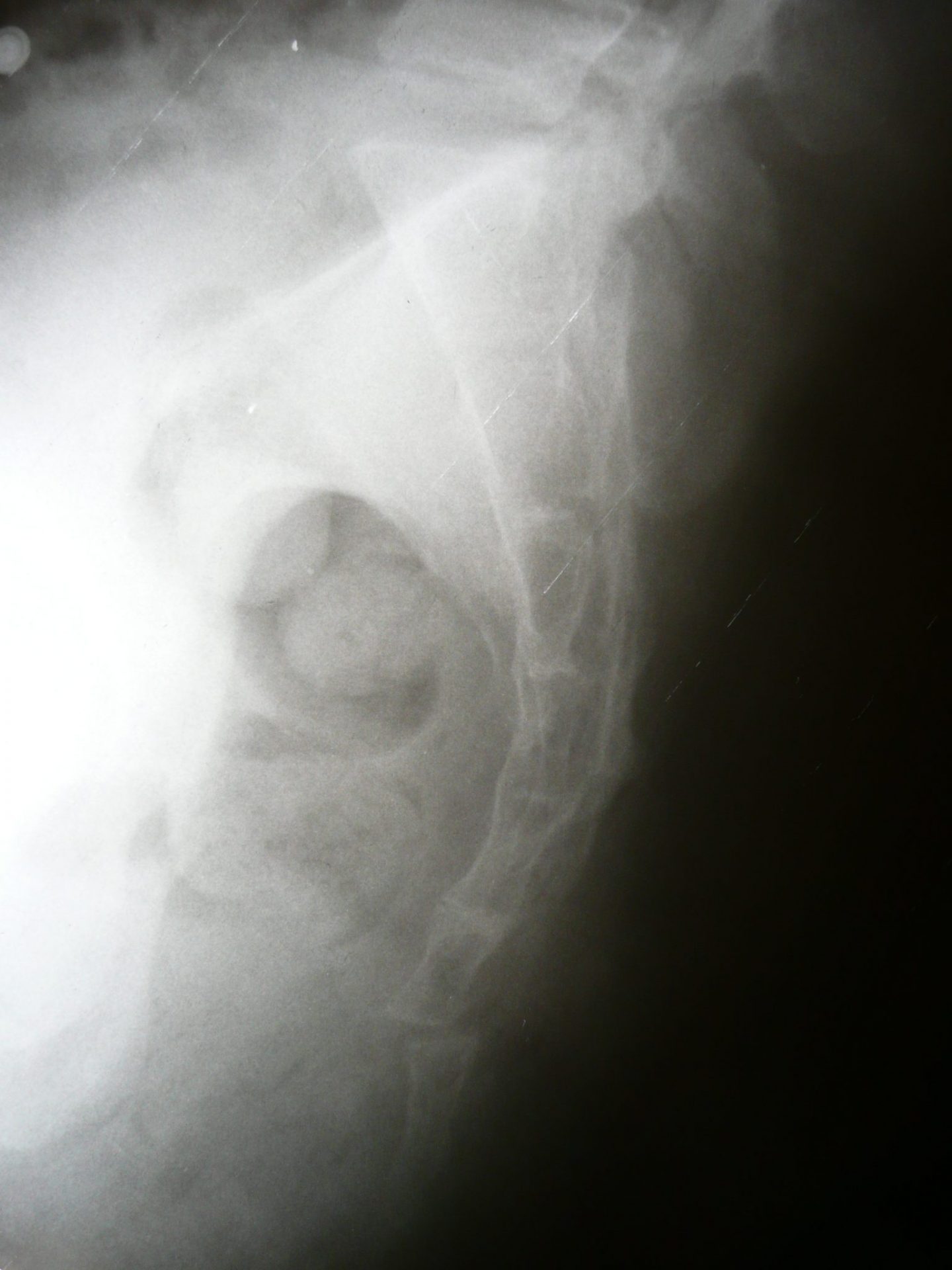
A coccyx fracture is a more common condition than one can imagine. It can be acute or chronic, and can take a long time to resolve.
Here are signs and symptoms which can be synonymous with broken coccyx :
- Localized pain in the coccyx
- Pain increased with prolonged sitting, bending backwards, prolonged standing, and rising from a chair
- Pain during intercourse or defecation
- Recent fall (skiing, biking, etc.)
