Le hydrocephalus term designates a situation byexcess cerebrospinal fluid (LCS) in the cerebral ventricular cavities. It is a disorder with multiple forms both clinically and etiologically (cause), which can progress to coma if no neurosurgical treatment is carried out urgently. Find out in this article what to do during hydrocephalus.
Definition of hydrocephalus
THEhydrocephalus (from ancient Greek hýdôr meaning “water” and kéfalé: “head”) is a severe neurological abnormality which designates a increase du volume of cerebrospinal fluid ou cerebrospinal (CRL). This liquid circulates in the brain and plays a key role in the protection of the neurological sphere. In particular, it eliminates waste and absorbs shocks that can damage brain structures.
The dilation may be due to hypersecretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a lack of resorption or a mechanical obstruction of the circulation routes.
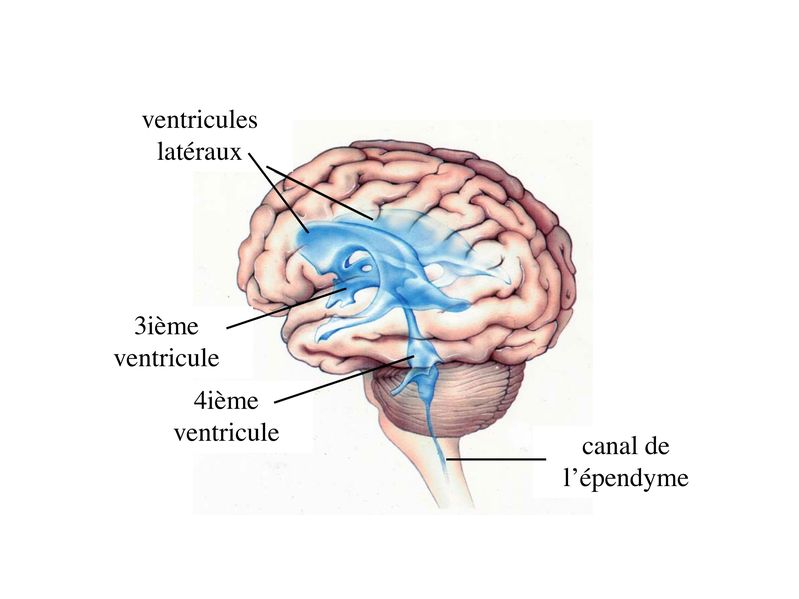
Every day, the brain produces half a liter of cerebrospinal fluid which is distributed in pockets of fluid located in the center of the brain (the 4 ventricles) and around the brain. In normal conditions, there is a delicate balance between the production, circulation and rate of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebral ventricles.
Hydrocephalus develops when cerebrospinal fluid cannot properly flow through the ventricular system, or when absorption into the bloodstream is not equal to the amount of cerebrospinal fluid produced.
Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid can cause dilatation of the cerebral ventricles. The cranial box being inextensible (at least in the adult), it follows a increased intracranial pressure which significantly interferes with the proper functioning of the brain. The consequences of hydrocephalus are numerous and can affect the body at different levels.
The different types of hydrocephalus
Acute hydrocephalus : characterized by difficulty in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. It can be brutal and often linked to a meningeal hemorrhage or a tumor compressing the ventricles. The liquid then accumulates in the ventricles and exerts a pressure from the inside on the brain.
Chronic hydrocephalus : it corresponds to a problem of resorption of cerebrospinal fluid. This dysfunction in the evacuation of the CSF leads to stagnation in the brain.
normal pressure hydrocephalus (without increased intracranial pressure): this is a chronic form linked to partial obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways.
This pathology can occur at all ages of life, from newborn to old (in the case of normal pressure hydrocephalus). Hydrocephalus is a fairly rare disease. It would affect 1 in 1000 children at birth. It concerns between 0,5 and 1% of people aged over 60.
Causes of Cerebral Fluid Buildup-spinal in the skull
In principle, there is a balance between the production, passage and reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid in the cavities of the brain. If the cerebrospinal fluid is not well reabsorbed, the volume of the ventricles increases, and this is what causes hydrocephalus.
