La spinal stenosis cervical is a clinical syndrome that includes all the signs and complications suggesting a narrowing of the cervical canal.
This channel, supposed to be a protective rampart of the spinal cord and its nerve roots, its shrinkage may cause neurological damage serious and sometimes irreversible.
If you are looking for relevant information on this pathology in general, and on how it is treated, you have come to the right place!
Cervical spine anatomy
To fully understand this condition, here is a brief overview of the normal anatomy of the cervical spine.
Le cervical spine (spine cervical) constitutes the skeleton of the neck, the part separating the head from the trunk.
This skeleton is made of 7 bones called vertebrae cervical, named from C1 to C7. Apart from the first two C1 vertebrae (Atlas) and C2 (Axis), the rest of the vertebrae are stacked on top of each other via intervertebral discs.
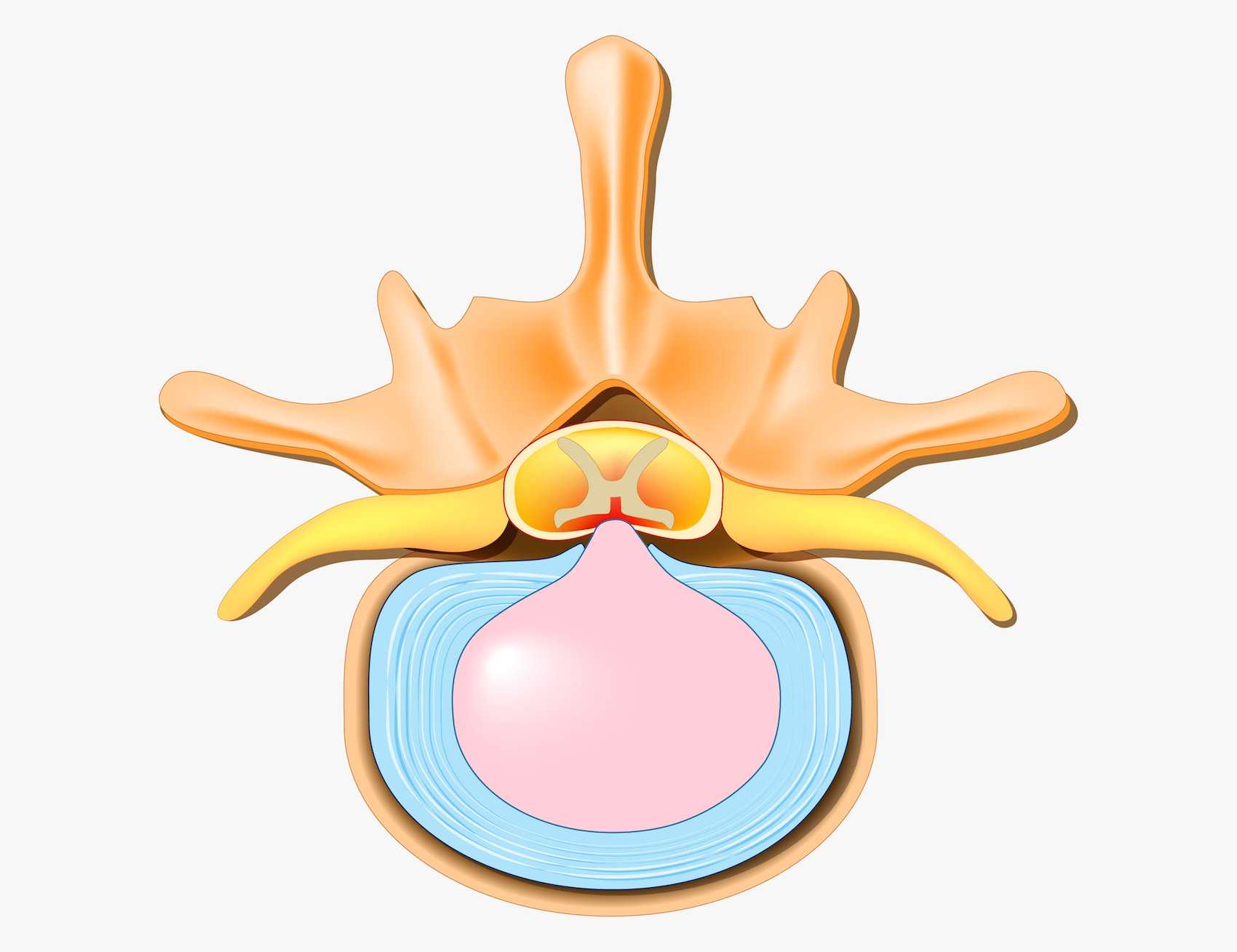
All of these structures delimit in their center a channel, called Spinal canal (cervical canal), which houses the spinal cord. From either side of the spinal cord emerge nerve roots (spinal nerves), these leave the spinal canal via holes called foramina.
Naturally, the diameter of the cervical canal is adequate enough to pass the spinal cord and its nerve roots. However, various causes can cause this channel to narrow as well as compress its contents.
What is cervical spinal stenosis?
La cervical spinal stenosis is a condition of the cervical spine that is characterized by a decrease in the diameter of the cervical canal and compression of the structures it protects (spinal cord and nerve roots).
Most often, the diameter is reduced at the level of the bony part of the vertebrae or at the level of the intervertebral discs. But, sometimes the reduction develops at the level of one of the two structures (either at the level of the bone or at the level of the disc).