- Swelling in the tailbone area
- Numbness and paresthesias in the coccyx region
- Feeling of weakness in the legs
Considering the anatomy and depth of the coccyx, many fractures are not immediately diagnosed. And as mentioned before, the coccyx, even without injury, can be fragmented into several small bones.
Thus, this anatomical peculiarity can make it difficult to diagnose a fracture, because it is not known whether the fragments were present or not before the injury.
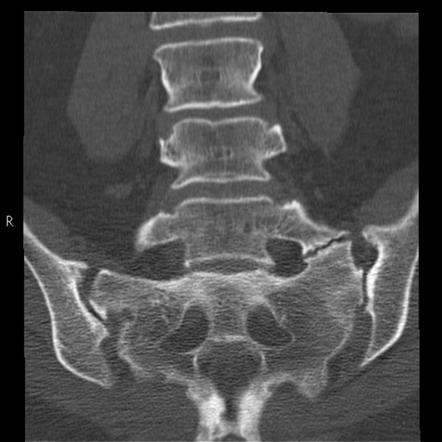
The best way to diagnose a coccyx fracture is to have a medical imaging. It may be a radiography, CT scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Sometimes the doctor orders tests in different positions (such as sitting then standing) to compare the position of the coccyx, and determine the mobility of this bone.
To know everything about coccyx fracture, see the following article.
How long does coccyx pain last?
Unfortunately, coccyx pain can persist over time, lasting from several weeks to several months.
Depending on the cause, the pain may take longer to pass. It is for this reason that it is essential to be diagnosed, especially if the symptoms do not seem to fade within 4 weeks.
By applying adequate treatment strategies, one can speed up the healing process and avoid worsening the inflammation.
Don't worry, the pain should go away after a while. It is extremely rare to develop coccyx pain that lasts indefinitely (unlike chronic low back pain).
How to treat a coccyx dislocation?
This is a question frequently asked by patients who suffer from pain in the coccyx, and who assume that it is a dislocation. This diagnosis is also made by some practitioners such as osteopaths.
On the one hand, the dislocation of the coccyx is difficult to prove, in particular because of the minimal movement that exists at the level of the coccyx. To really know if the coccyx has been reached, a medical imaging examination is necessary.
In some cases, however, an osteopath will try to mobilize or manipulate the sacrum to correct a dysfunction. It can be done superficially via the spine, or via the rectum.
This manual therapy often offers relief to patients, although one can wonder about the exact mechanism of these techniques (non-specific effect vs repositioning of the coccyx).
My coccyx hurts: What should I do?
In the presence of coccyx pain that persists, it is important to consult a health professional. This can clarify the diagnosis and determine the cause of your symptoms (if possible). Above all, he will suggest various means of treating your pain, and will follow up on your condition.
Here are several strategies for relieving tailbone pain (including a broken tailbone), the majority of which can be implemented immediately:
- Anti-inflammatories oral, creams anti-inflammatories, tiger balm, etc.
- Electro-stimulation (TENS and Compex)
- IMMEDIATE PAIN RELIEF: with 8 preset and targeted programs. The Perfect TENS is an easy-to-use device that uses clinically proven TENS technology. It helps relieve chronic, acute and musculoskeletal pain such as arthritis, back pain and sciatica.
- DUAL CHANNEL: Two independent channels allow you to target two areas simultaneously or focus on a larger pain area and relieve acute or chronic pain in a more effective and targeted way.
- PROGRAMS: 8 clinically designed preset programs and 1 manual program. It will be quick and easy for you to find the pain relief you need that targets your specific pain. The manual program even allows you to choose specific settings, meaning you can create your own bespoke program and use it again and again.
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Muscle stimulator offering 30 programs: 10 physical preparation programs, 8 pain relief programs, 5 recovery programs, 2 rehabilitation programs and 5 fitness programs.
- The partner of your sports preparation, allowing you to prevent injuries, recover better but also relieve your pain.
- 4 independent channels allowing you to work 2 muscle groups simultaneously.
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Avoid sitting on hard surfaces. There are many seats and cushions which make the sitting position more comfortable. Indeed, vou can use a cushion specially designed to reduce coccyx pain while sitting. An ergonomic U-shaped cushion allows you to sit while limiting the pressure on the coccyx.