The causes of hydrocephalus is Outputs : they can be congenital ou acquired. This means that they can be present from birth or be the consequence of certain external parameters.
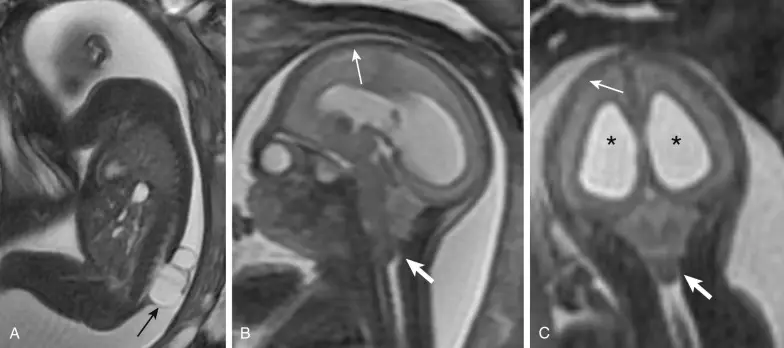
Congenital hydrocephalus is most often discovered at the end of pregnancy or in the period around birth. They are usually due to congenital malformations (a spina bifida, for example), or following an intraventricular cerebral hemorrhage favored by prematurity.
Other causes of hydrocephalus in children can have several explanations:
- brain tumors and cysts;
- malformations of the central nervous system (Dandy-Walker malformation);
- head trauma;
- central nervous system surgery;
- or meningitis (due to defective CSF absorption in the subarachnoid spaces).
In the case of a normal pressure hydrocephalus (common in people aged 60-70), risk factors is still poorly known nowadays. Family history has an influence. However, many other external parameters could also have an impact. Premature infants have a higher risk of developing hydrocephalus once they are older.
What are the symptoms of hydrocephalus ?
La symptomatology hydrocephalus covers various aspects, depending on the cause, the age of onset and especially the speed of onset of the disease: acute, subacute or chronic.
Acute or subacute hydrocephalus
This mode of revelation results in a syndrome ofintracranial hypertension (HTIC). The latter typically combines: cephalalgia, nausea, vomiting et visual disturbances. Headaches are most often relieved by vomiting and aggravated by the effort of coughing. Nausea and vomiting (called "jet") are inconstant. Visual disturbances may involve a decrease in visual acuity and visual blurring due to papilledema. Other symptoms are sometimes found, such as dizziness or gait disturbances.
The appearance of consciousness disorders (possibly going as far as coma) should raise fears of cerebral involvement.
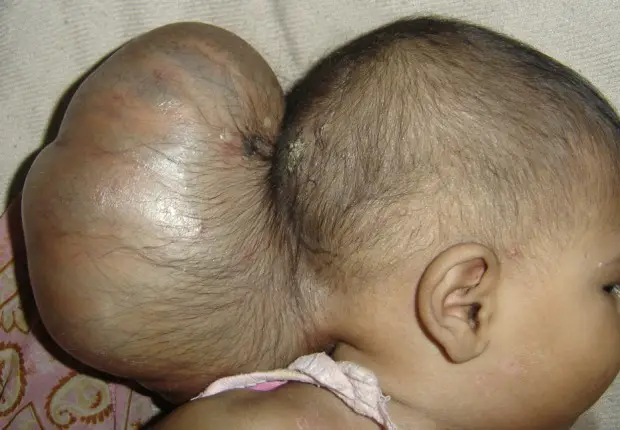
For the special case of the infant, the neurological consequences of ICHT may include irritability, piercing cries, vomiting, a lethargy, strabismus (gaze in "sunset"), a bulge of the fontanel or at a more advanced stage, a macrocranium (increase in skull size “head circumference”).
Chronic hydrocephalus
Clinical signs in children are often linked to the causative disease: acquisition delay, Autonomy loss, psychomotor retardation et headache.
At the elderly subjects, the clinical picture is characterized by the Hakim and Adams triad associating gait disorders, sphincter disorders (urinary leakage) and a dementia syndrome.
The gait and balance disorders typically constitute the first symptoms observed. Its onset is mainly manifested by a slowing of walking with balance disorders. In the advanced stage, there is a slow gait and a marked tendency to drag the feet.
