Article reviewed and approved by Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, physician specializing in family medicine
La syringomyelia is a pathology related to formation of a cavity inside the spinal cord. It often evolves slowly and its symptoms are often concealed.
In this article, we will see everything you need to know about syringomyelia: characteristics, symptoms, causes, prognosis for recovery and treatment.
What is syringomyelia?
To help you better understand this spinal cord disease, here is a little reminder regarding this component of the nervous system.
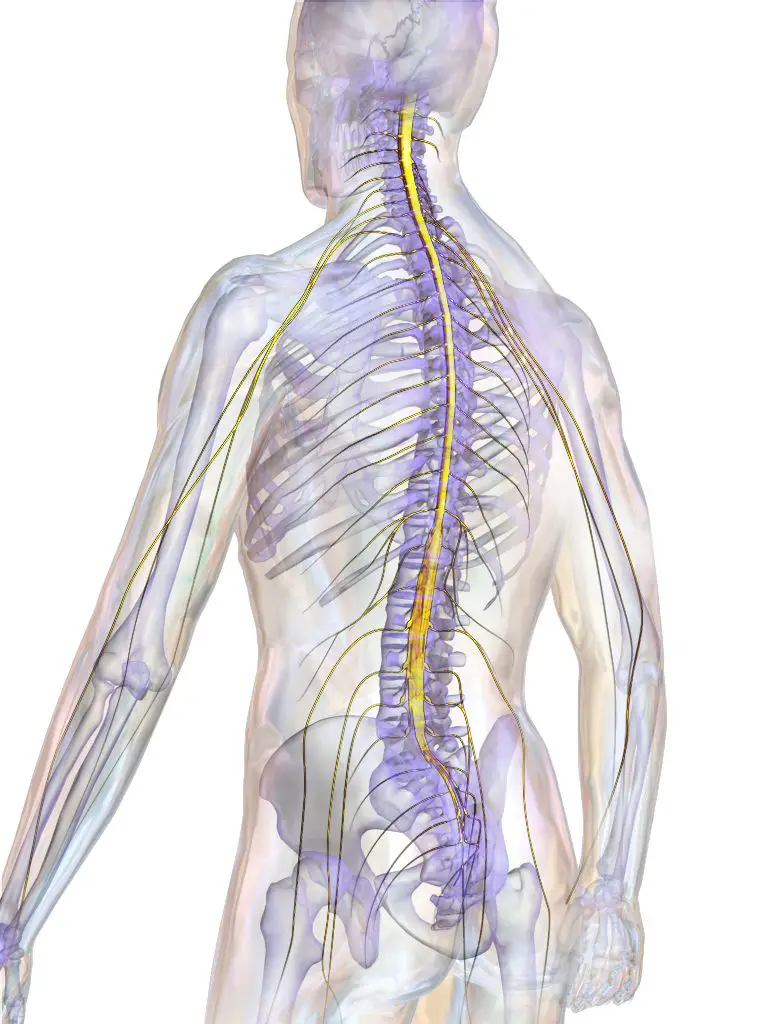
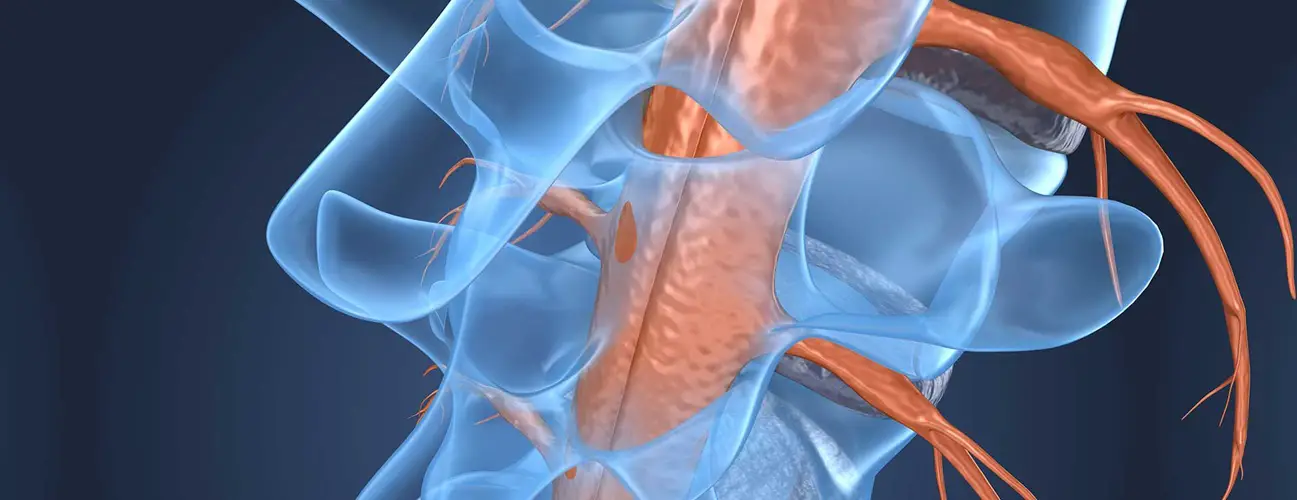
Being part of central nervous system, spinal cord is the extension of the brain. It extends from the medulla oblongata down the back. It looks like a long cord of about 50 cm which is lodged inside the vertebrae full spine.
The spinal cord has two functions:
- transmission of nerve messages from the brain to different parts of the body via motor nerves;
- transmission of nerve messages from different parts of the body to the brain using sensory nerves.