- Postural correction: For example, lean slightly forward when sitting down to avoid increasing stress on the tailbone. Also adjust your sitting posture to reduce symptoms.
- In case of constipation, take laxatives (or others) to reduce stress on the coccyx.
- Avoid tight clothing which would put painful pressure on the coccyx.
- Sleep on the side to avoid putting pressure on the coccyx.
- Pelvic floor exercises (prescribed in physiotherapy or physiotherapy)
- Therapeutic exercises aimed at reducing stress on the coccyx (prescribed in physiotherapy or physiotherapy)
- massage and mobilizations (for example with a mini massage gun around the coccyx area)
- [COMPACT YET POWERFUL] Mebak Mini is your pocket partner, giving you Mebak quality muscle treatment with unique portability. Even women can easily handle it with one hand. It can exert pressure up to about 14 kg. Even if you press hard, it won't stop easily. The comfortable vibrations penetrate deep into your body, allowing you to experience ultimate relaxation.
- [SUPER QUIET - RELAX YOURSELF COMPLETELY] Adapted to the latest noise reduction technology, Mebak Mini is so quiet you can barely hear it. Whether you're on the go or in the comfort of your home, enjoy a moment of silence to unwind. With convenient USB-C charging, you can enjoy Mebak's excellent body care anytime, anywhere.
- [IDEAL FOR TOTAL BODY CARE] In addition to normal massage heads, there are also cushion heads for beginners, the elderly and those with sensitive skin and ball heads for muscle training of athletes. In addition, by easily changing the 6 heads and adjusting the 4 speeds, the device adapts to all parts of the body, from the feet to the neck, and makes it possible to obtain an ideal shape of the body at all times through care. professionals.
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Acupuncture et acupressure mat
- 🧘 𝐔𝐍 𝐄𝐍𝐒𝐄𝐌𝐁𝐋𝐄 𝐔𝐍𝐈𝐐𝐔𝐄 𝐓𝐎𝐔𝐓-𝐄𝐍-𝐔𝐍 – Wellax acupressure set leaves nothing to desire: For a complete and perfect wellness experience, you will receive a matching spiked cushion with our acupressure mat!
- 🧘 𝐋𝐈𝐁È𝐑𝐄 𝐃𝐄 𝐋𝐀 𝐓𝐄𝐍𝐒𝐈𝐎𝐍 – Our fakir mat stimulates the muscles, promotes circulation and can thus effectively relieve tension. This is how you fight annoying back and neck pain!
- 🧘 𝐃𝐈𝐒𝐒𝐈𝐏𝐄 𝐋𝐄 𝐒𝐓𝐑𝐄𝐒𝐒 𝐑𝐎𝐔𝐓𝐈𝐍𝐈𝐄𝐑 – Whether after a training session, a match or a hard day work: The Wellax acupuncture mat is the ideal support for releasing daily tension. Pure relaxation for body and soul!
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Infiltration cortisone
- nerve block of the coccygeal nerve
- Surgery : It is extremely rare. This operation may be indicated for complex fractures involving damage to the surrounding tissues, or even fractures where the bone could break through the skin. In extreme cases, the coccyx may be partially or completely removed (coccygectomy partial or total).
The coccygeal cushion
As seen previously, coccyx pain can persist for several weeks several months. It is therefore wise to obtain a cushion specially designed to avoid pressure on the coccyx, promote healing, reduce pain and prevent aggravation of symptoms.
This type of cushion differs from a traditional cushion, its horseshoe shape will allow a comfortable seat while decreasing the contact between your support and your tailbone. It will be of great use to you if you have to sit for long hours. Made with a "shape memory" type material, this cushion will adapt to your morphology while avoiding excess pressure on the coccyx. It will be all the more useful if you have to travel by car, for example to help dampen shocks and vibrations.
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
As seen above, the coccyx, in a seated position, will help the two seat bones of the pelvis to support the weight of the body. When you use a coccyx cushion it is therefore wise to maintain optimal support for your spine and keep a good posture in order to avoid that certain vertebrae are under too much pressure.
Lumbar support can help keep your spine in a healthy posture, while decreasing the risk of lower back pain.