As a rule, theurinary incontinence appears late. It is manifested, initially, by urgent urination and reflex incontinence.
The intensity of cognitive deficits (dementia) varies according to the stage of the disease. It typically causes a decrease in interests and activities, impaired concentration and short-term memory, psychomotor retardation and problems with higher functions (mental fatigue, regression of intellectual abilities, temporal-spatial disorientation).
How is the diagnosis made ?
Le diagnosis of hydrocephalus is most often worn precociously during the first months of the child's life in front of a increase too fast du cranial perimeter. In older children, progressive hydrocephalus is manifested by symptoms of increased intracranial pressure : headache, vomiting, drowsiness or decreased vision.
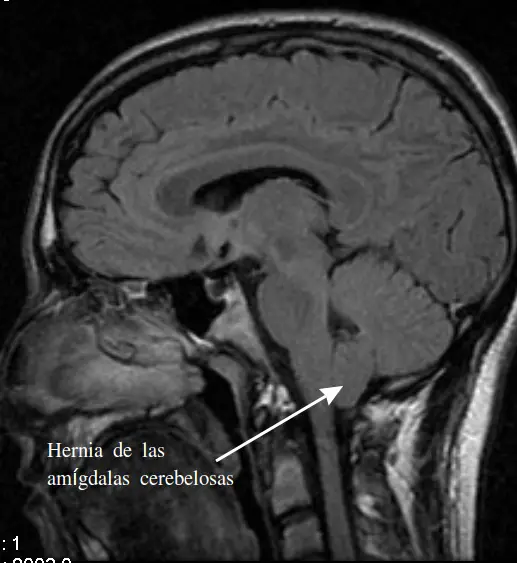
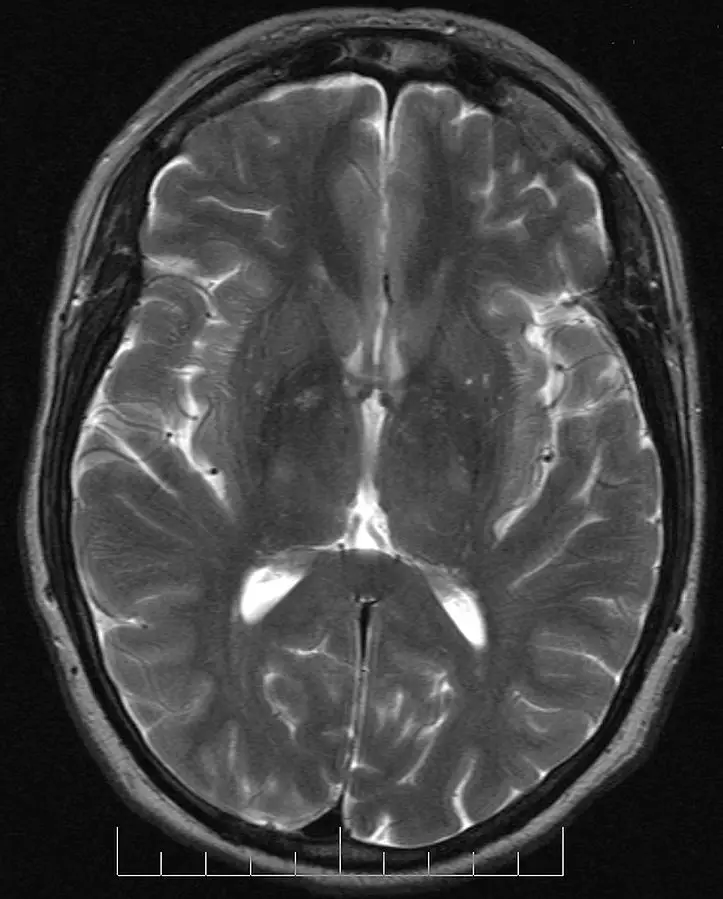
It is not always easy to diagnose hydrocephalus. For this, it is generally recommended to make a cranial ultrasound in newborns or brain scan associated with a IRM (magnetic resonance imaging) in children and adults.