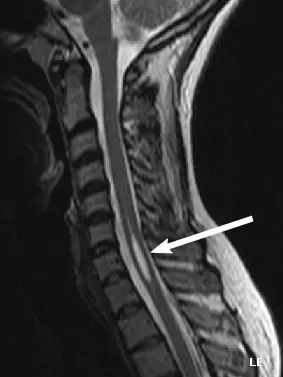
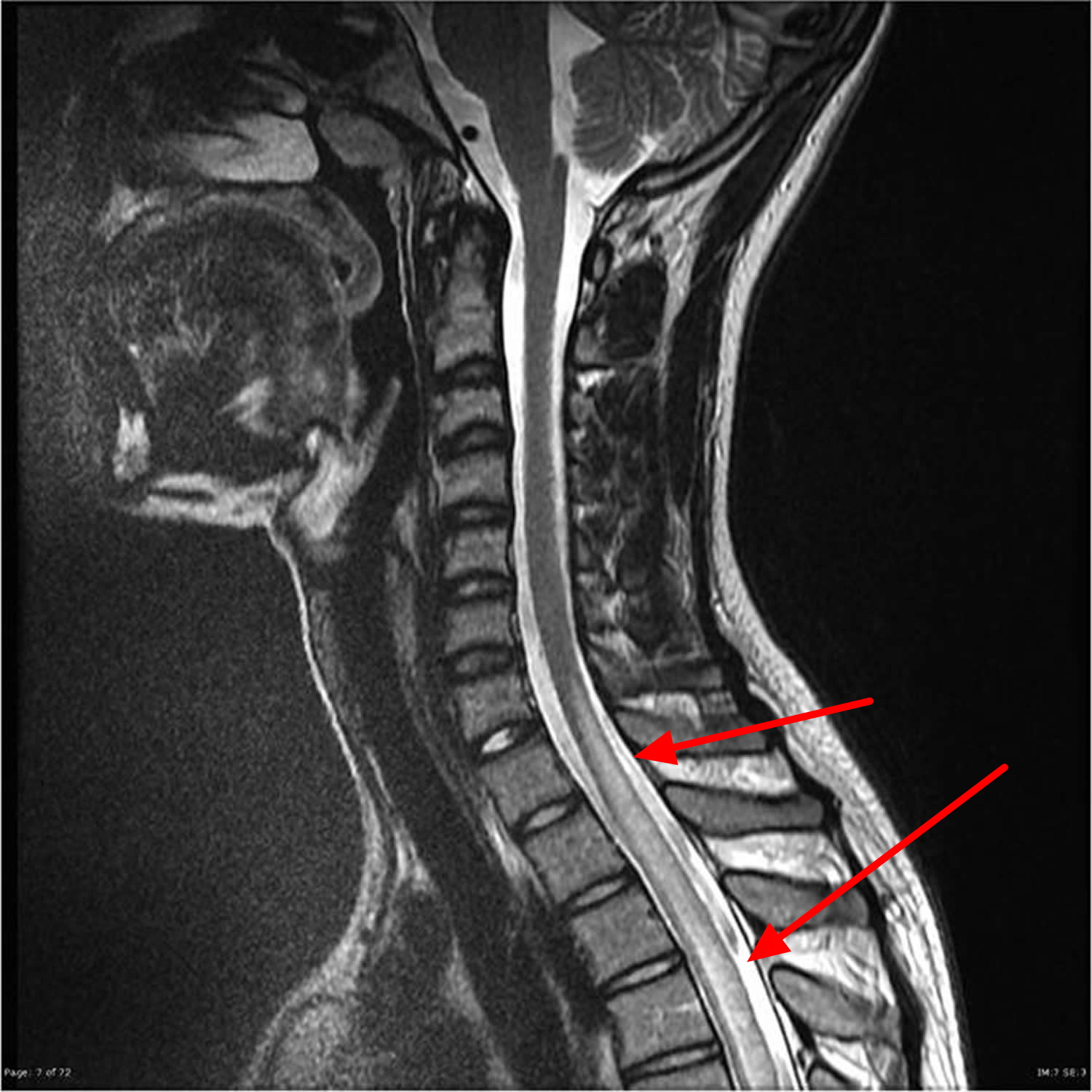
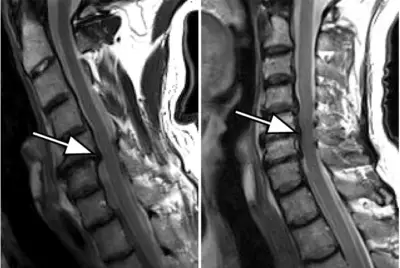
La syringomyelia is a disease characterized by the formation of one or more cavities inside the spinal cord. Inside these cavities is cerebrospinal fluid. They are called "syrinx".
Over time, the cavities may gradually expand to the level of the brainstem bulb. This can damage the functions of the spinal cord and cause neurological disorders, severe chronic pain, motor disability, even loss of autonomy.
What are the symptoms of syringomyelia?
La syringomyelia can grow silently for several years. The first signs may only appear between the ages of 20 and 40.
Almost half of people with this condition have no symptoms, or only some signs of minor disabilities.
Moreover, even when the symptoms show themselves, they can vary from one person to another. They depend on the cause of the disease and the characteristics of the syrinx: size, shape, location and progression.
The typical symptoms of syringomyelia are :
- insensitivity or hypersensitivity to heat, cold and pain;
- urinary and anal incontinence;
- disorders of sexual functions such as erectile dysfunction;
- feelings of numbness, muscle weakness, decreased reflexes especially in the upper limbs;
- chronic pain;
- balance disorders or jerky movements.
Other symptoms can be added such as dizziness, headaches, slurred speech, swallowing, or sometimes facial paralysis. These occur especially when syringomyelia affects the base of the brain.
Be aware that even if there is a loss of thermal sensitivity, deep sensitivity is retained. That is, those affected can still feel the tact. The fibers that carry the fine tact in the spinal cord do not cross the midline until they have arrived in the medulla. This is not the case for the sensory pathways responsible for transporting thermal and painful sensitivities.
What causes syringomyelia?
Men are the most affected by this disease. It most often occurs around the age of XNUMX.
Depending on its origins, there are two types of syringomyelia: primary syringomyelia and secondary syringomyelia.
La primary syringomyelia is usually of unknown cause (idiopathic). Note also that it is neither a hereditary disease nor a genetic disease.
