Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
During recent years, the surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniations went from the open surgery full spine to the tubal surgery, then to fully endoscopic techniques. The development of new technologies has made it possible to considerably reduce muscle trauma during surgery and facilitate post-operative follow-up while allowing decompression to be performed as effectively as conventional surgery. We focus on the microdiscectomy.
Definition
Correct a herniated disc is the most frequently performed surgical procedure in lumbar spinal surgery.
La discectomy is an intervention by which one removes the fragment of the disc which forms the herniation and which compresses the neighboring nerve or nerves. Once the nerve root(s) are released, the pain of sciatica should calm down.
La microdisectomy has the same principle, but using a minimally invasive technique. The operation is done from a small incision ranging from 1 to 3 cm using a surgical microscope or an endoscope (endoscopic microdisectomy).
Indications for surgery for a herniated disc
There is a professional consensus to propose a surgery for a herniated disc lumbar.
- In extreme emergency, in front of a cauda equina syndrome : this neurological condition is responsible for acute pain in the lower back, sensory and motor disorders in the lower limbs, as well as genito-sphincter disorders. The recovery rate is significantly higher if the surgery is early.
- We also agree that a sciatica morphine-resistant hyperalgesia and sciatica with a frank and recent motor deficit (paralyzing), less than 48 hours old, should benefit from rapid surgery.
- For uncomplicated sciatica, radical treatment of lumbar disc herniation should be practiced only if the medical treatment proved ineffective (after 6 to 8 weeks of well-conducted medical treatment when the pain remains disabling). The predominance of radiculalgia on low back pain is an essential criterion. It is also necessary that the disco-radicular compressive mechanism be demonstrated with a good concordance between the topography of the radiculalgia and compressed root.
How is the microdiscectomy performed?
Surgical microdiscectomy (for lumbar disc herniation)
It requires a Microscope which illuminates and enlarges the operating field. The patient is placed on his stomach under General anaesthesia.
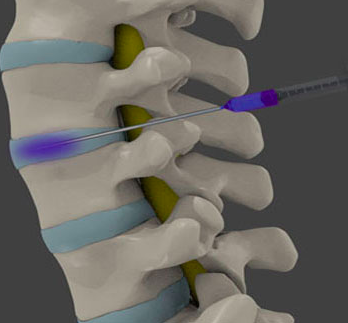
Le principle of this herniated disc treatment is to approach the intersomatic space (between the vertebral bodies) on the side of the hernia responsible for the impingement, after scopic identification (identification with an image intensifier during the operation).
The skin incision measures 3 cm. After crossing the subcutaneous fascia, the muscle aponeurosis is incised 1 cm from the midline.
The muscle masses are moved aside to access the posterior arch of both vertebrae framing the diseased disc. Subsequently, the speculum is introduced and then opened. The microscope (or magnifying glasses), including a zoom lens, placed in front of the operator, is positioned above the incision.
After exposing the posterior part of the vertebrae (the spinal blades), an incision is made and a slight amputation of the yellow ligament. THE dural bag (the dura mater containing cerebrospinal fluids and nerve roots) is located and carefully reclined to gain anterior access to the disc space and the herniated disc.
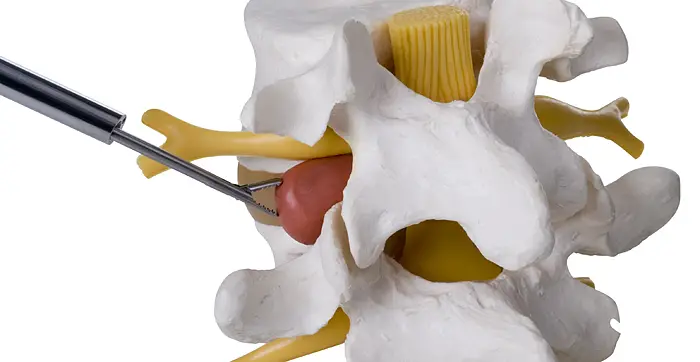
The hernia is often clearly visible in contact with the dural sac and the nerve root. When performing the discectomy at a minimum, using disc forceps, the surgeon takes care to protect the nerve root while removing the disc fragment.