The structures compressed by this narrowing can be:
- Spinal cord: whose resulting signs are defined by what is called the myelopathy cervicarthrosis
- The nerve roots ou cervical roots: the compression of which generates disorders with types of cervico-brachial neuralgia.
The causes of cervical spinal stenosis
THEOsteoarthritis is the most common cause found in people with cervical spinal stenosis. It is a degenerative consequence to which the aging process of the body in general and in particular, the cervical spine leads.
From a pathophysiological point of view, osteoarthritis indirectly leads to the narrowing of the cervical canal by causing dehydration of the posterior joints and intervertebral discs.
As time passes, this dehydration will inevitably lead to degeneration of these structures which can be recognized by characteristic lesions called in medical jargon " osteophytes " or " parrot beak bones ».
Several other etiologies can be added to osteoarthritis, such as:
- La constitutional cervical spinal stenosis : or congenital, this is the case of people who are born with a spinal canal that is naturally narrower than average
- Disc narrowing can be linked to a disc protrusion ou herniated disc (cervical hernia)
- Hypertrophy or thickening of yellow ligament
- Le cervical synovial cyst, of congenital or acquired origin
- Spinal slip: spondylolisthesis ou retrolisthesis
- Cervical tumors
- Trauma
- Etc
Symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis
Cervical spinal stenosis can be asymptomatic for a long time. Its slow and silent evolution often leads to a diagnostic delay.
When the narrowing of the cervical canal becomes symptomatic, it can manifest itself, among other things, by the following signs:
- Neck pain or neck pain
When they are chronic, these pains are very suggestive of cervical osteoarthritis of degenerative origin. They are generally moderate at first, then become disabling, especially when associated with disc disease.
As mentioned in the anatomy section, cervico-brachial neuralgia is the consequence of compression of the nerve roots emerging on either side of the spinal cord.
Ce radicular syndrome is manifested by characteristic pain. Each pain has a well-defined path leading to a well-defined root.
- Sensory or motor disorders
The patient may develop sensory or motor deficits more or less serious. The early detection of these disorders prevents the transition to a partial paralysis ou total may remain as permanent sequelae.
- Paresthesias and dysesthesias
The paresthesias are felt like an electric shock along the upper limbs, tingling or even tingling. THE dysesthesias, for their part, are characterized by an alteration in the sensitivity of all or part of the upper limb.
- cervico-osteoarthritis myelopathy
Myelopathy corresponds to damage to the nerve roots responsible for the innervation of the lower limbs. Clinically, the patient may complain of a simple walking difficulty or a slight loss of equilibrium, as he can see a paralysis to sphincter disorders.
The diagnostic approach for cervical spinal stenosis
THEmagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become, today, a systematic examination in the context of the management of diseases affecting the cervical spine.
Its interest is based on its ability to allow a good evaluation of the compression of the spinal cord and these nerve roots. However, she must complete, beforehand, the realization of a complete radiological assessment including: the plain x-ray and cervical scanner (CT).
La cervical x-ray is mainly used to highlight the different lesions characterizing a cervical spondylosis (osteophytes or parrot beak bones).
In practice, static incidences are performed (face, profile and three-quarters) and dynamic incidences with movements of flexion and extension of the neck.
Obviously, the priority of the complementary examinations varies from one team to another, but most of the time, once the spinal stenosis has been evoked, the CT scan is always the examination to be carried out in first intention.
Treatment of cervical spinal stenosis
Despite the frequent delay in diagnosis, today there are several therapeutic approaches to overcome cervical spinal stenosis.
Medical treatment
This is a conservative treatment, initially used in the management of painful crises related to cervical stricture.
It combines the following treatment options:
Medication
The molecules most frequently used are analgesics (paracetamol, aspirin), anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, muscle relaxants, etc.
Rest
Even if the drugs should sufficiently cover the pain, rest is ideally recommended to speed up your recovery.
Be careful, we do not mean by rest, prolonged bed rest, because this can be more dangerous than the disease itself.
Wearing a neck brace (cervical collar)
This orthopedic treatment can only bring you good. It is generally indicated in cases of trauma, or in patients practicing activities that involve significant physical work.
Physiotherapy
Thanks to its various manual techniques and therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy contributes considerably to relieving pain and strengthening the muscles of the neck.
On the other hand, resorting to physiotherapy alone is not enough to cure such a condition.
Surgical treatment
As a general rule, surgeons are contacted when recourse to all the previous therapeutic approaches has proven to be a failure, or in the event of an emergency corresponding to situations where the vital or functional prognosis is compromised.
Technically, the main purpose of surgery is to widen the cervical canal and thus free the spinal cord. To do this, surgeons perform specific surgical techniques such as:
- La laminectomies or surgical release of the spinal cord
- THEcervical arthrodesis previous
Admittedly, surgery is the option that makes it possible to correct the problem of spinal narrowing for sure. However, recovery remains relative, particularly in the event of prolonged evolution of neurological deficits.
The time factor therefore plays a very important role in the management and prognosis of cervical spinal stenosis. The earlier the treatment, the better the prognosis.
My name is Sidali. I am a general practitioner and Web Editor. As a healthcare professional, my mission is to contribute to the relief of my patients' ailments. Being also passionate about writing, I have the pleasure of sharing my solid medical knowledge with the greatest number of readers, by writing popular articles that are very pleasant to read.