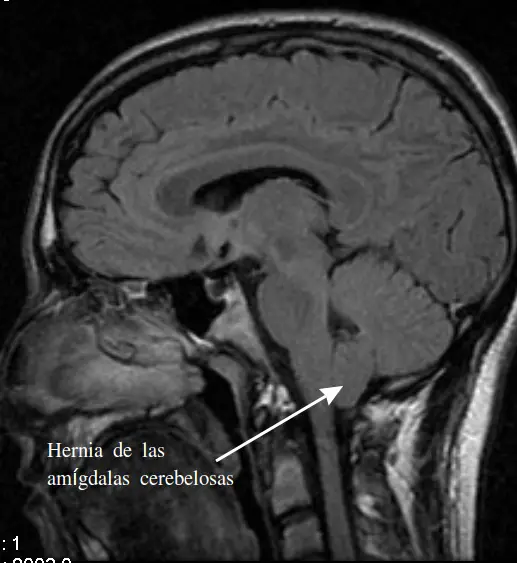
La secondary syringomyelia, meanwhile, indicates a spinal cord damage or abnormal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the spinal canal. This may follow a Arnold-Chiari malformation, a congenital malformation of the cerebellum that promotes the flow of cerebrospinal fluid into the spinal cord.
Furthermore, other causes of syringomyelia may also be cited: arachnoiditis, meningitis, tumour, trauma or haemorrhage.
How to diagnose syringomyelia?
For screen for syringomyelia, you have several types of exams:
- x-ray,
- lumbar puncture,
- computed tomography (scanner),
- IRM
However, MRI is the most likely to provide more precision in the context of syringomyelia. Some symptoms of syringomyelia may be confused with those of other diseases such as multiple sclerosis, scoliosis or other neurological diseases. Hence the importance of a diagnosis of the spinal cord made using an MRI. This allows the syrinx to be visualized and the cause to be determined if it is secondary syringomyelia.
Syringomyelia: what about prognosis and life expectancy?
In general, the idiopathic syringomyelia is benign. More than half of people with the disease have no deficit.
About the secondary syringomyelia, about 50% of people affected by Arnlod-Chiari malformation have no major neurological handicap.
Most of those affected survive without too many after-effects and life expectancy remains comparable to that of the general population.
However, the prognosis becomes poor when the only solution available to patients is syrinx bypass. In addition to a high risk of recurrences, this can cause significant neurological deficits.
How to treat syringomyelia?
Le syringomyelia treatment is based on long-term follow-up. In case of significant neurological deterioration, surgery may be necessary. The type of intervention will be determined according to the type and cause of the disease. All operations should be performed by an experienced neurosurgeon.
Strictly speaking, syringomyelia has no specific medical treatment. Treatments are most aimed at relieving symptoms and improving the patient's quality of life. This is why it is essential to know the cause for secondary syringomyelia in order to make an adequate correction.
As for the cases of primary syringomyelia, they do not require any treatment since in addition to being benign, their symptoms almost never appear.
In addition to surgery, medication may also be prescribed to relieve severe pain problems in some patients. It is up to the doctor to decide on a case-by-case basis which drugs are suitable and which do not cause undesirable side effects. You can also opt for other unconventional therapies such as physiotherapy, sophrology, acupuncture, etc.
Among other things, if it is a spinal cord tumor that is the origin of syringomyelia, the intervention of the doctor is to remove it. Radiotherapy may be indicated in addition to completely get rid of the syrinx.
La management of syringomyelia can therefore be multidisciplinary. At the same time, you can be followed by a neurosurgeon, a urologist, a rehabilitation doctor, a psychologist… This is above all necessary to better live with the disease while being less and less affected by the symptoms.
Conclusion
Remember that the syringomyelia is an extremely rare pathology that progresses very slowly. It is due to a formation of cavities in the spinal cord. If in some people, it can remain benign, in others, it can lead to severe pain as well as motor and sensory disorders. For complete care and to limit the sequelae, it is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as the symptoms appear. You could be referred to various specialists in order to benefit from an appropriate follow-up.