Disc fragments that occur in addition to the herniation are also removed. Then we move on to washing with or without drainage, controlling bleeding and closing the wound.
To date, the microdiscectomy stay here reference technique with the best results reported for the management of a herniated lumbar disc. In particular, the minimally invasive approach makes it possible to reduce blood loss, postoperative length of stay and the consumption of analgesics compared to a conventional discetomy.
Endoscopic microdiscectomy with working channel (for lumbar disc herniation)
The intervention is carried out under general anesthesia in the strict aseptic conditions of the operating room. The endoscopic microdiscectomy requires equipment consisting of:
- dilators of increasing size ;
- specific endoscope (METx™ system, Medtronic or Endospine™, Stortz, for example);
- speculum containing several channels (for introducing the endoscope and instruments).
The working window can be identified by image intensifier and a 2 cm incision opposite it (technical intervention via the posterior approach). The instrumentation is introduced into the 18 mm diameter working chain towards the yellow ligament.
The rest of the operation is carried out under endoscopic control (on a high-definition screen) with constant irrigation of physiological saline. The beveled endoscope helps identify and protect the nerve root to access the intervertebral disc and herniated disc. The herniated disc is gently removed while securing the nerve. Minimal cleaning of the disc will be performed to avoid any early mobilization of another disc fragment.
At the end, only the fascia and the skin are sutured, without a Redon drain. The surgeon is very careful not to perforate the ligamentum flavum and to penetrate the dilators intra-canal.
In post-operative follow-up, the first sunrise is done on the day of the operation with a physiotherapist. Its objective is to teach the patient the steps to take to protect him, but also to begin rehabilitation with exercises adapted to his daily life.
En classic hospitalization, the physio comes twice a day to allow an early rise and a quick recovery.
This procedure is frequently performed on an outpatient basis with a return home on the day of surgery. The patient is contacted by a nurse the day before and the day after the operation with particular attention to pain prevention in order to facilitate post-operative recovery.
These methods should be preferred for extraforaminal disc herniations in L5-S1. They sometimes remain very difficult if the vertebrate L5 is recessed.
The risks and complications with microdiscectomy
All surgery involves risks that must be considered.
- Anesthetic risks: related to the history, to the reactivity of the organism, or to unknown allergy problems. You can ask all your questions to the anesthesiologist during the preoperative consultation.
- Infectious risks: surgical site infection. The risk of postoperative bacterial discitis which is very low, but difficult to diagnose.
- The hemorrhagic risk: the hematoma remains more than exceptional.
- The neurological risk: the spinal cord stops at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra and therefore cannot be injured below this level. It is exceptional (<1%) for nerves to be damaged with an impact on the mobility or sensitivity of the limb.
Similarly, the breach of the dura mater (envelope below L2 which contains the cerebrospinal fluid and the roots) can occur during the operation despite the precautions taken. It can cause headaches or even a cerebrospinal fluid leak.
- Insufficient result: despite perfect technique, simple follow-up and well-conducted rehabilitation. Pain may persist, often less than before the intervention, but the guarantee of total indolence is impossible.
- La recurrence (5%): this is the most frequent risk, and it is unpredictable, but remains limited if the post-operative instructions are respected.
- La fibrosis (0,1%): extremely rare when your tissues heal abnormally, there is a gradual reappearance of pain. The state of psychological stress is a primary factor in its occurrence.
- The healing disorders are very rare. They can impose a new intervention. Tobacco is a negative factor for wound healing.
- Le risk of phlebitis is weak. Preventive anticoagulant treatment is only necessary in case of predisposition, or when bed rest continues beyond 24 hours. A pulmonary embolism can, in the extreme, occur. This is a serious, sometimes fatal complication.