Simply place it on your car seat or office chair. Lean forward slightly when you sit on it to limit stress on the tailbone.
Please also readjust your seat (seat height) if necessary to maintain a healthy posture. You can place a small support under your feet if necessary in order to have a more comfortable position. Also, if you put it on a very soft support, for example on the sofa or the bed, you can put a solid board under it to give you more support.
If your cushion does not relieve you or aggravates your symptoms, it may be necessary to opt for a firmer, softer or thicker model, it will depend on you, your situation and your morphology. You can also ask your doctor or healthcare professional for advice.
What about natural remedies?
Although they are not supported by solid scientific evidence, several natural products and home remedies are used to treat various body pains, especially for their anti-inflammatory power.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of plants and essential oils that are effective in controlling pain and inflammation:
- Turmeric : Thanks to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory powers very powerful, turmeric is one of the most used plants in a culinary and therapeutic context. The composition of turmeric is essentially made of essential oils, vitamins (B1, B2, B6, C, E, K) and trace elements. But it is to its composition rich in curcumin and curcuminoids that we owe them and calm skin of this spice.
- REASON TO CHOOSE OUR TURMERIC CAPSULES WITH GINGER AND BLACK PEPPER – Our complex turmeric…
- POWERFUL TURMERIC CAPSULES - Turmeric is an excellent source of Vitamin C, antioxidants,…
- IDEAL AND PRACTICAL FORMULA – The powders we use are delicately harvested,…
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Ginger : In addition to the special flavor it brings to the kitchen and its aphrodisiac properties, ginger is a root well known for its anti-inflammatory powers. THE gingerol gives it its anti-inflammatory action. It is an active component acting on the inflammatory pain related to chronic joint inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, rheumatic diseases, etc. It has been proven that this active element is also effective in acting on the inflammation linked to arthritis and sciatica. Ginger also has other benefits thanks to its high potassium content and its richness in trace elements (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium) and vitamins (provitamin and vitamin B9).
- 【Natural Ginger Foot Patches】: Natural Foot Detox Patch with Ginger and…
- 【Ginger Anti Swelling Detox Patch】: Ginger Detox Patches are natural,…
- 【Removes Body Toxins】: Ginger Foot Patches helps reduce the buildup of…
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- Omega-3s : Omega-3 are polyunsaturated fatty acids that play a very important role in the functioning of our body. They are provided by food in three natural forms: docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), alpha linolenic acid (ALA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Beyond their action on the brain and the cardiovascular system, omega-3s prove very effective against inflammation. Indeed, they have the ability to act on the inflammatory mechanisms in osteoarthritis by slowing down cartilage destruction, thus they reduce the intensity of osteoarthritis pain. Sciatica, being most often linked to an inflammation secondary to a herniated disc, it can also respond to omega-3 provided it is consumed regularly.
No product found.
- Lemon eucalyptus: Eucalyptus is a plant most often used in the form of herbal tea or essential oil. She would have anti-inflammatory effects which give it the ability to act on the bone and joint pain in general and the pain of sciatica in particular.
- Eucalyptus Citriodora Essential Oil.
- 100% pure.
- Botanical name: eucalyptus citriodo.
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
- wintergreen : Wintergreen is a shrub from which a very interesting essential oil is extracted. It is one of the most used essential oils in aromatherapy. This oil extracted from the shrub bearing the same name, is used in massage to relieve sciatica and act like a analgesic. Indeed, it provides a heating effect thanks to its ability toactivate blood circulation locally.
- PROPERTIES ORGANIC WINTERGOOD ESSENTIAL OIL: Wintergreen essential oil is…
- DIRECTIONS FOR USE: Refer to the instructions or ask your pharmacist for advice, This…
- PURESSENTIEL DNA: A range of 55 essential oils essential for well-being in the…
Last updated on 2024-04-22 / Affiliate links / Images from the Amazon Partners API
Conclusion
Coccyx pain comes from multiple causes, and greatly limits the quality of life by restricting gestures and postures.
Once the cause has been determined, treatment strategies can be applied to reduce tailbone pain. On the other hand, you have to be patient because these pains do not disappear as quickly as one might imagine.
If in doubt, it is best to consult a health professional who can refer you to imaging tests if necessary, and perform manual or other techniques to accelerate healing.
Good recovery !