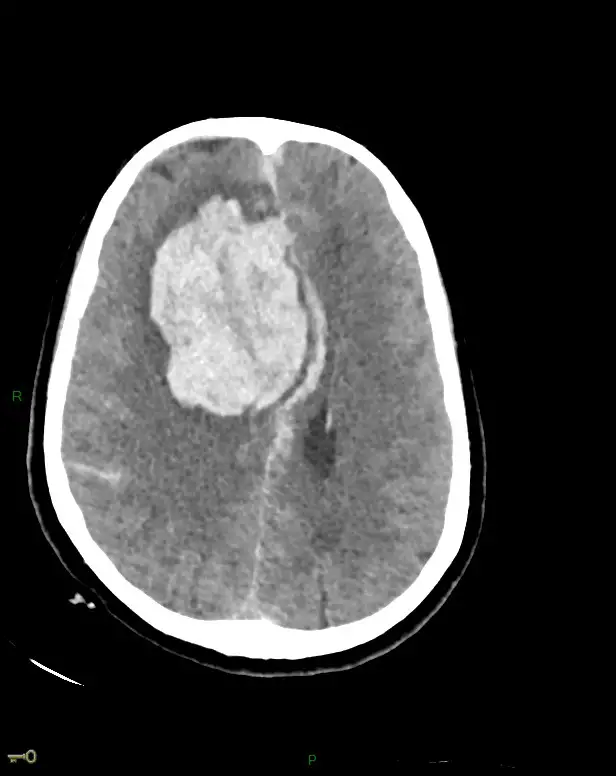
Brain imaging (scan or MRI) shows a enlargement of the ventricles (intracerebral cavities in which cerebrospinal fluid is produced).
Le brain scan is an imaging technique that consists of scanning the various anatomical structures of the cranial box (brain, auditory and visual nerves, vessels, meninges, etc.).
The principle is quite simple: X-rays are more or less absorbed by tissues depending on their density. The computer support makes it possible to analyze this data and create images of the explored region. The structures of the cranial box are displayed in different shades of gray, this makes it possible to identify them and to control their volume, their morphology and possibly, to detect an anomaly.
THEMRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a radiology examination that uses a device that emits electromagnetic waves. This is an examination that provides images of the inside of the cranial box. It is usually prescribed to visualize soft tissues, such as the brain.
MRI characterizes hydrocephalus in the same way as CT from a morphological point of view. It is more sensitive than the scanner, in particular better exploring the evolution of the disease (more precise volumetric study of the ventricles).
Sometimes the doctor takes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through a lumbar puncture to see if the symptoms improve. This has diagnostic value. However, it is contraindicated in cases of occlusive hydrocephalus.
How to Treat Hydrocephalus ?
Acute hydrocephalus is a neurosurgical emergency, it is imperative that a derivation of the cerebrospinal fluid be carried out quickly, otherwise the vital prognosis is engaged.
Treatment of the cause
Le etiology treatment hydrocephalus must be mentioned in order to avoid the laying of unnecessary internal shunts. In practice, it mainly concerns the cure of a malformation or an arachnoid cyst, excision of compressive or obstructive tumours. These operations may be sufficient to treat hydrocephalus (sometimes with the help of drug treatment with acetazolamide).
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) diversions
For acute hydrocephalus, the treatment is surgical. The neurosurgeon offers a diversion of cerebrospinal fluid. The goal is to drain excess CSF to an anatomical site that can accommodate this excess fluid.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and requires hospitalization for a few days. This operation consists of introducing a catheter (tube) at the level of a ventricle, which first lets the CSF flow outwards.
If the problem persists, the bypass will be connected to a bypass valve which allows the drainage to be regulated. This valve is connected to another tube introduced into the abdominal cavity.
In case of'normal pressure hydrocephalus, a lumbar puncture removes cerebrospinal fluid. It is a stitch in the back, at the level of the space surrounding the spinal cord. This usually improves symptoms.
References
https://neuro-dev.unilim.fr/spip.php?article210
https://www.primomedico.com/fr/cure/hydrocephalie/
https://www.revmed.ch/view/526818/4279832/RMS_idPAS_D_ISBN_pu2010-15s_sa08_art08.pdf